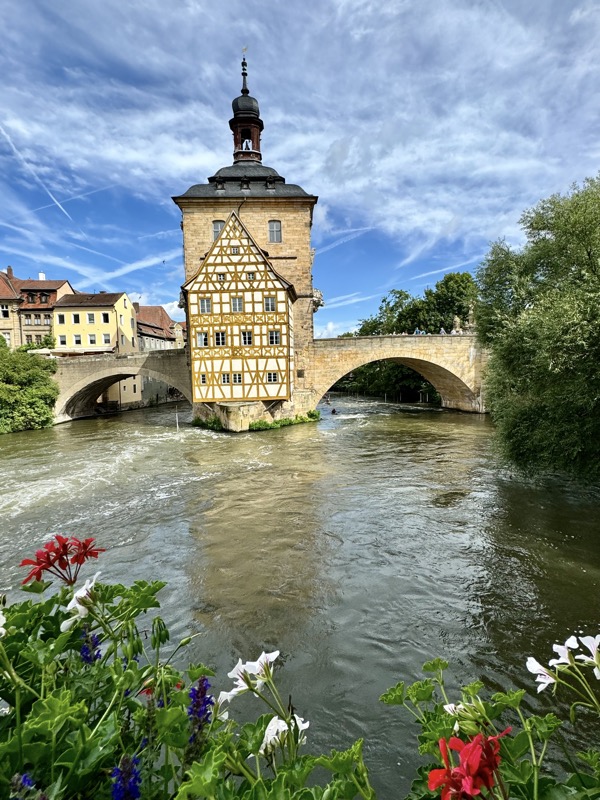
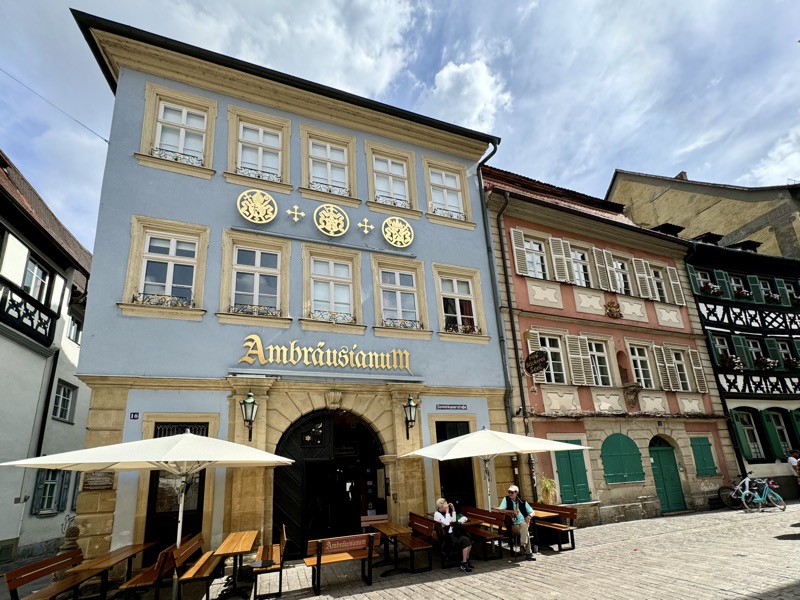
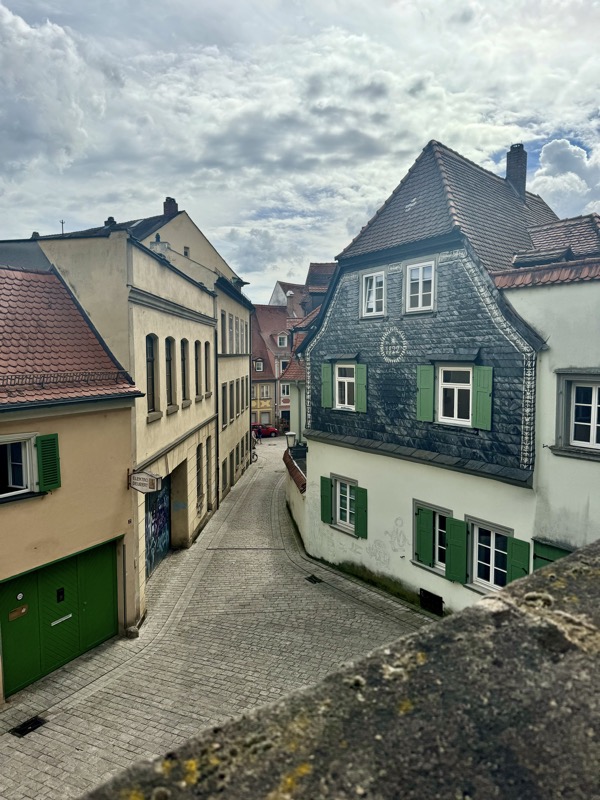
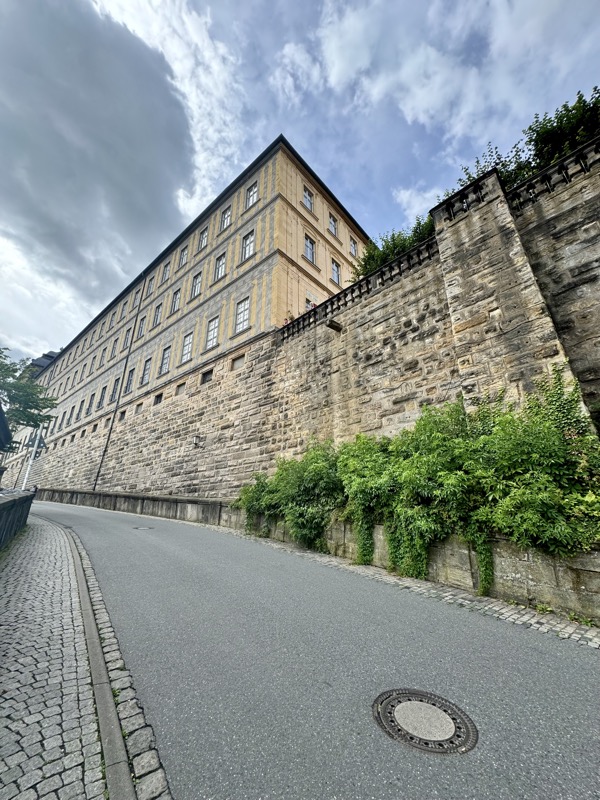
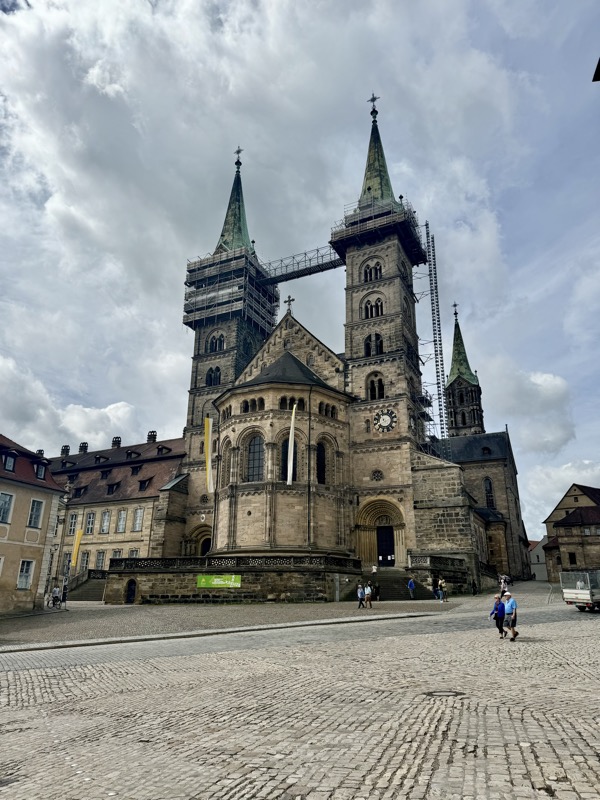
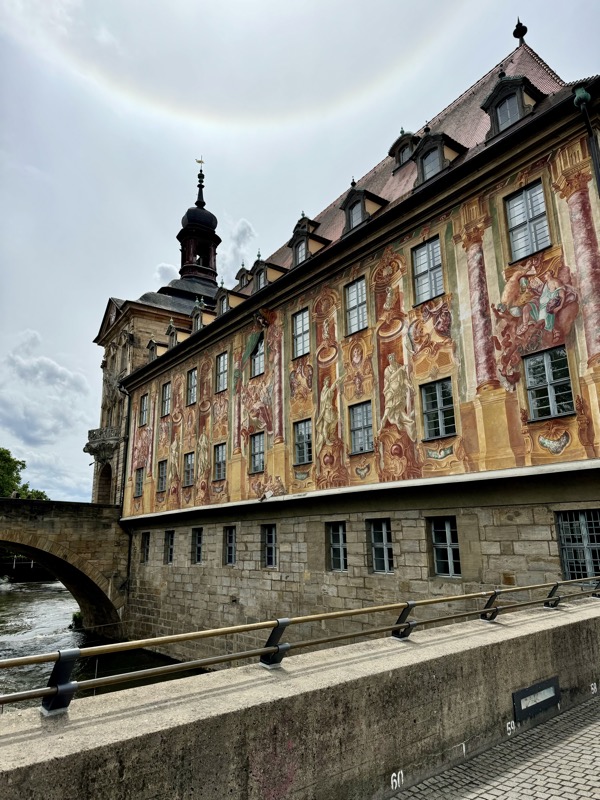
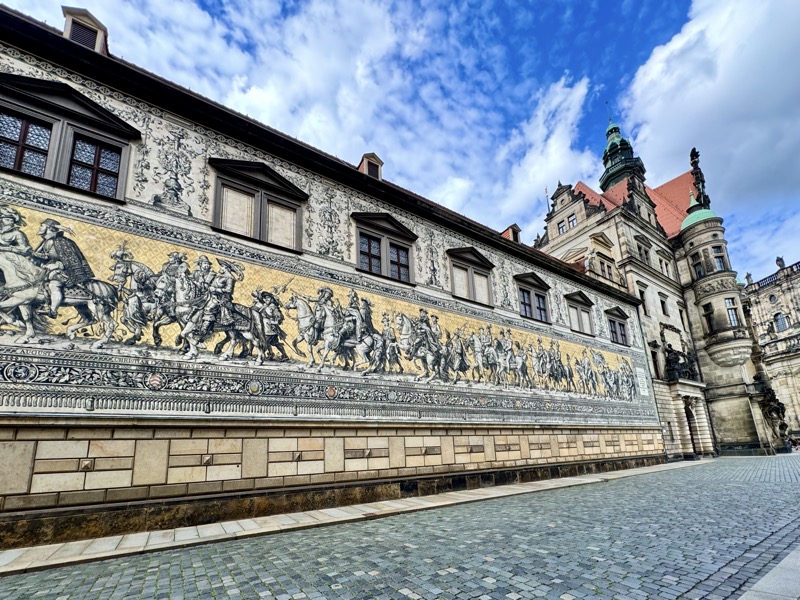
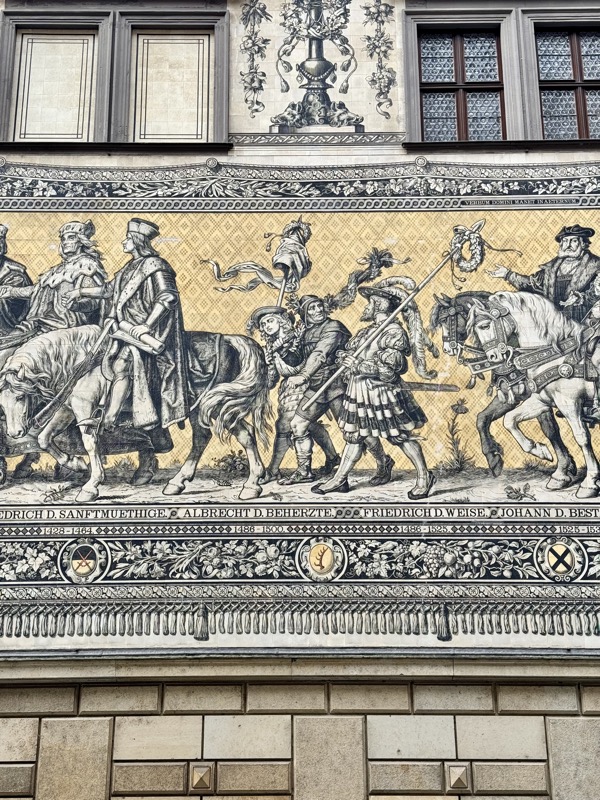
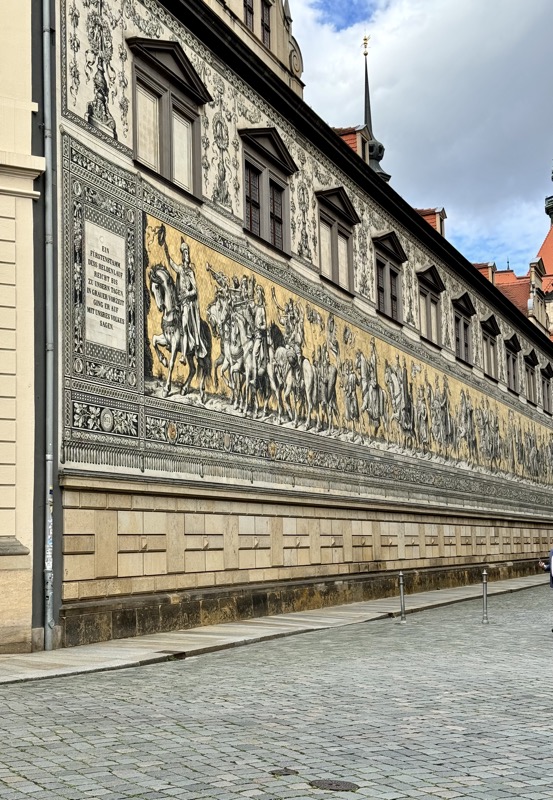
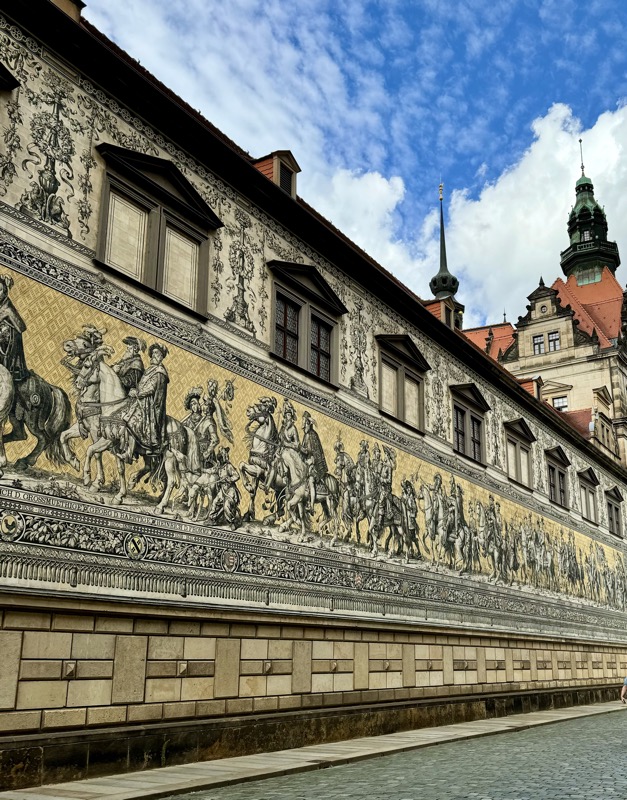
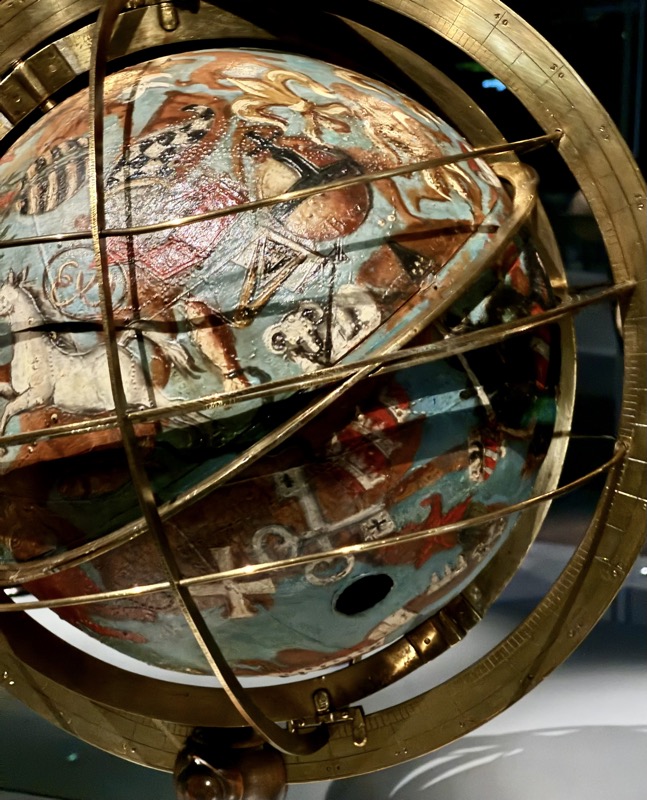
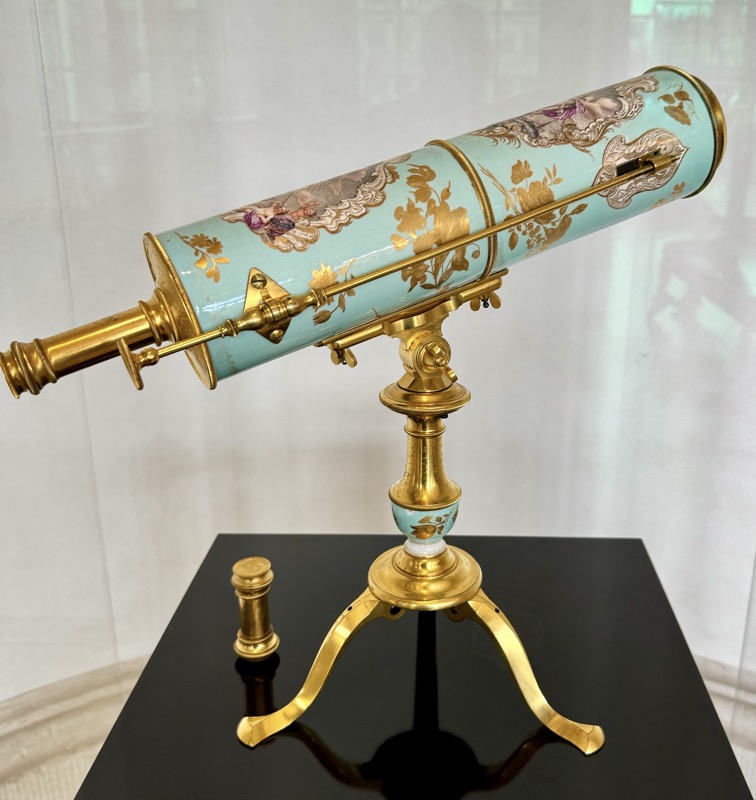
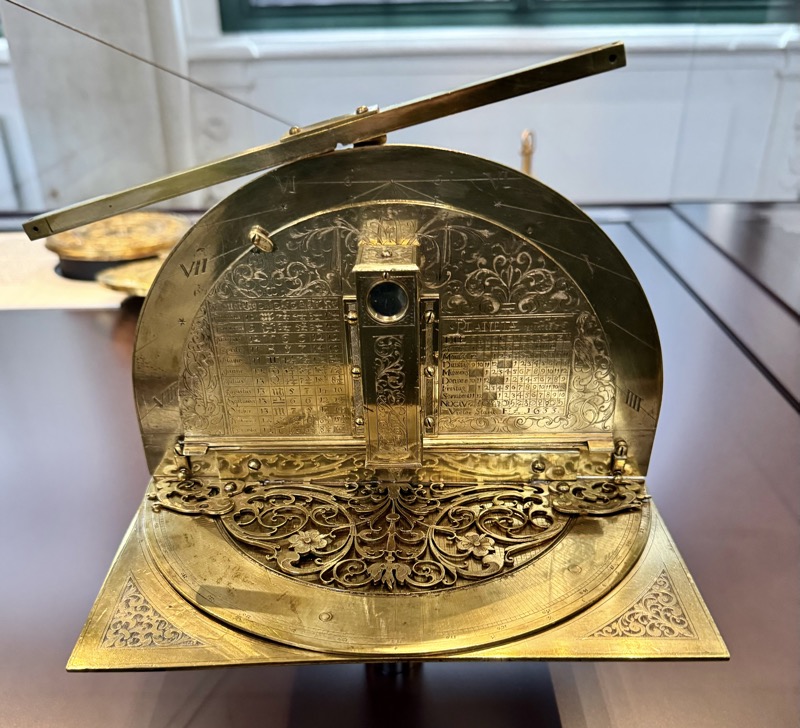
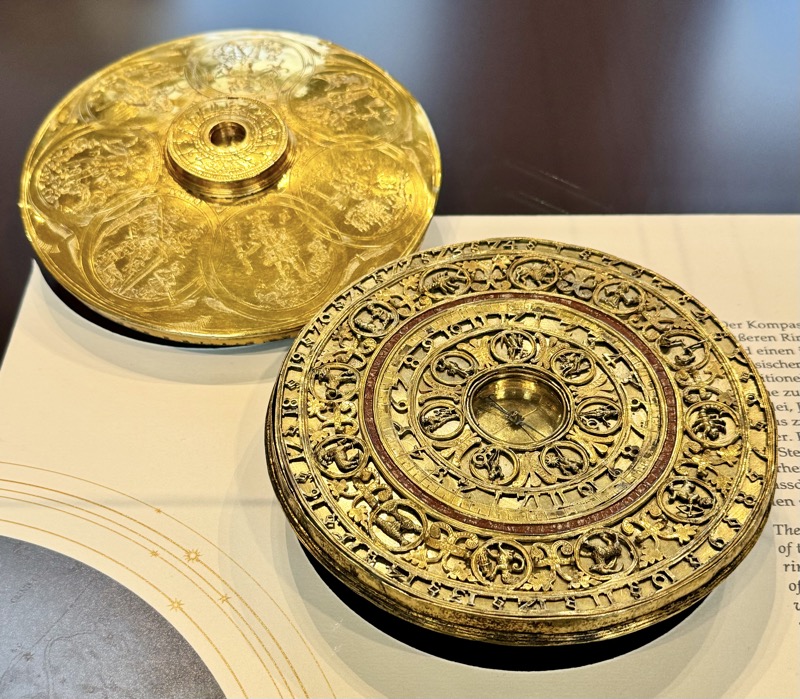
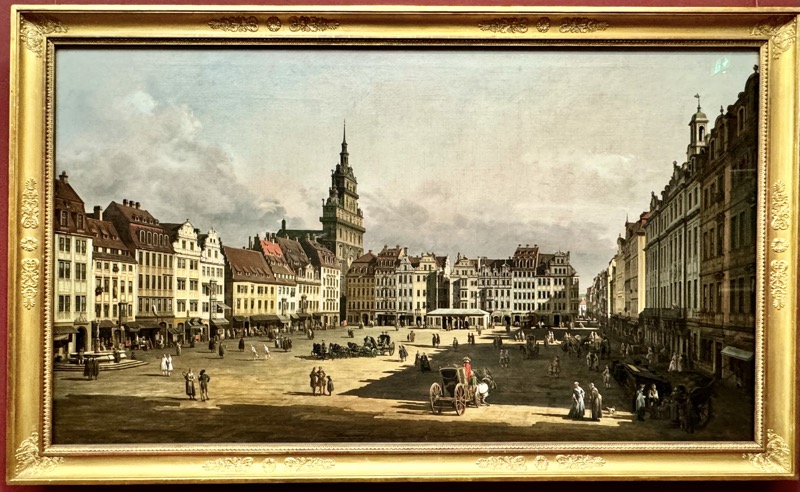Short drive today to Nuremberg. Uneventful for the most part, though we were mightily amused by this road sign telling drivers to slow down to 120 kmph for roadworks… for serious, it was needed though. We were in a 130 zone on the autobahn and doing roughly the speed limit with people whizzing past us like we were standing still. I don’t know how there aren’t more accidents here… but I bet when they do connect it’s horrific.

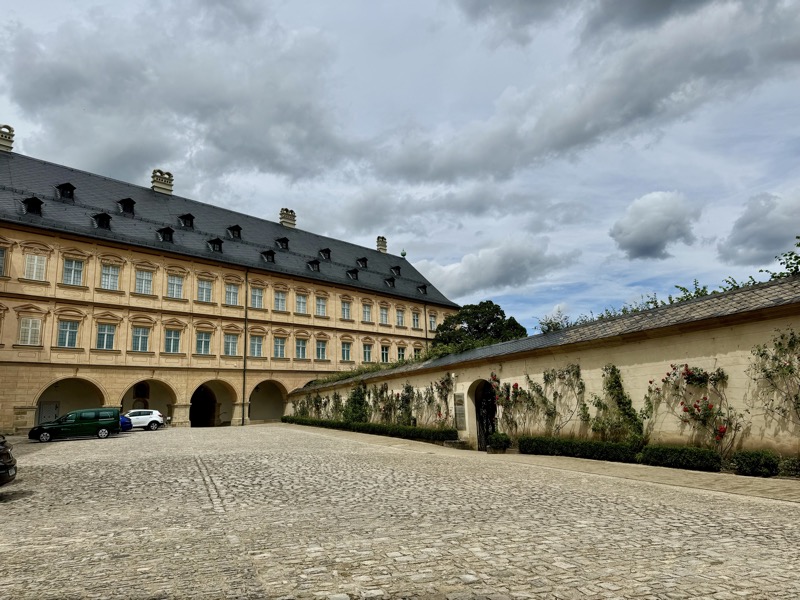
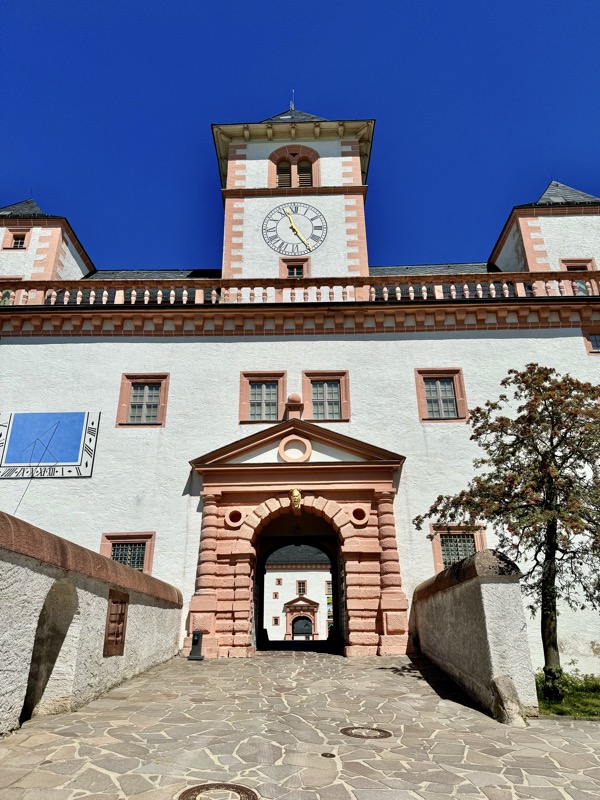
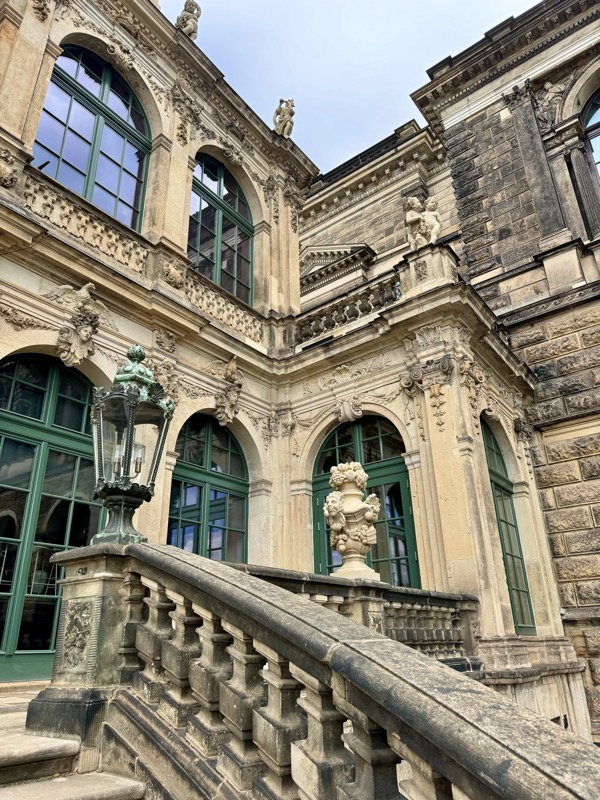
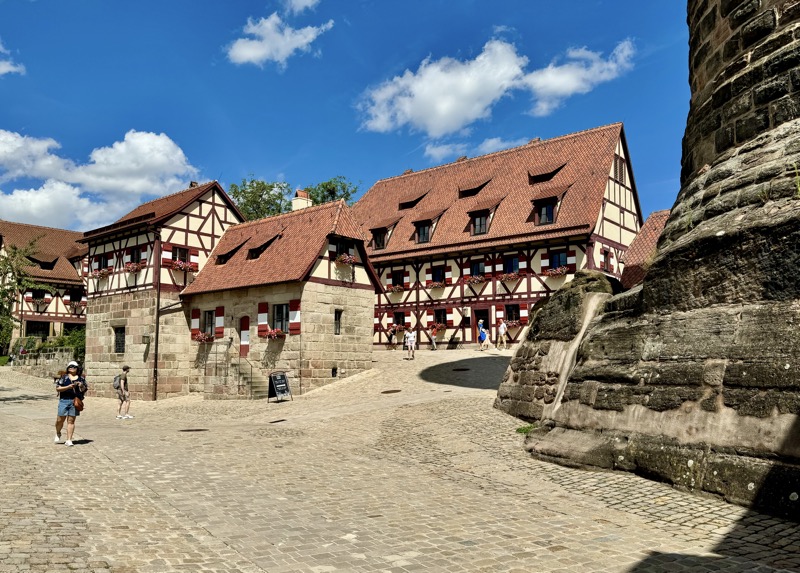
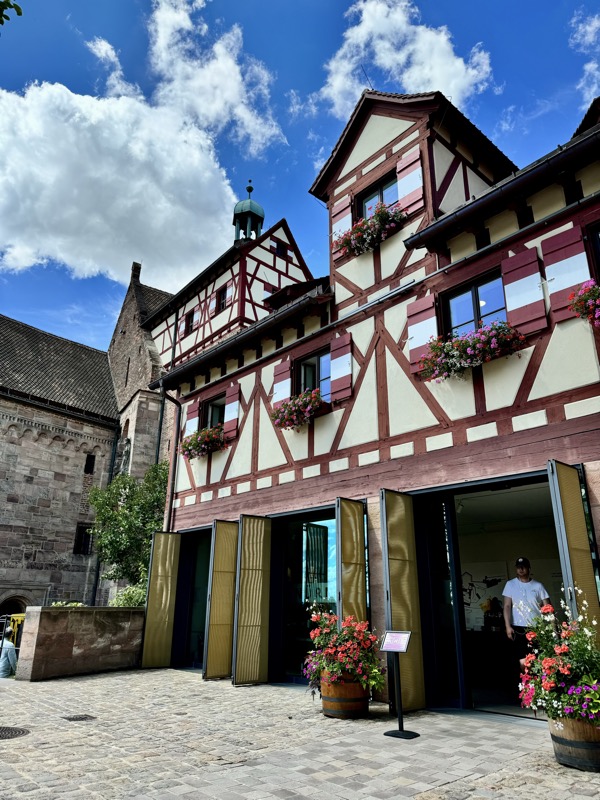
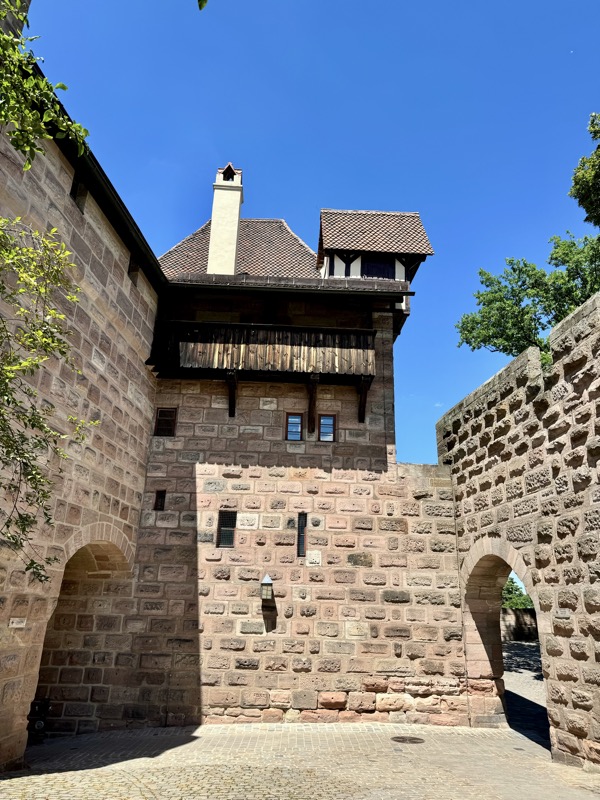
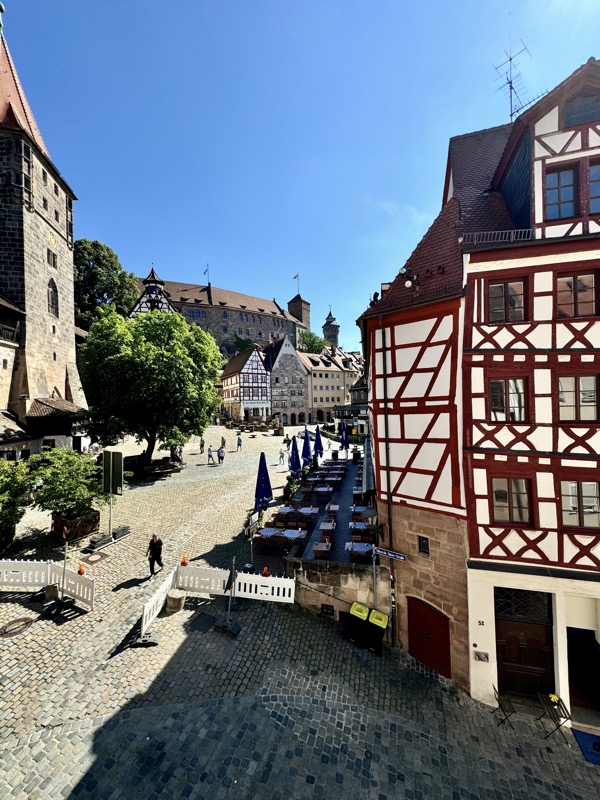
Given Europe’s typical Mondayitis, there were quite a few places that were not open today, but thankfully the well famous Nuremberg Castle wasn’t closed. Also known as the Nürnberger Burg, the castle is actually a large complex of medieval fortified buildings built on a ridge that overlooks the historical Altstadt of Nuremberg. Well located in Bavaria, the castle and its formidable city walls are considered one of Europe’s most impregnable fortified castles. The whole place was designed to represent the power and influence on the Holy Roman Empire and the distinctive role the Imperial City of Nuremberg held.
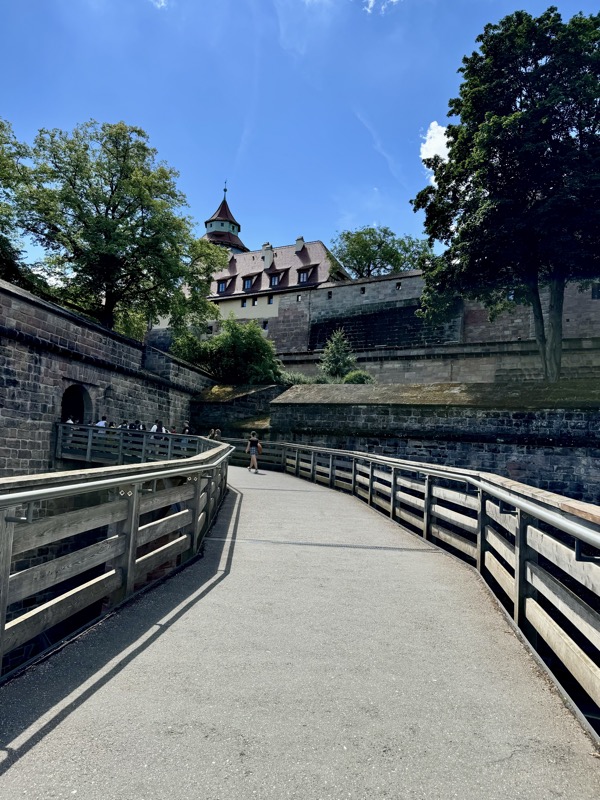

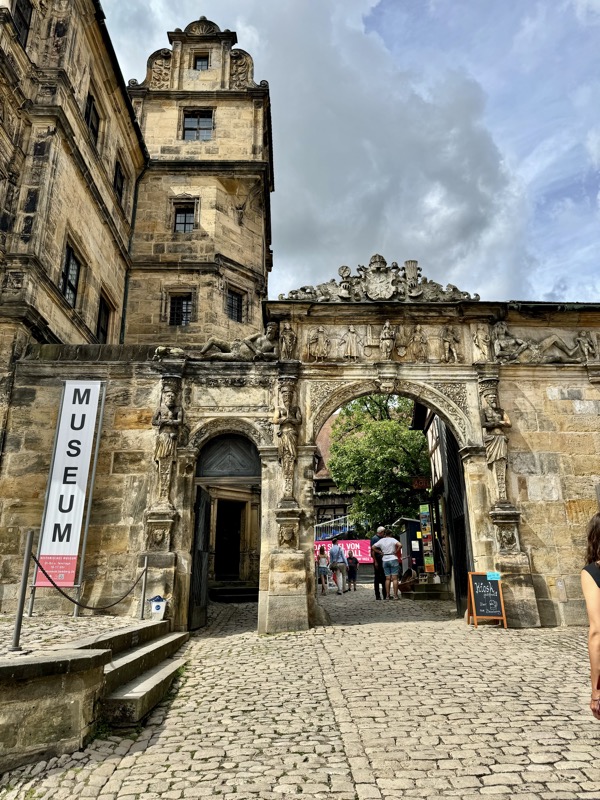
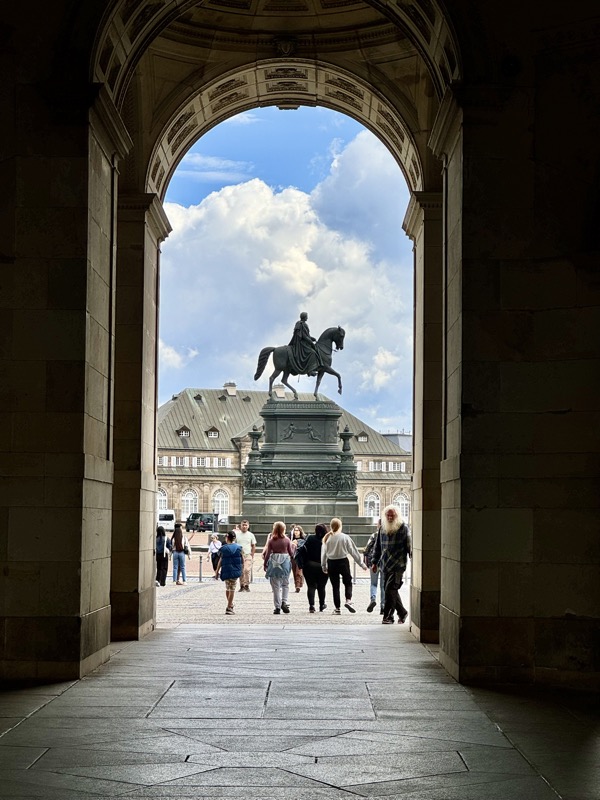
The main entrance (above) isn’t that much to look at, but as soon as you make your way into the castle walls, the extent and size of the fortress becomes apparent.
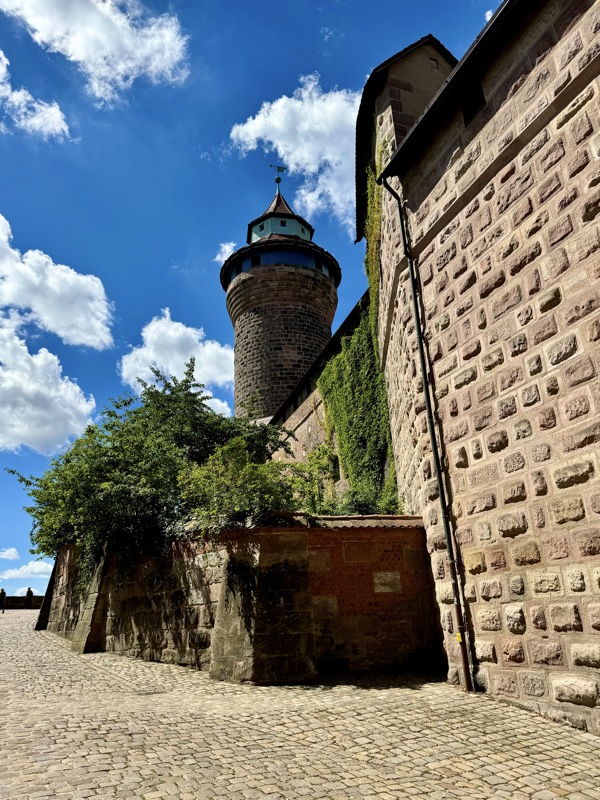

The construction of the castle was originally started around 1000, and after that there were three main periods of expansion that can be seen. 1) the main castle built under the Salian kings and respective Holy Roman Emperors front he period of about 1027-1125, 2) a newer castle section that was built under the Hohenstaufen Emperors from 1138-1254 and the reconstructed areas of the castle that became more palace in the later medieval period.
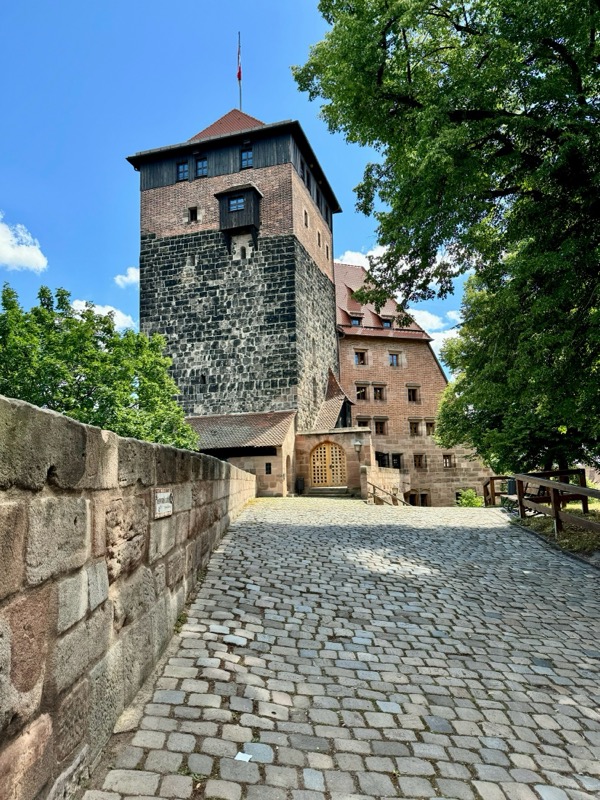
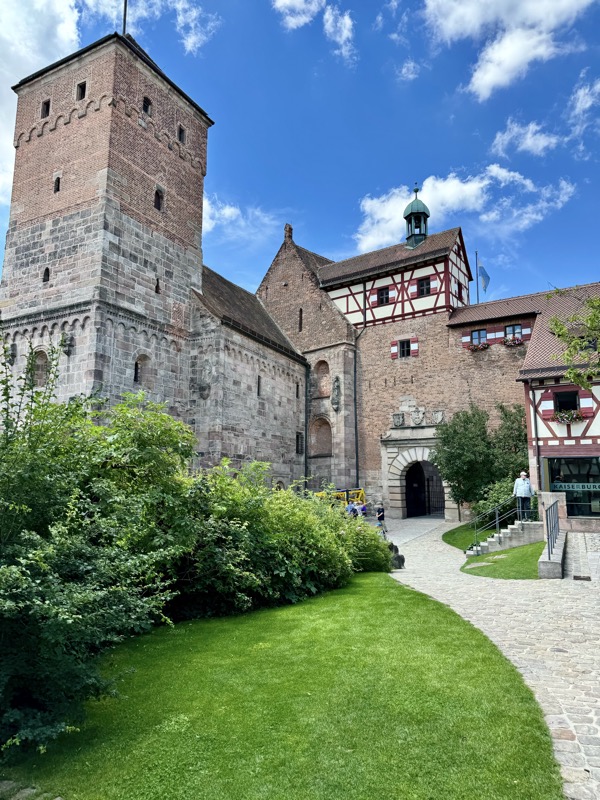


In the Middle Ages, the city of Nuremberg was one of the larges and organised municipalities in all of Europe, and was at various periods the Imperial Capital.

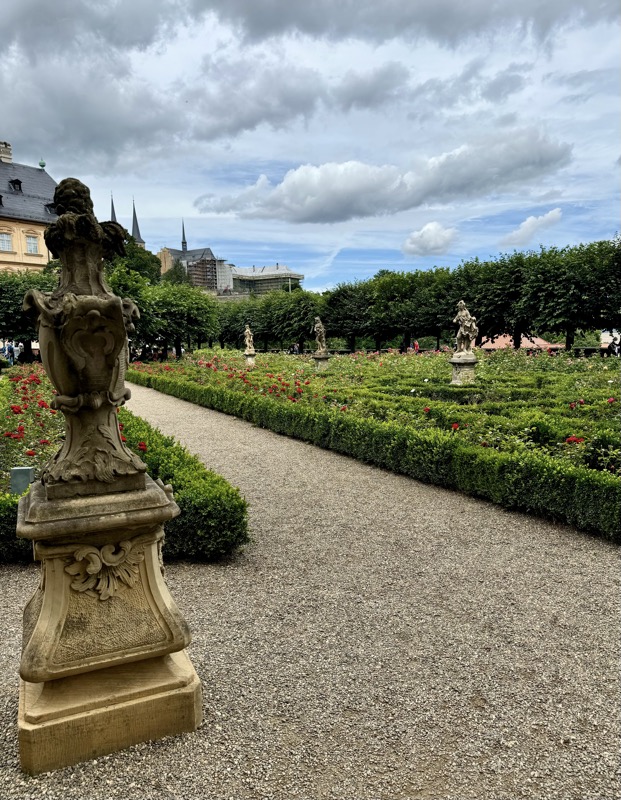
I could not get over the sky today – the clouds just looked absolutely surreal, and the sky so blue, I thought we were in the tropics.
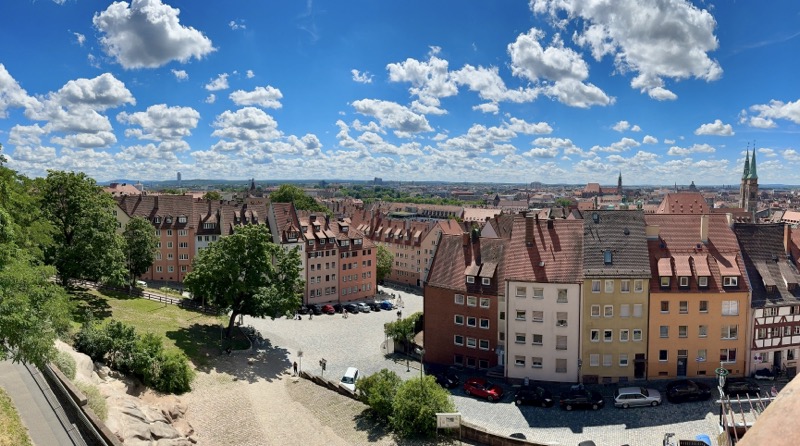
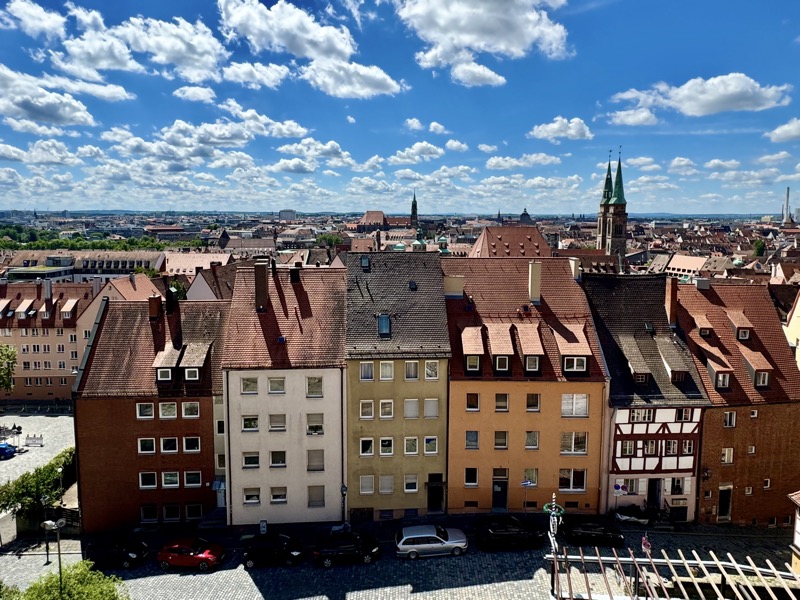


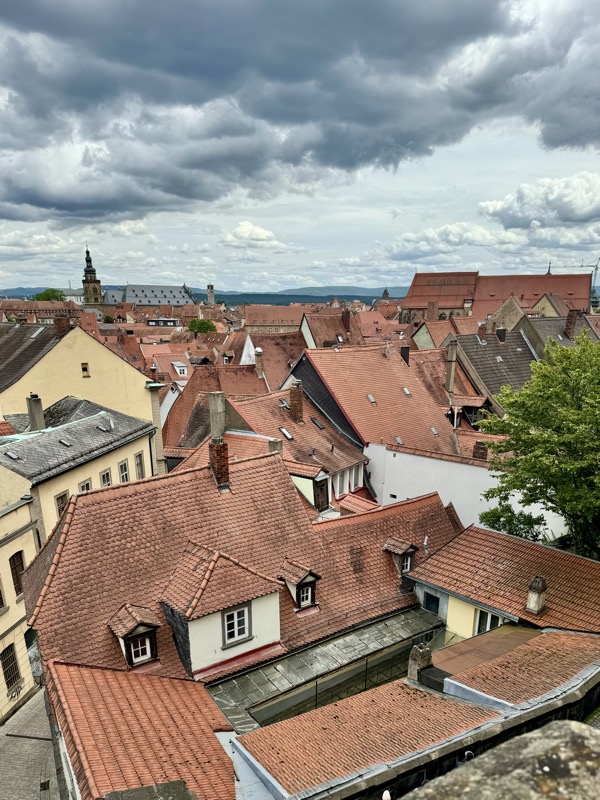
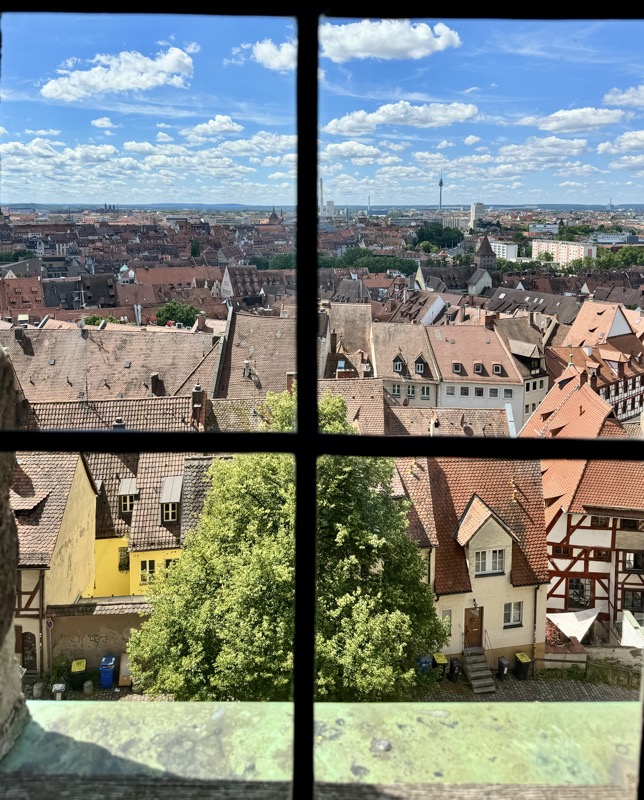
The stunning panorama from the ramparts of the castle looking over the medieval city of Nuremberg.
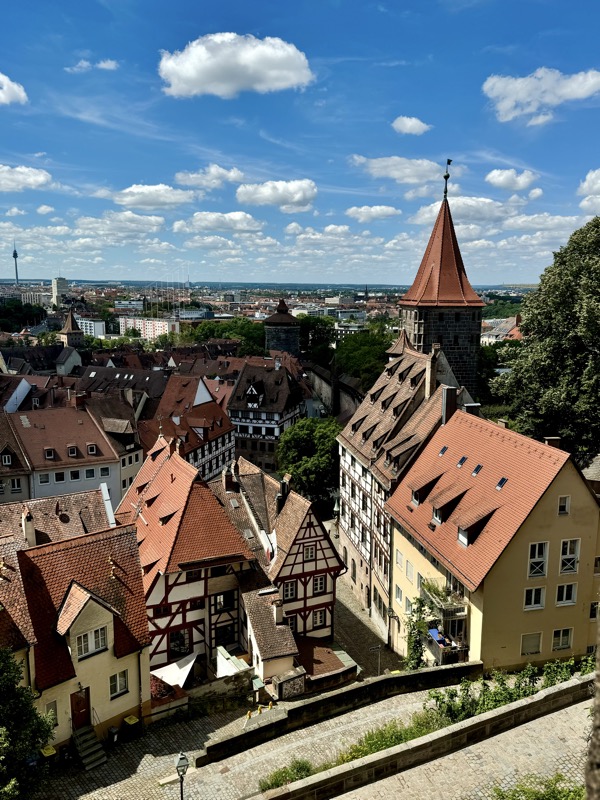


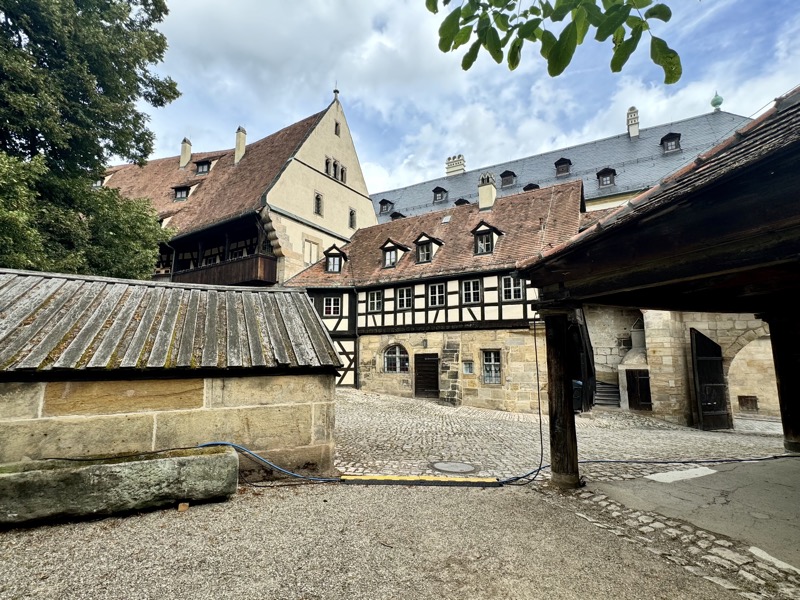
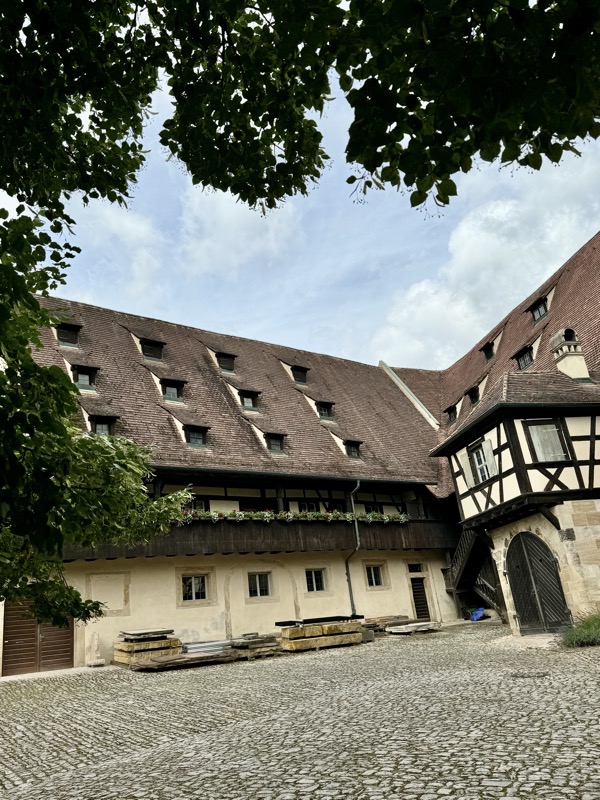
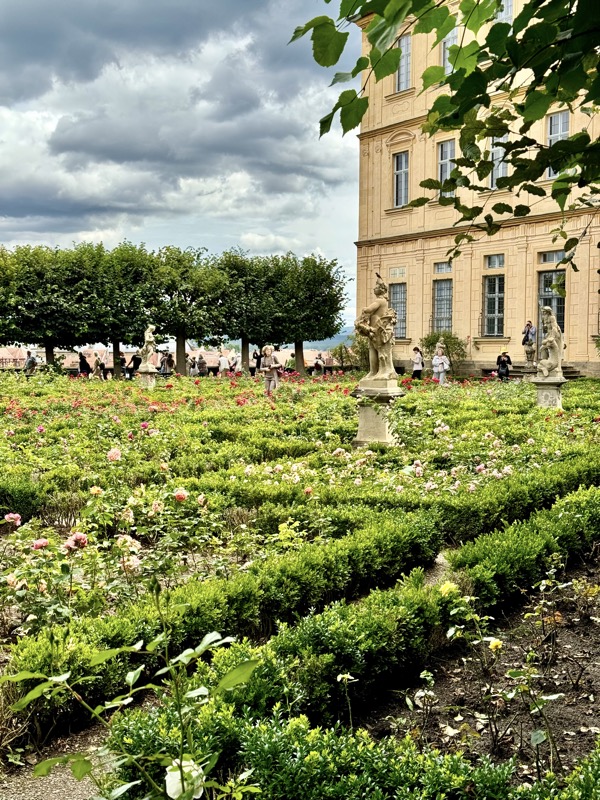
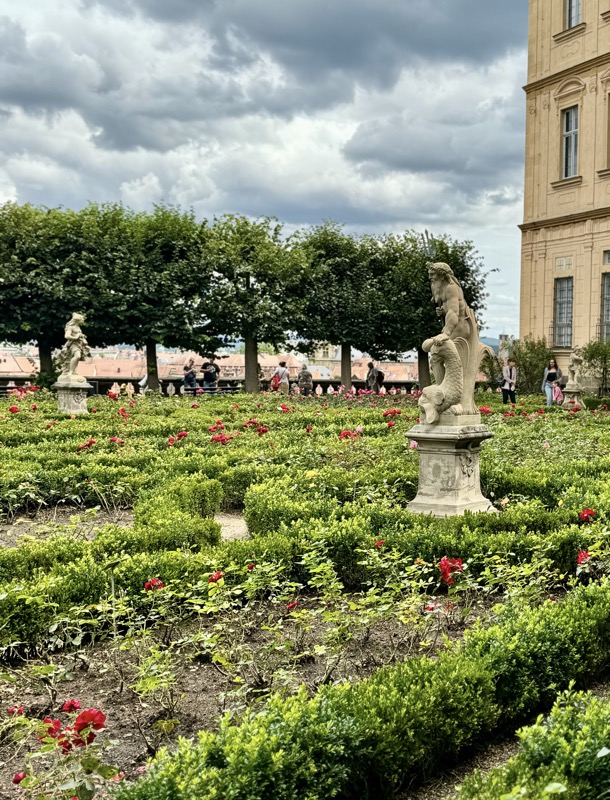
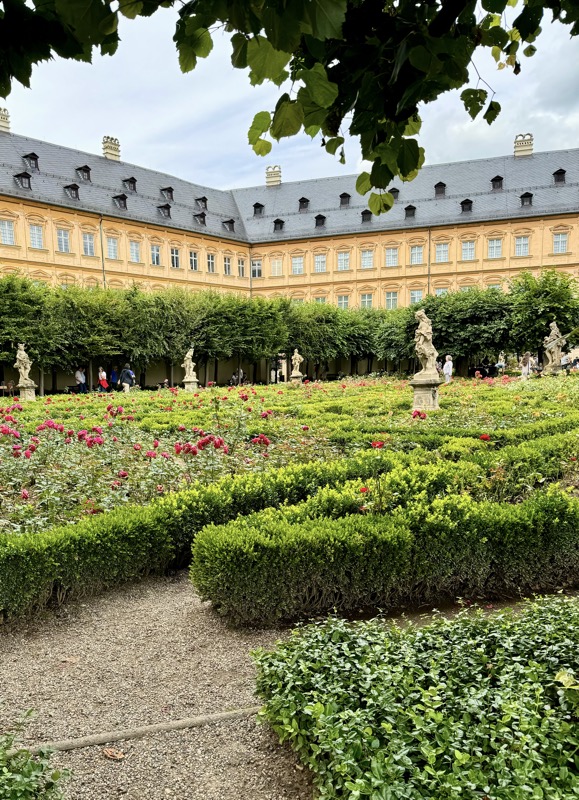
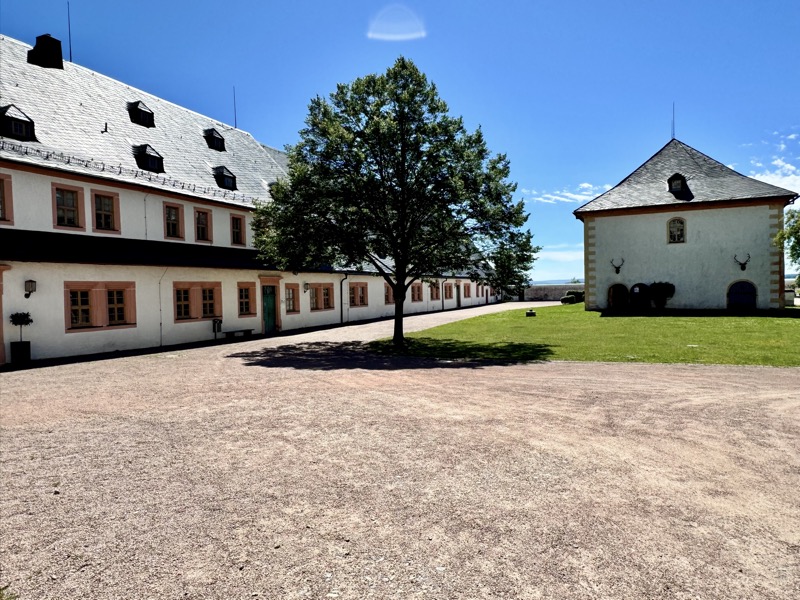
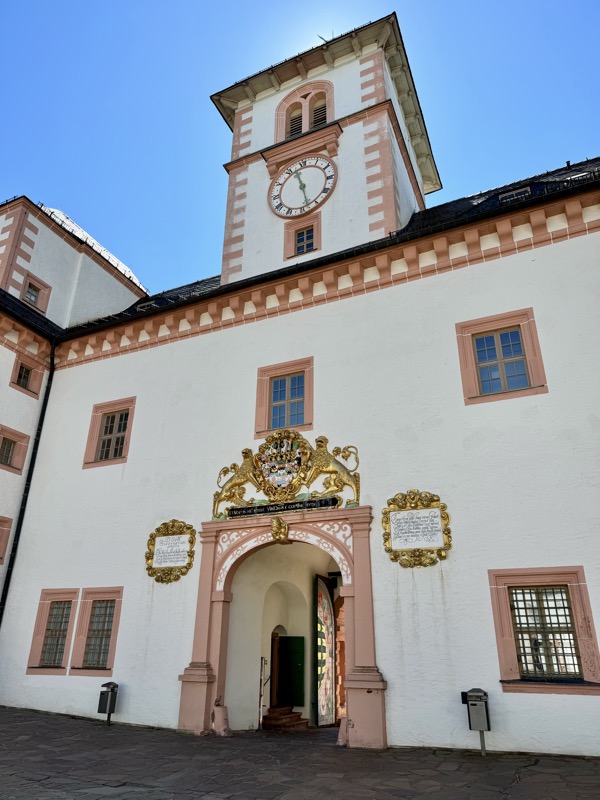
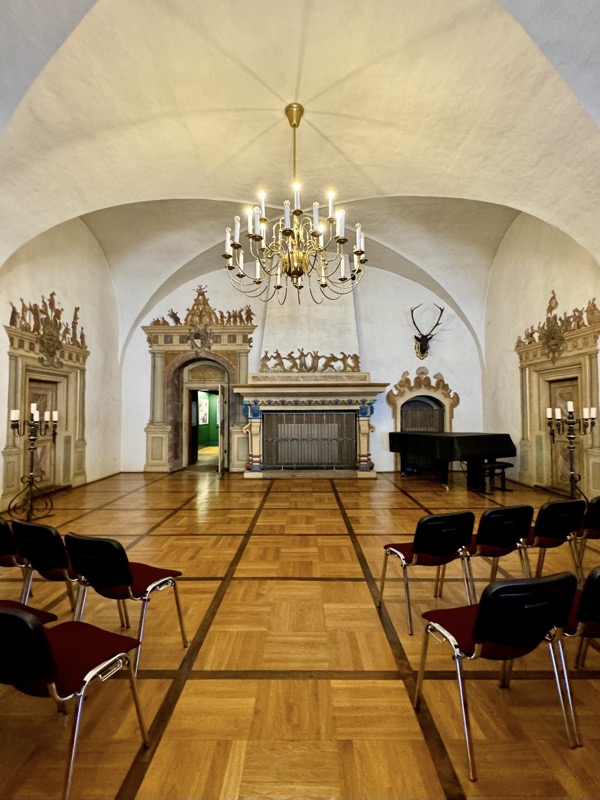
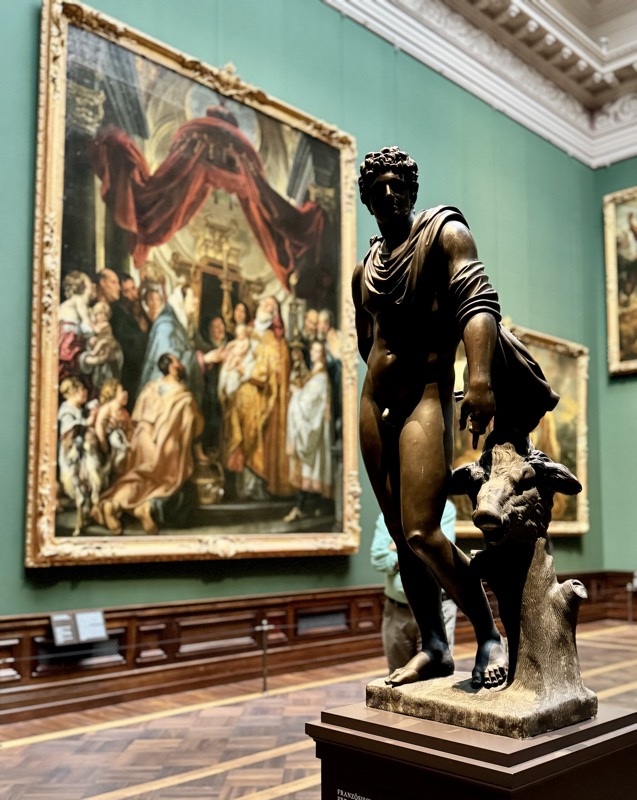
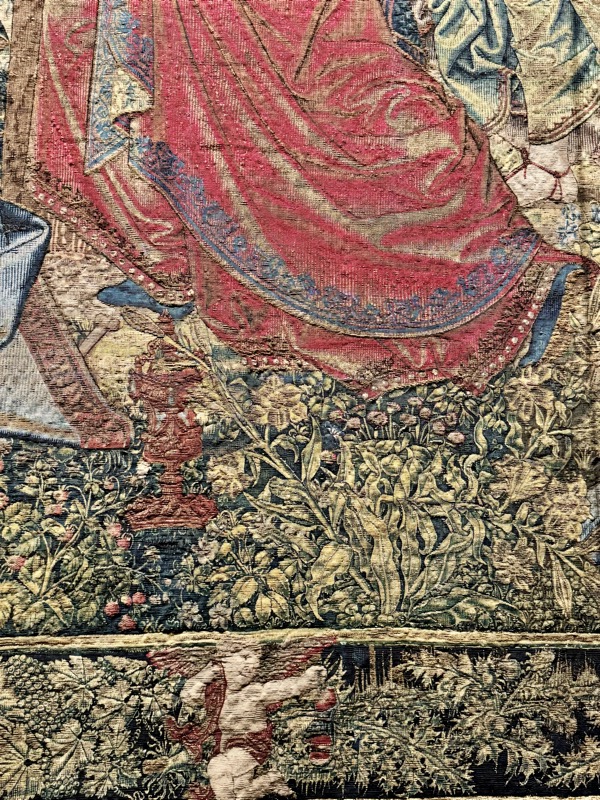
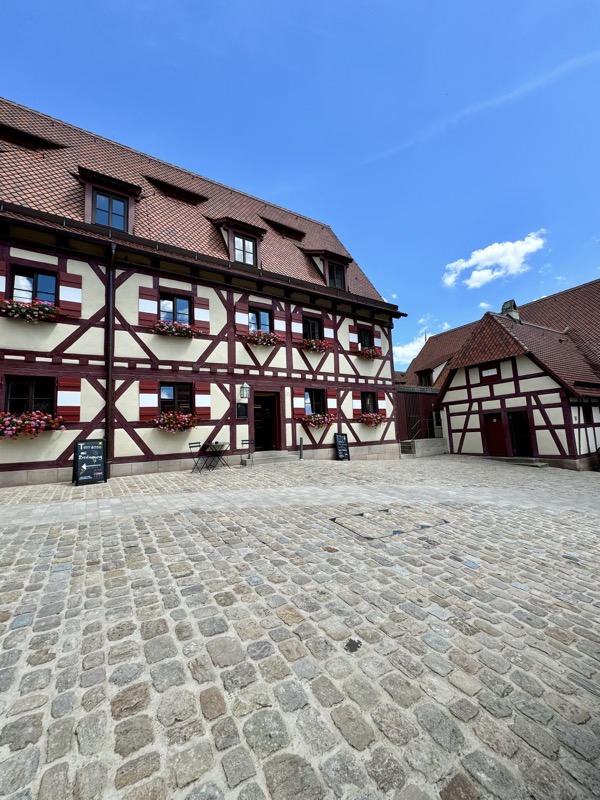
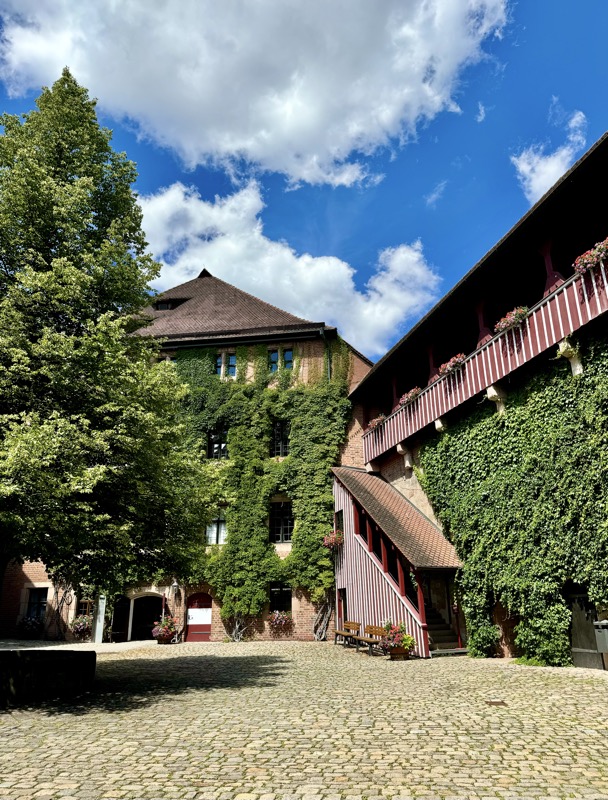
Inner courtyard of the main keep… the buildings are so beautiful and we were fortunately not swamped with people when we arrived that I went a little nuts with the photos…
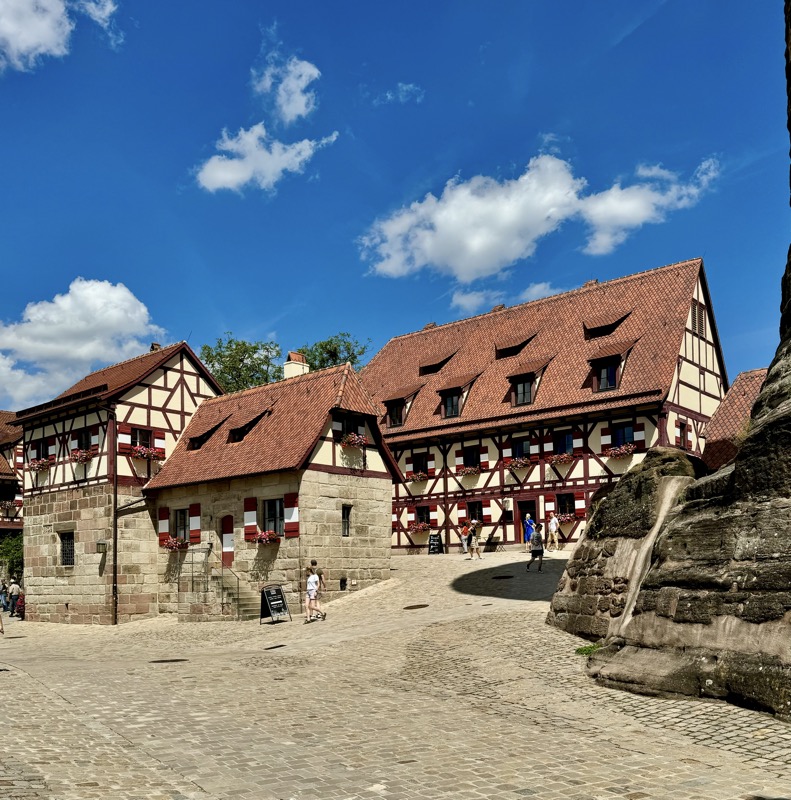


The building on the left here has been converted into a super modern cafe, but thankfully on the outside, it is still in keeping with its medieval location.
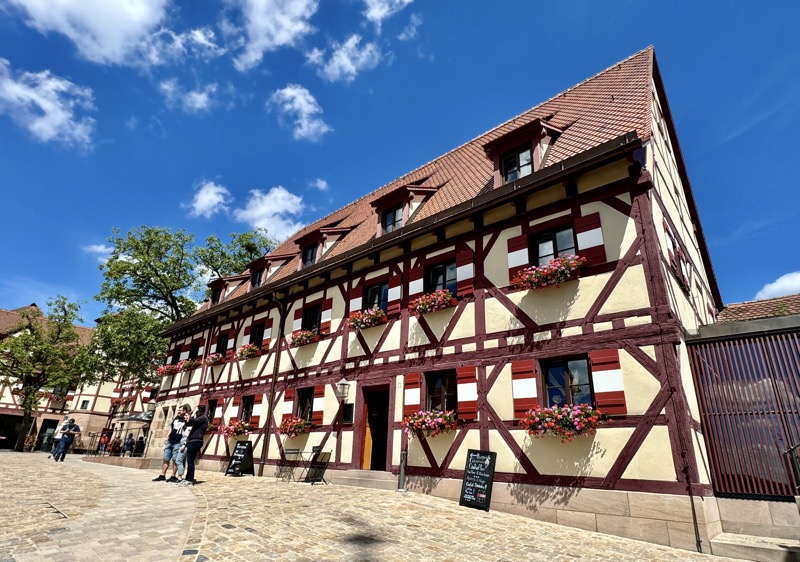
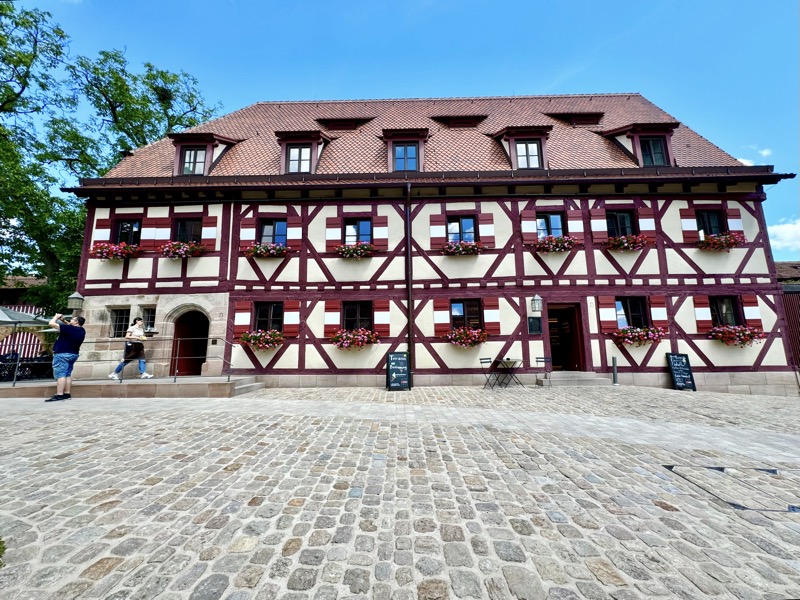



Even the museum entrance/exit and gift shop are well hidden.


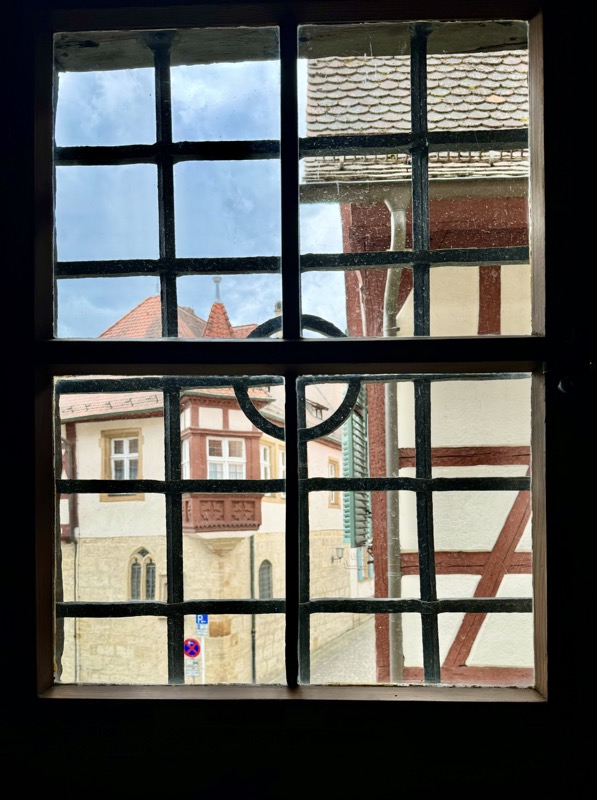
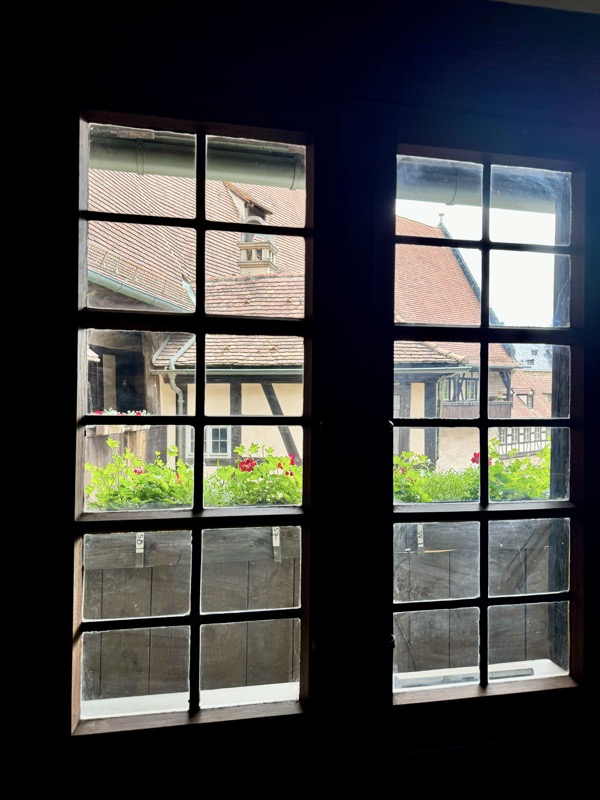
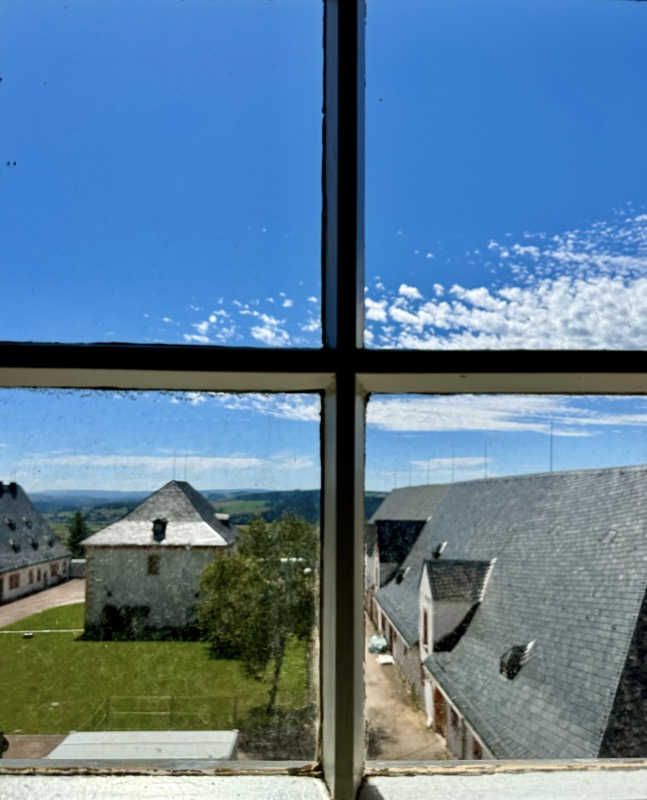
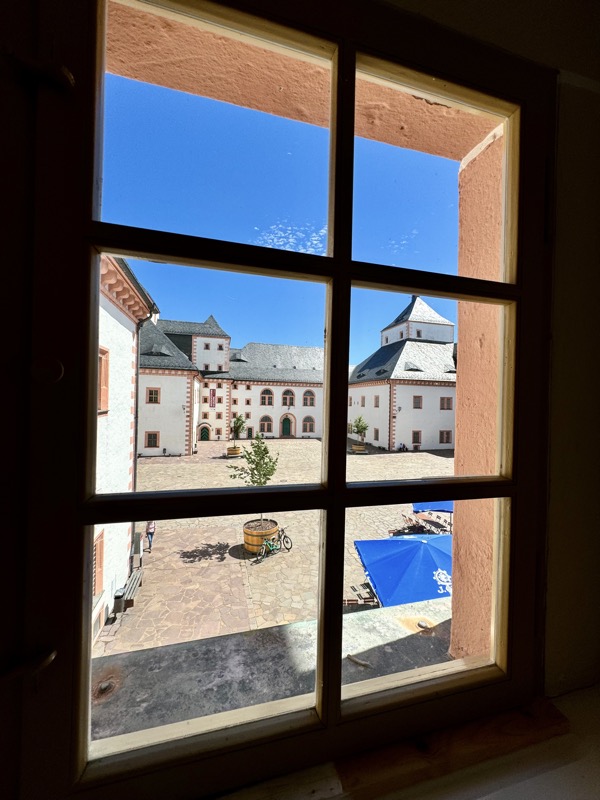
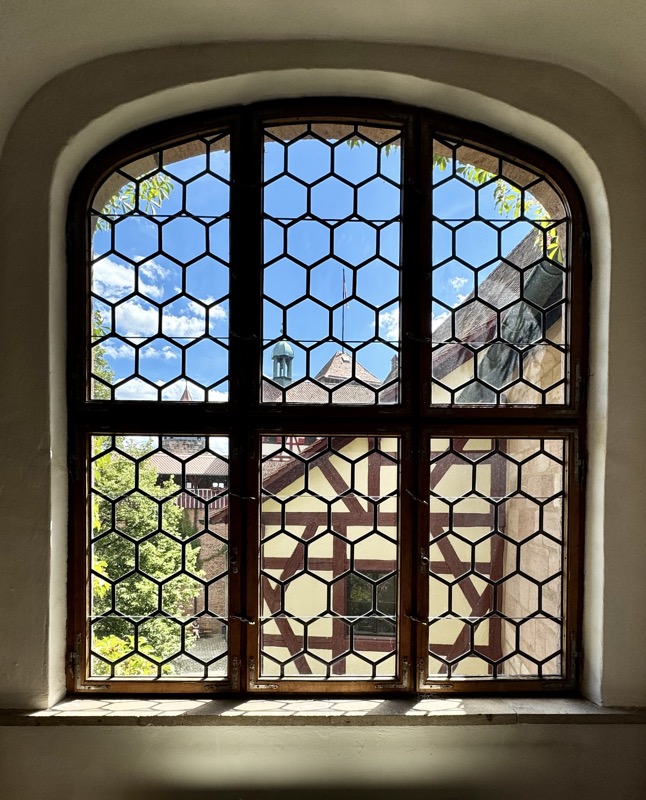
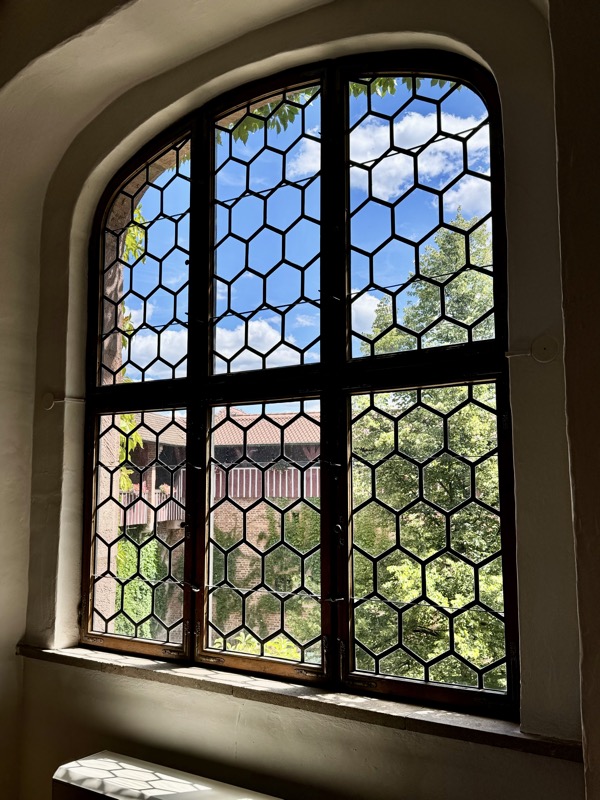
Views over the city through old glass windows.

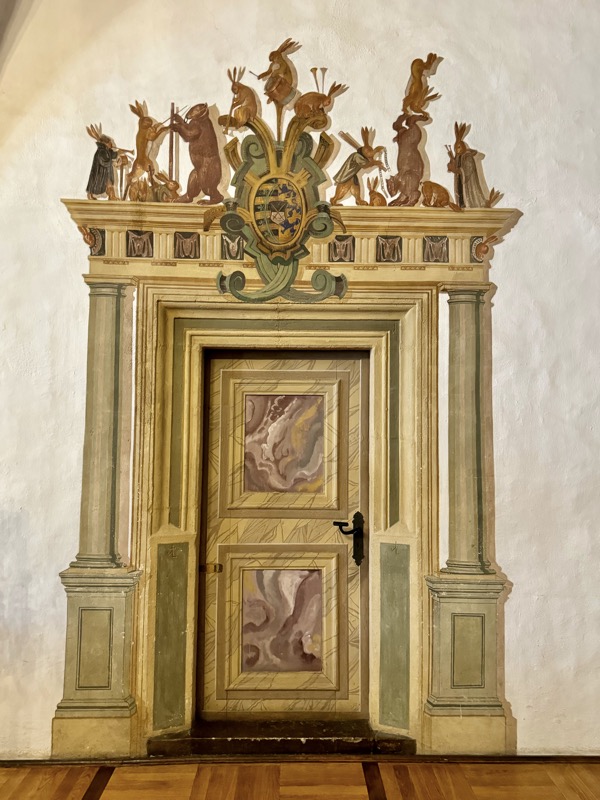
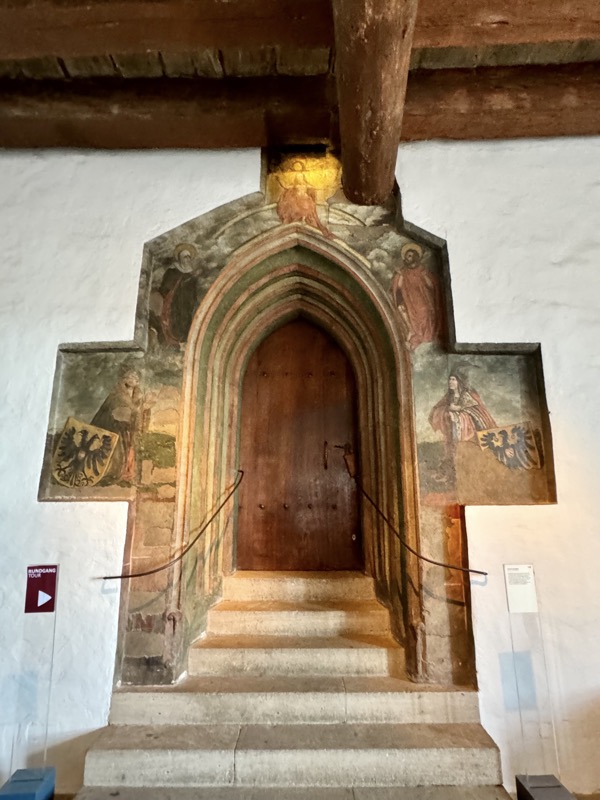
Doorway from the palace hall to the private imperial chapel.


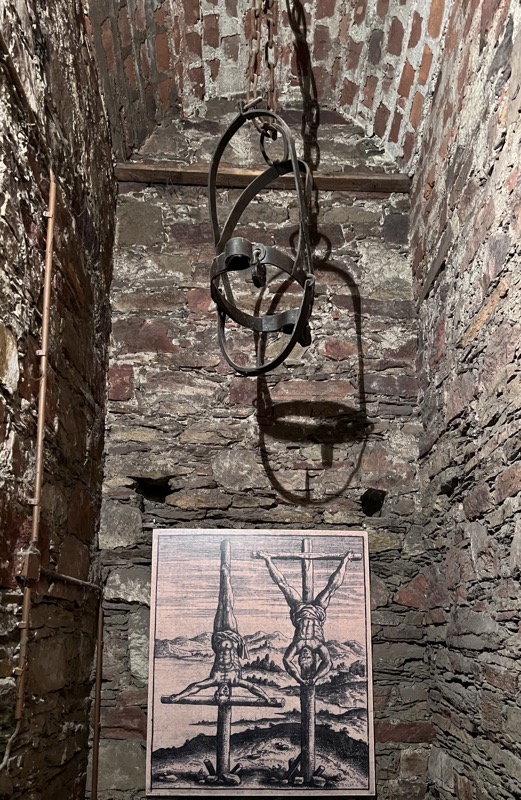
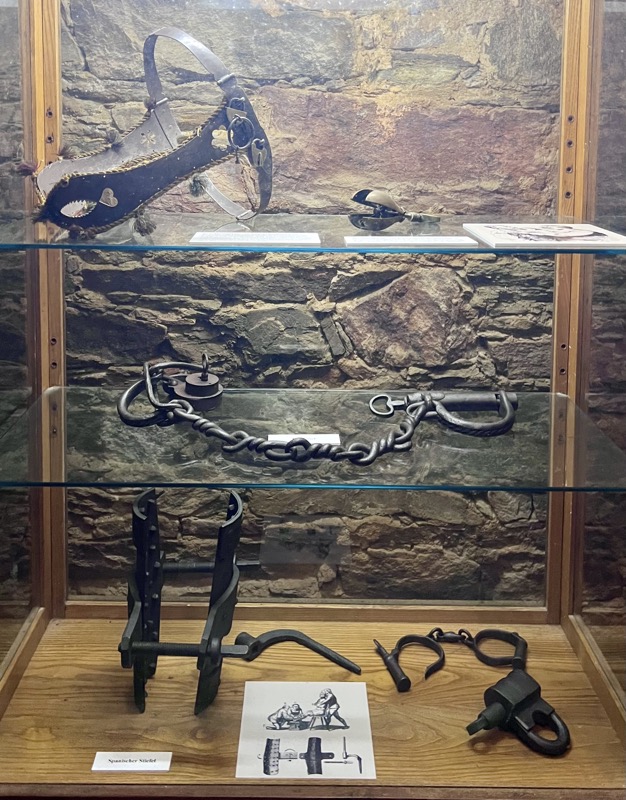
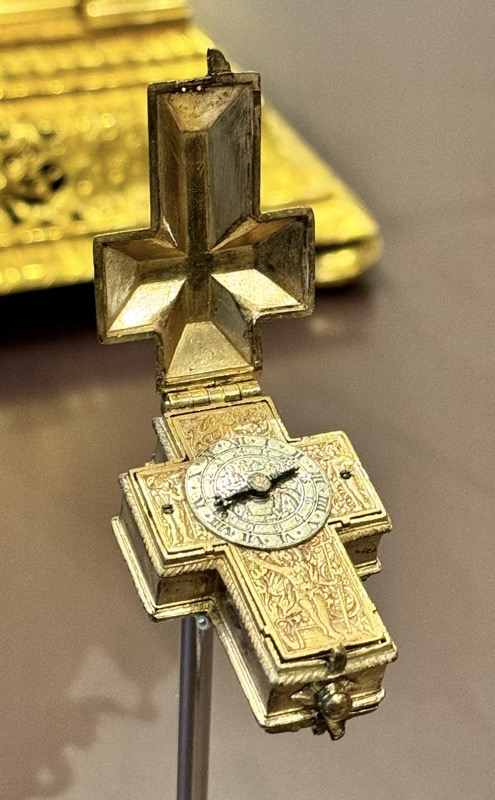
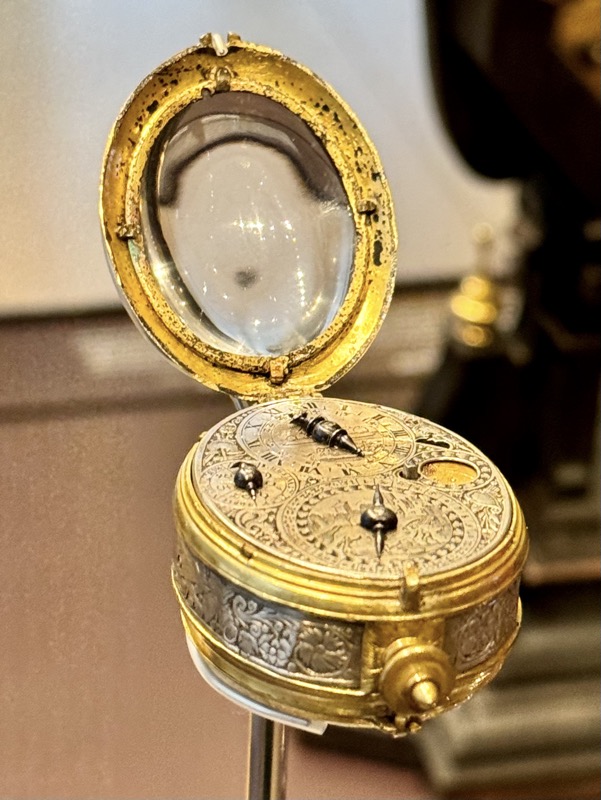
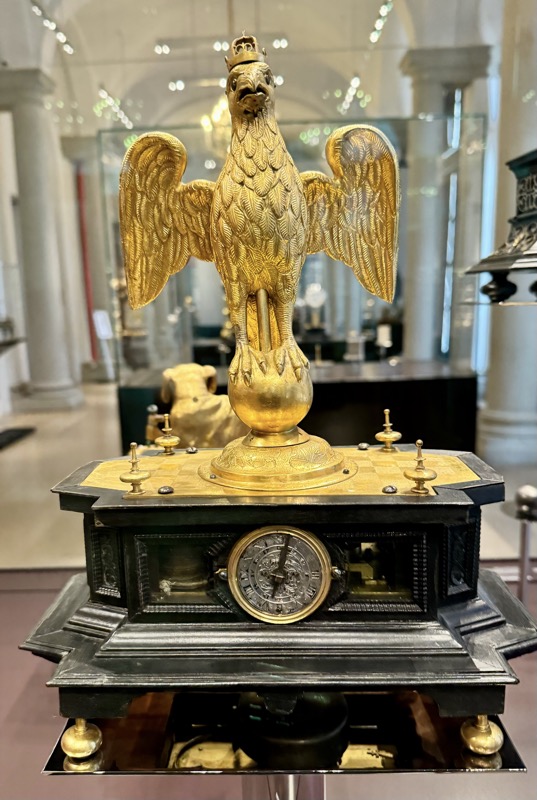
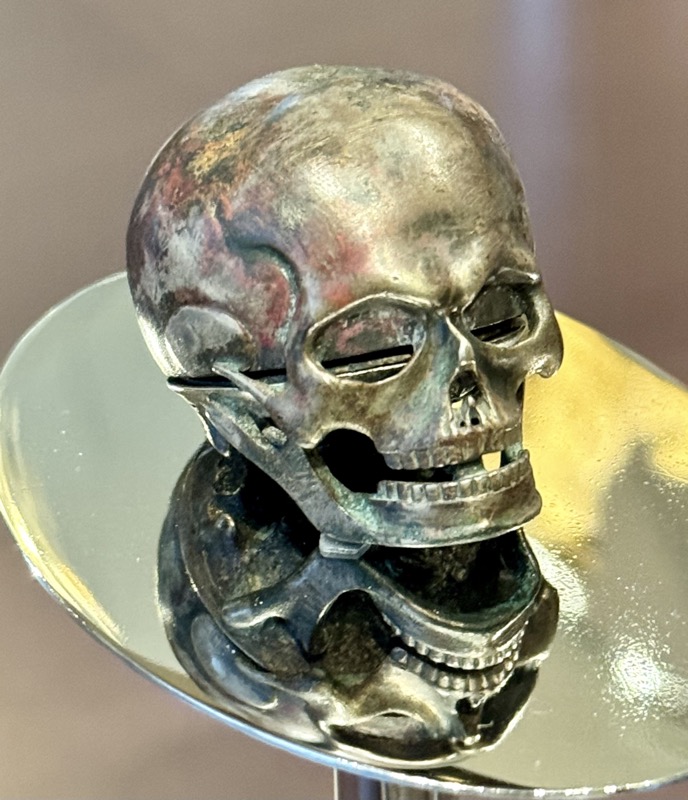
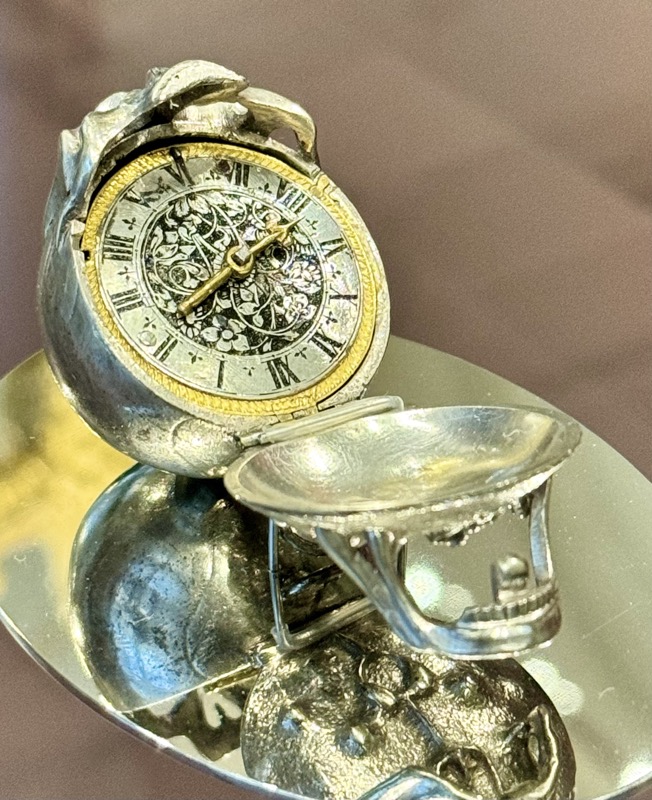
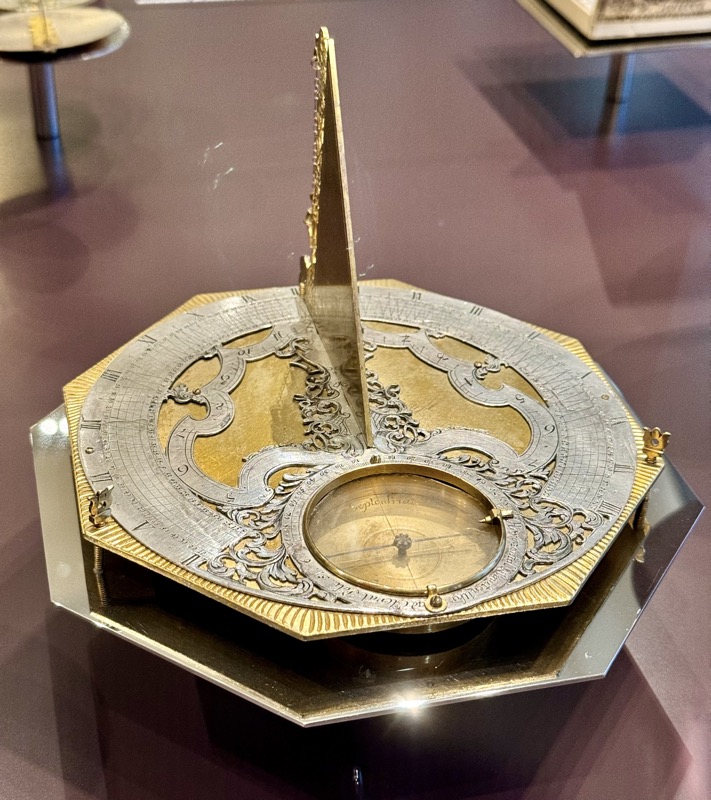
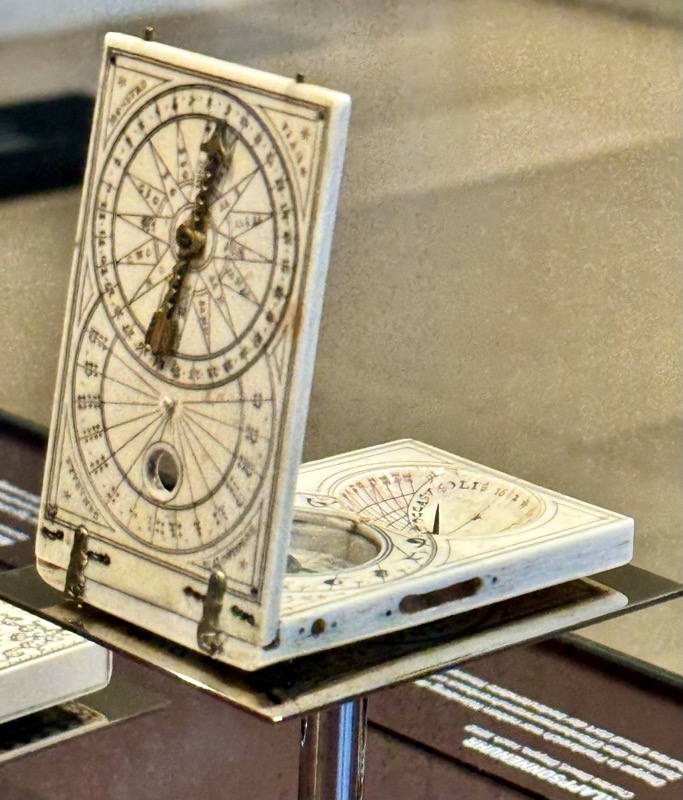
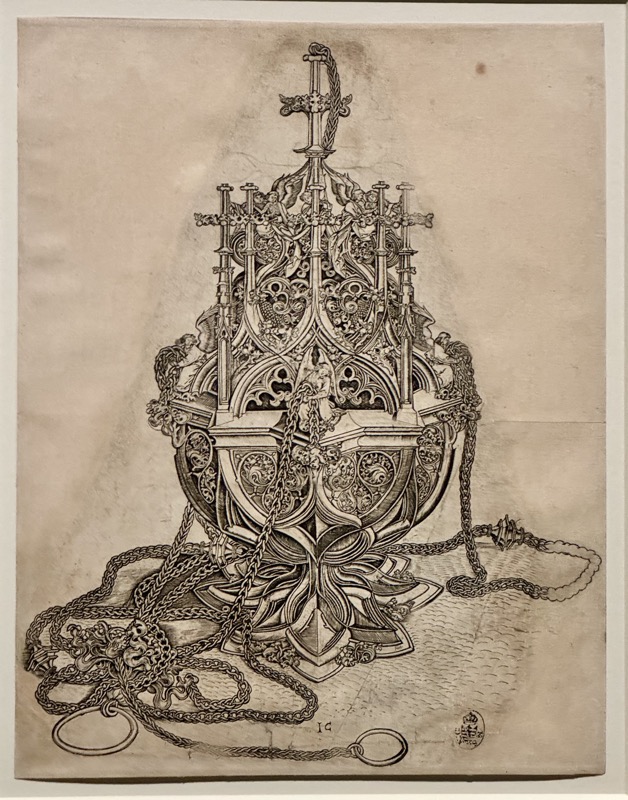
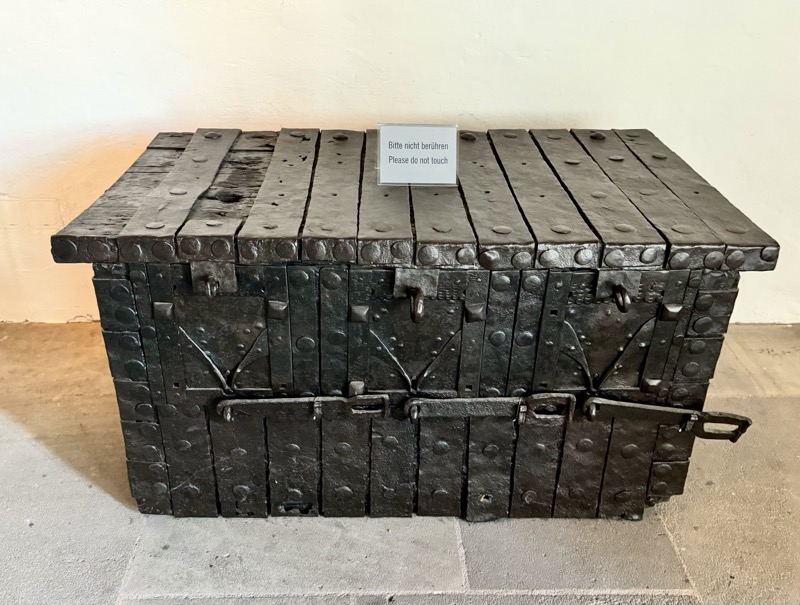
A strongbox… sadly without a description plaque.


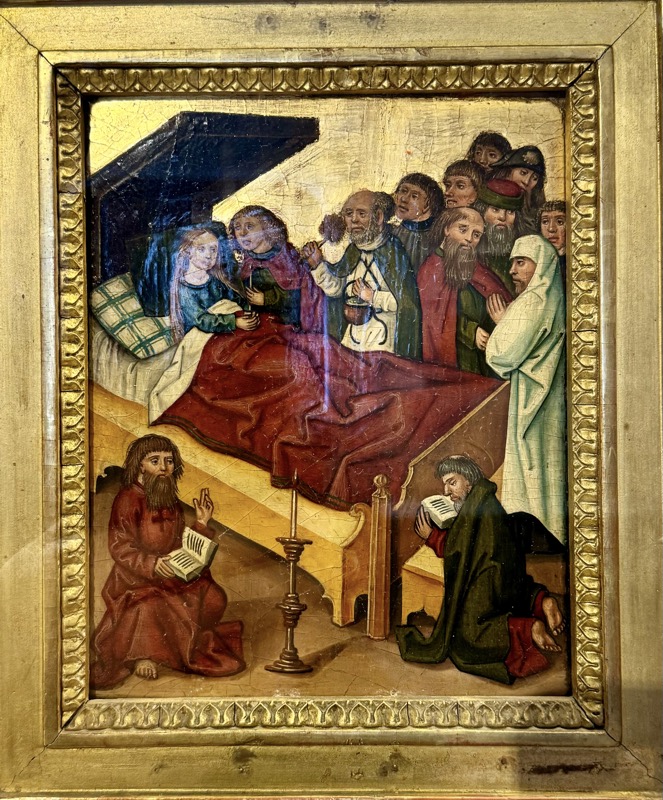
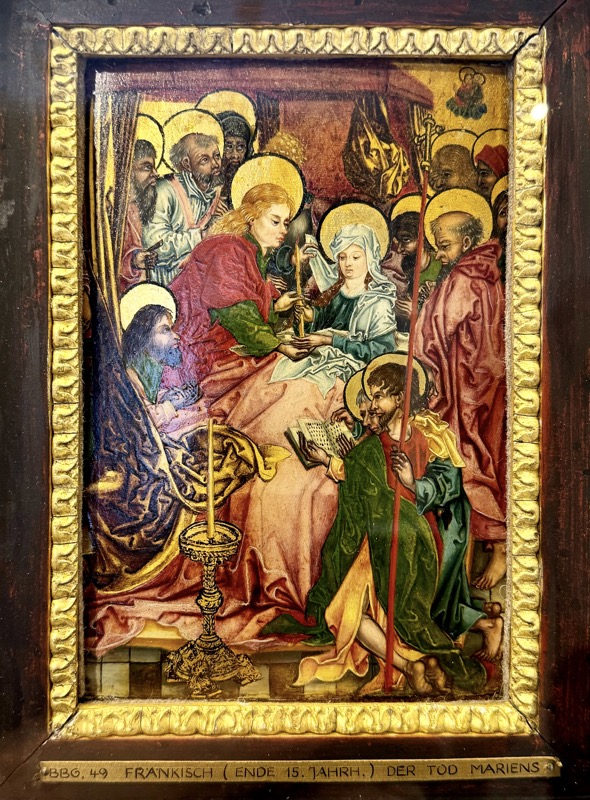
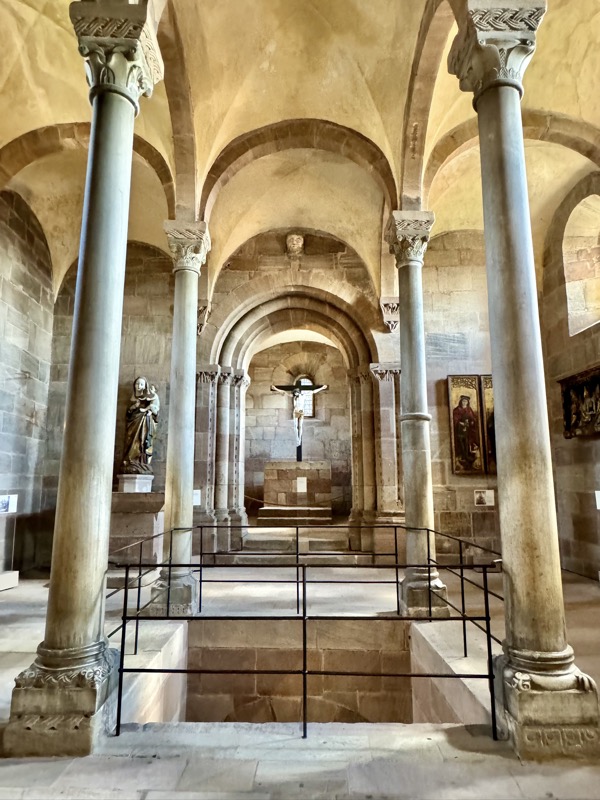
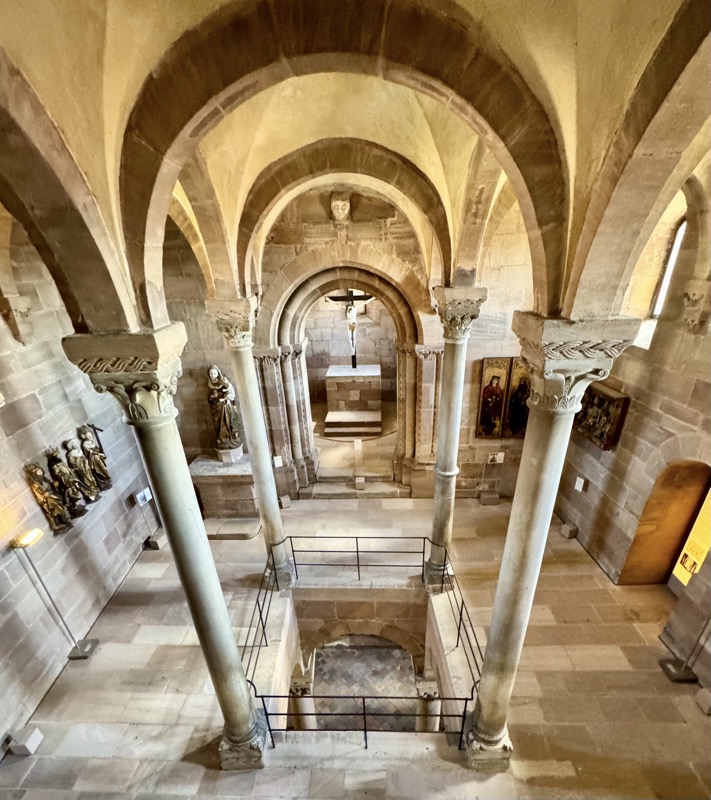
The private imperial chapel – there is a large hole in the floor, and another hall below where commoners could come to hear services without interacting with the castle’s more elevated inhabitants! This double chapel saw daily masses since 1216. The Emperor’s, (top part of the) chapel was likely only used when the emperor/king was in residence and was only accessible through the upper hallways of the ruler’s chambers.

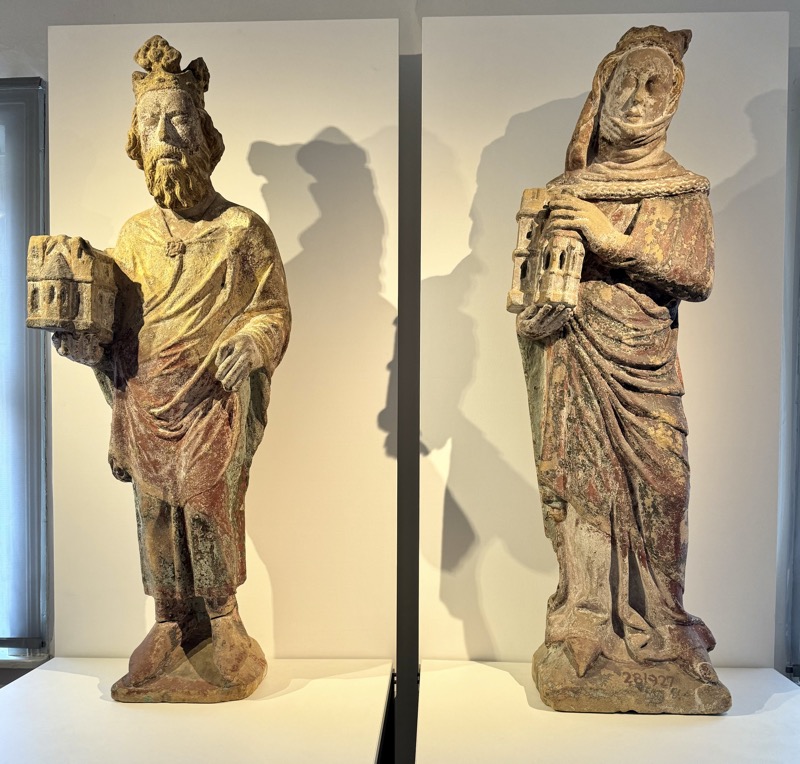
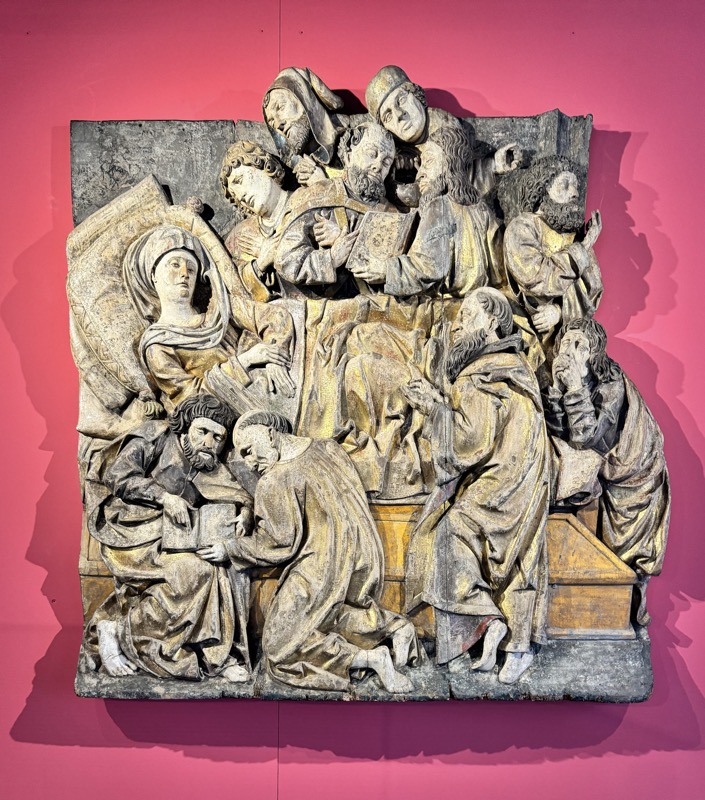
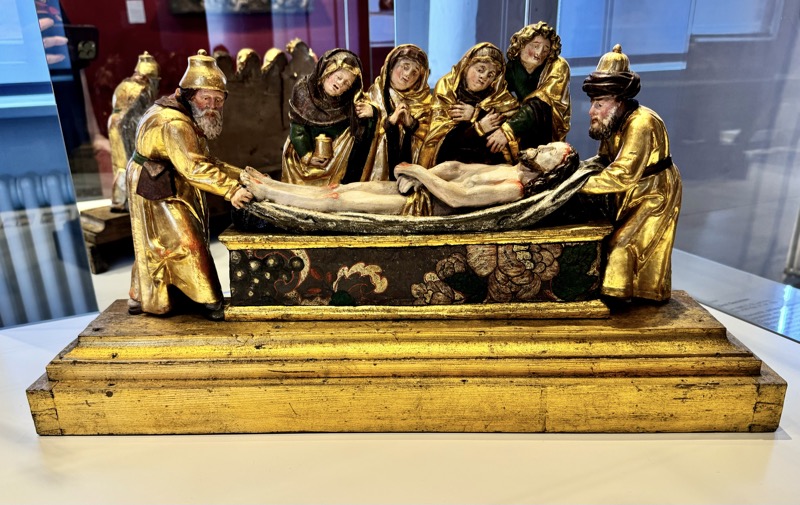
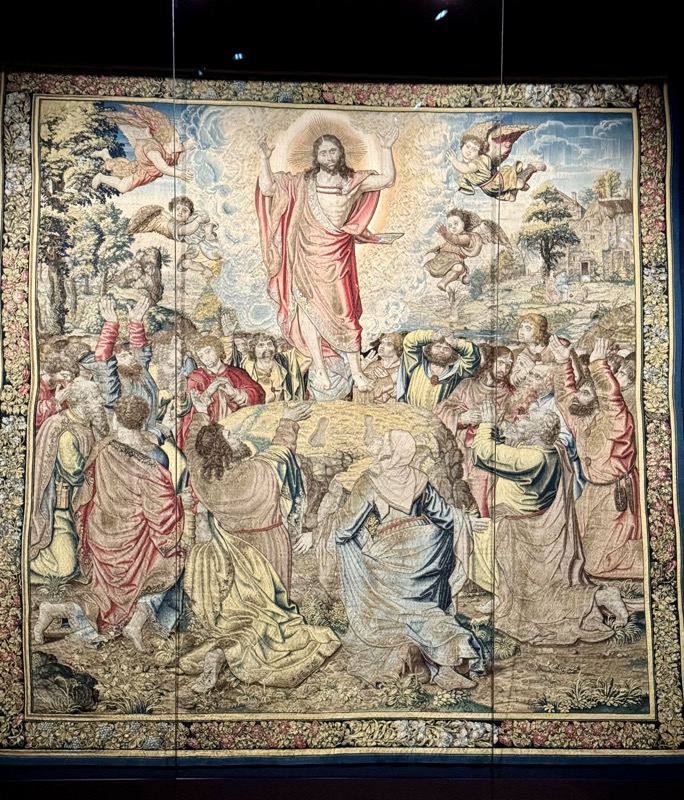
Stone relics ‘The Resurrection of Christ’ and ‘The Ascension of Mary’, Augsburg, c.1530.
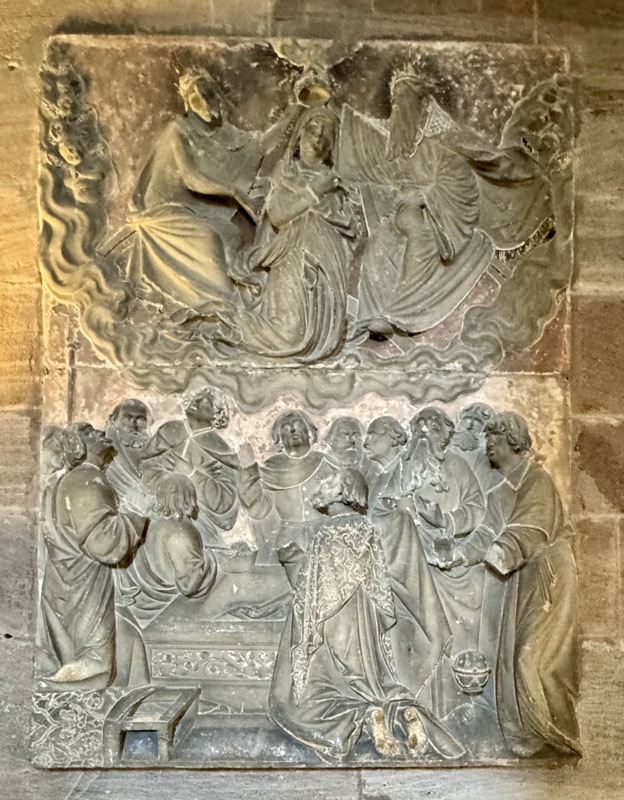

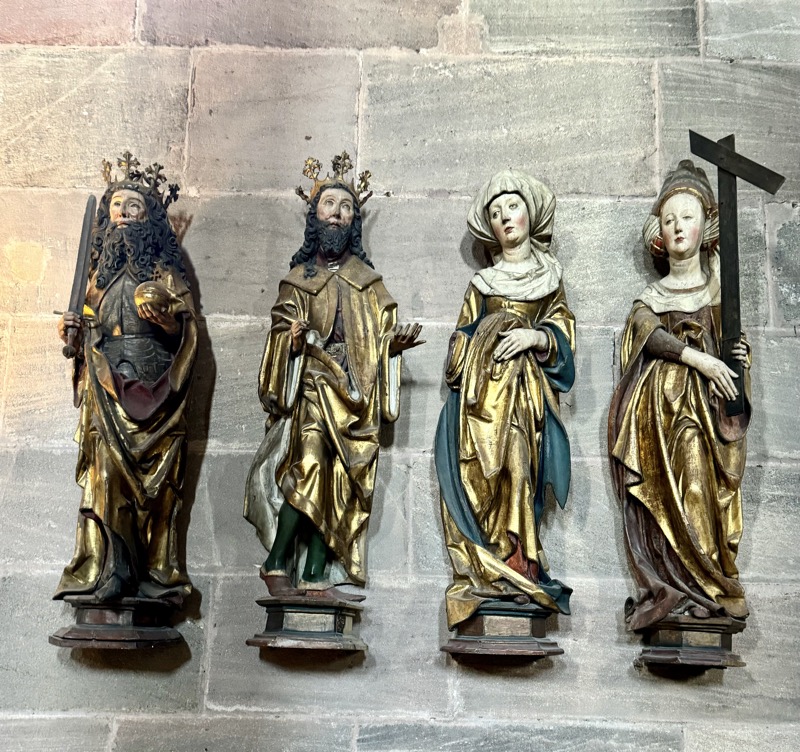
The side altar of the Emperor Frederick III. Figures from the shrine are (left to right) Charlamagne, St Henry, St Kunigunde, St Helena of Nuremberg, c.1487/.


Figures below are wings from a larger, now lost, altarpiece, c.1401.

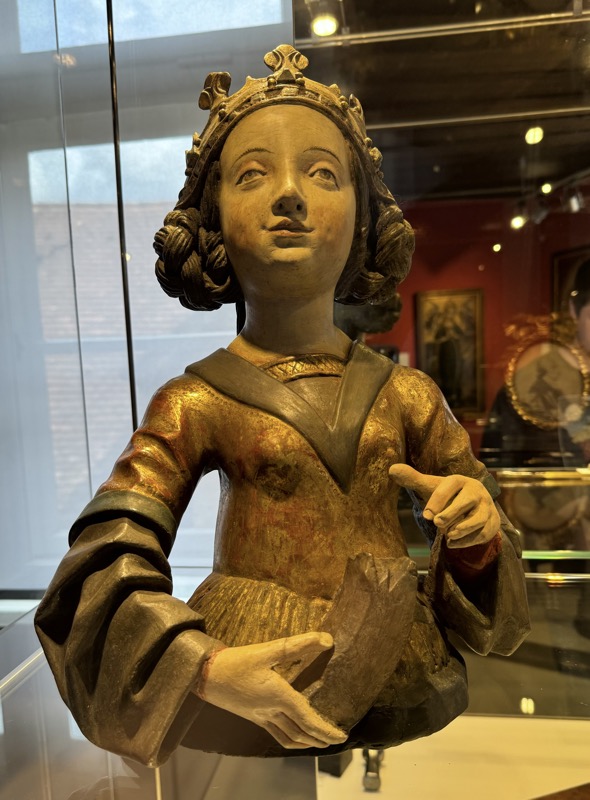
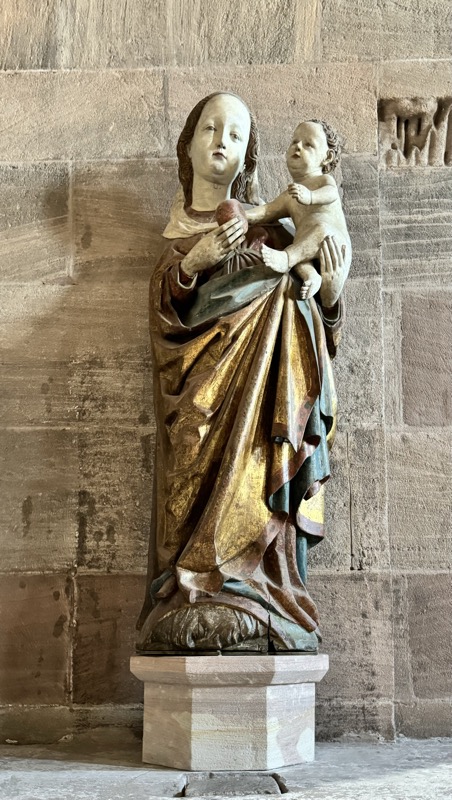
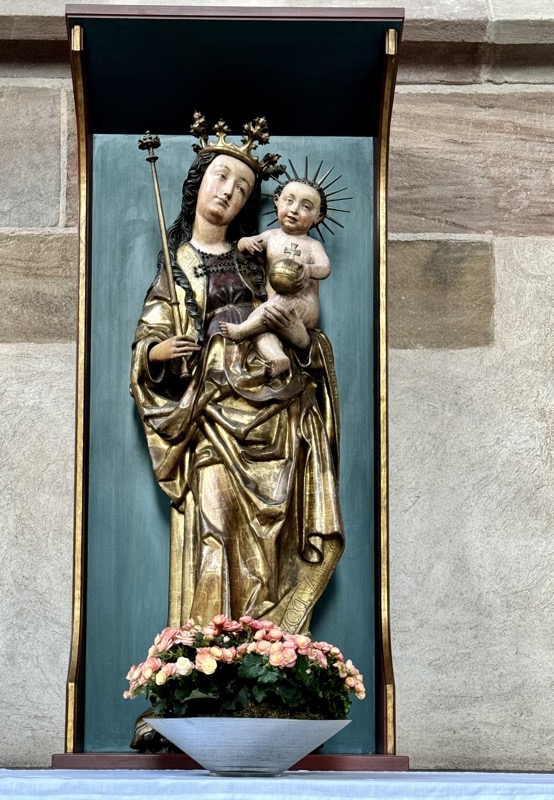
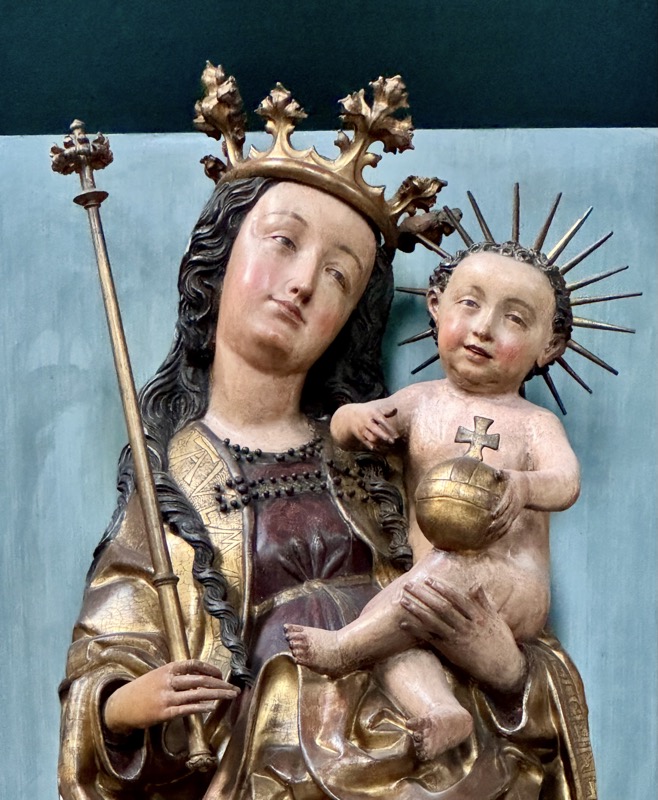
Mother of God, Nuremberg, c.1450-1460… this is one of a small collection of Nuremberg Madonna’s that are characterised by being life-sized and close to resembling natural people.
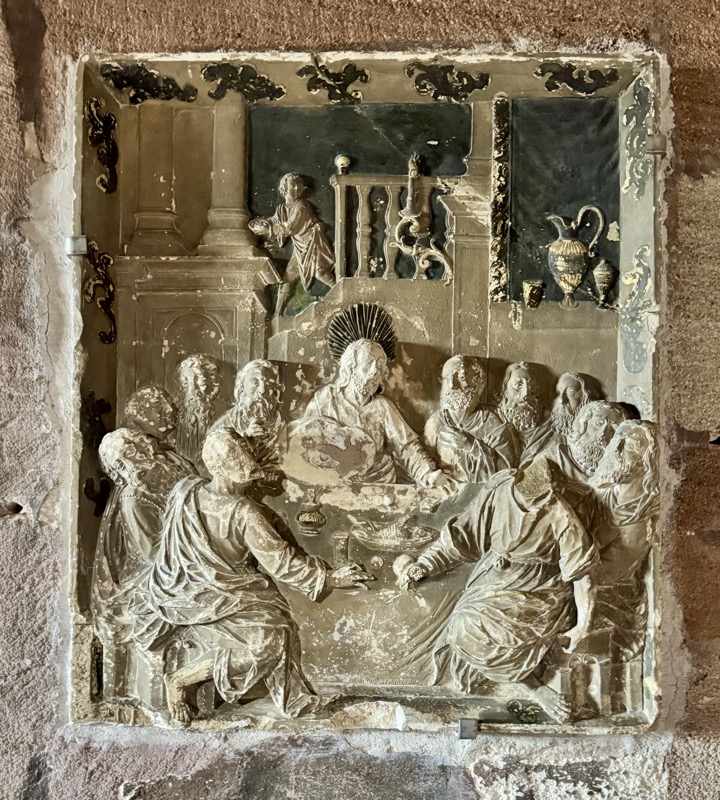


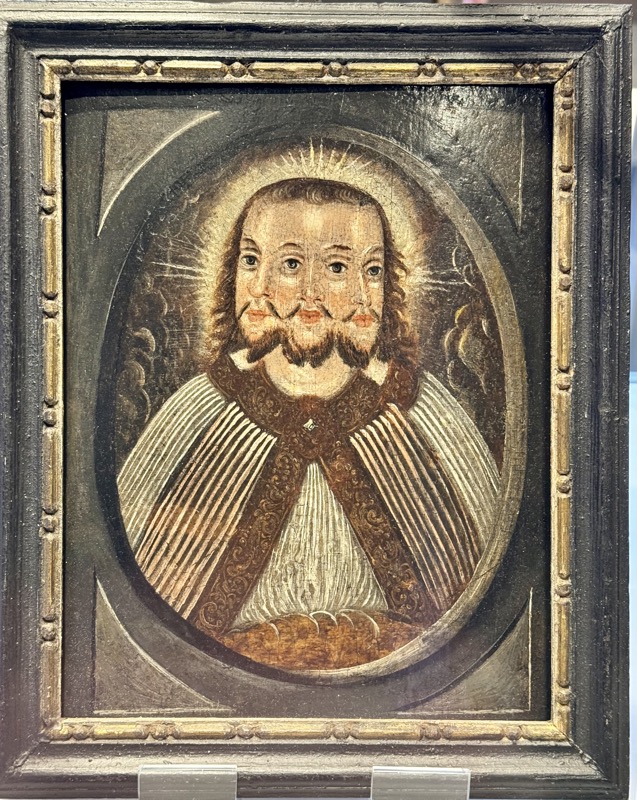
These frescos are believed to have been installed prior to a visit from Charles V, King of Spain who was crowned King in 1520 and referred to himself as the ‘Chosen Roman Emperor’.
Frescoes attributed to Hans Weiditz, Augsburg, c.1519.
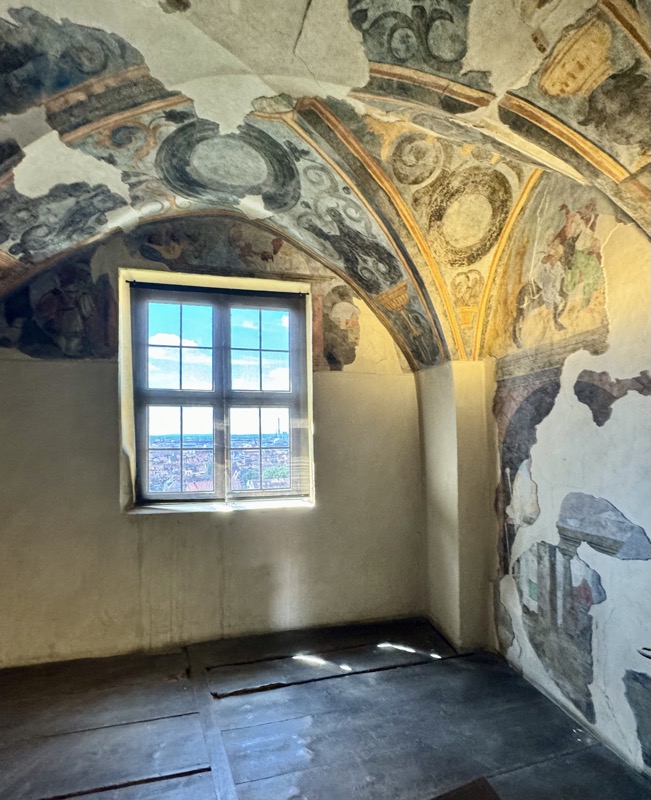

Looking down from the Emperor’s Chapel at the multi-layered chapel for the masses.

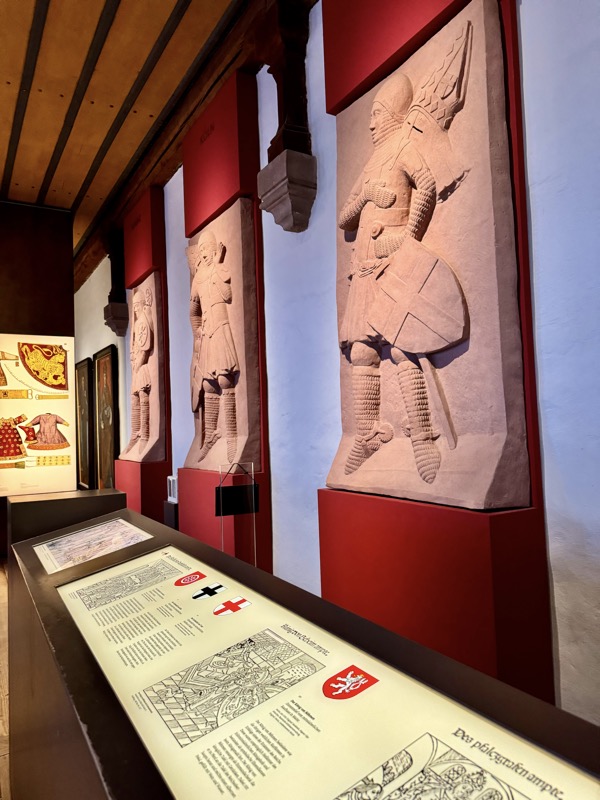
Relief of Emperor Ludwig IV the Bavarian, from the Nuremberg Town Hall, c.1340, cast after a model in Munich… sigh. Hate this shit : a lot of the info I’m saving is acquired by translating stuff after we leave a place. I’m looking at these things in situ and thinking, that doesn’t look right, get some time later and translate any info only to find out that we are looking at a late 18thC plaster replicas or something. :/
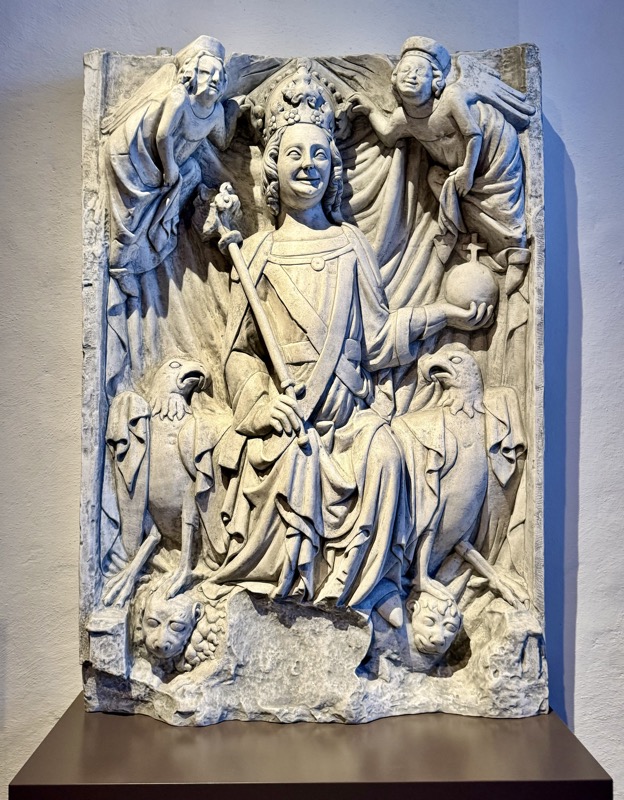

Same with this one…
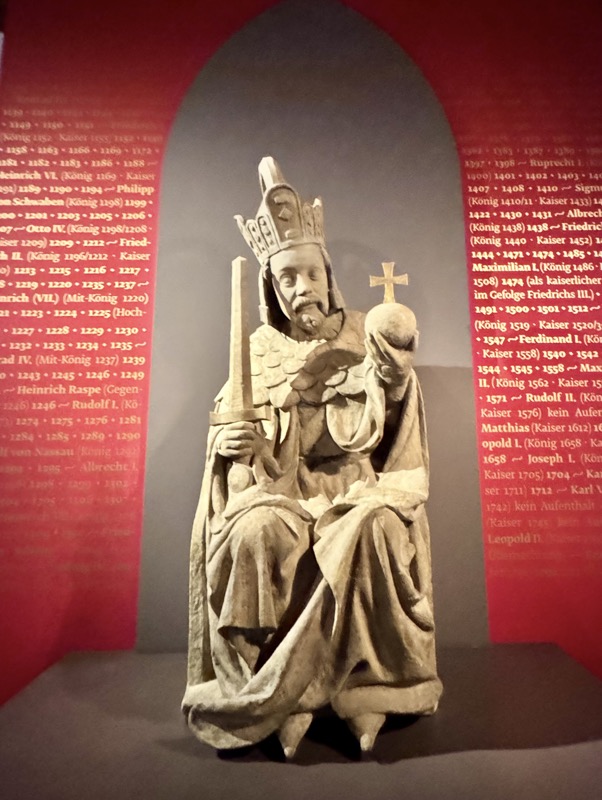
Monumental statue of Emperor Charles IV from the Old Town Bridge Tower of Prague’s Charles Bridge, Peter Parker, c.1370-1400. Original in sandstone, cast (below) in plaster.

Magnificne manuscript of the Golden Bull, Prague, 1400, leather, pen and parchment… reads the first half of the description. 

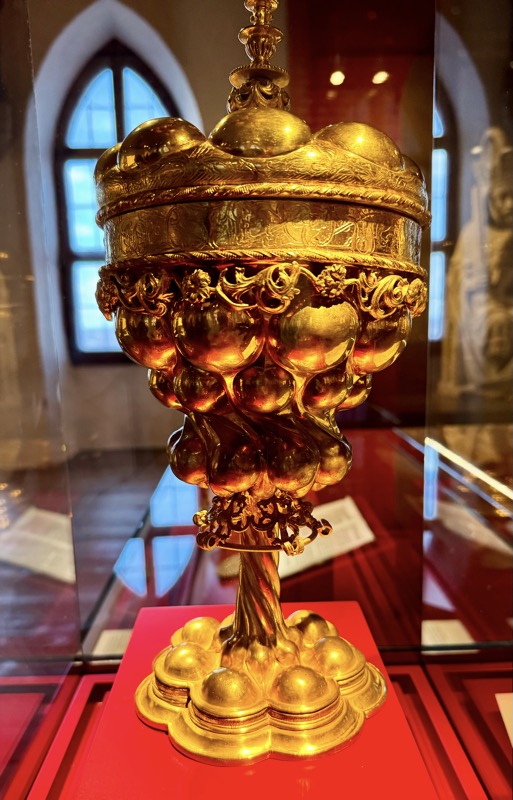
Humpback cup, Ellington & Co, Birmingham, c.1886. Copper brass, gilding… another fucking copy – is nothing in this museum original? The original 16thC cup is somewhere else and it doesn’t even tell us. The cup and other objects were part of the ceremonial table dictated for use in the Golden Bull.
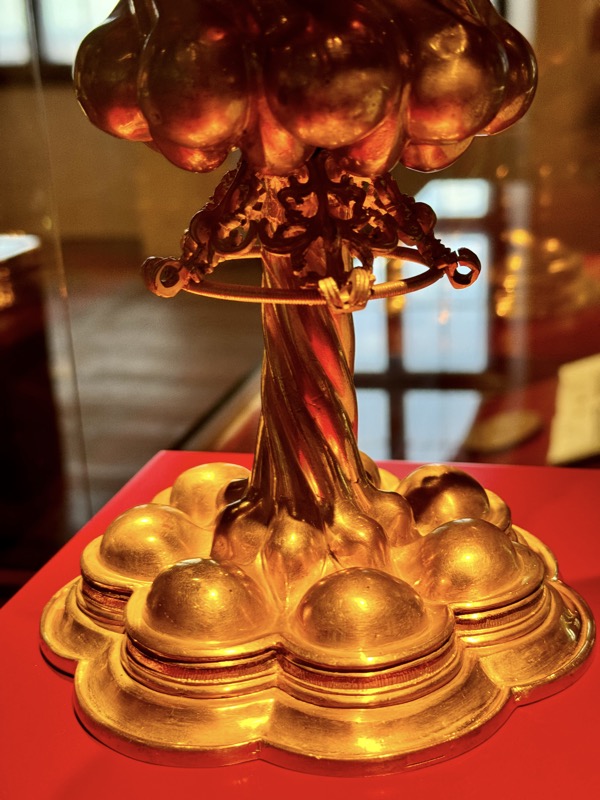




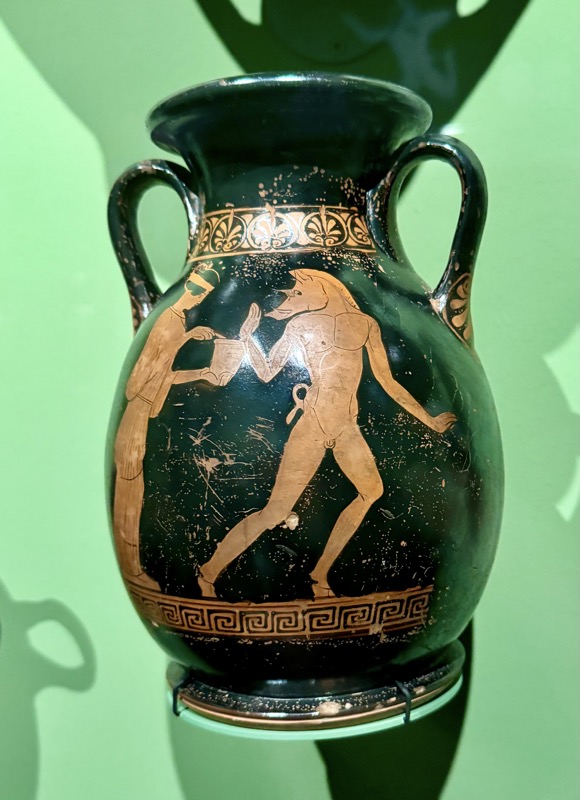
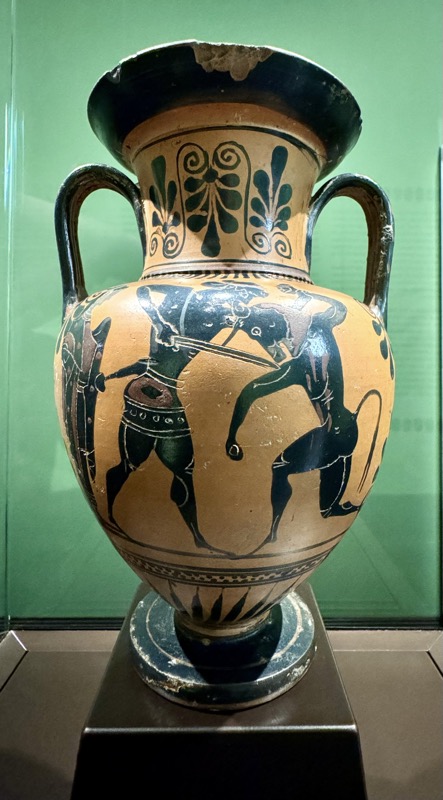
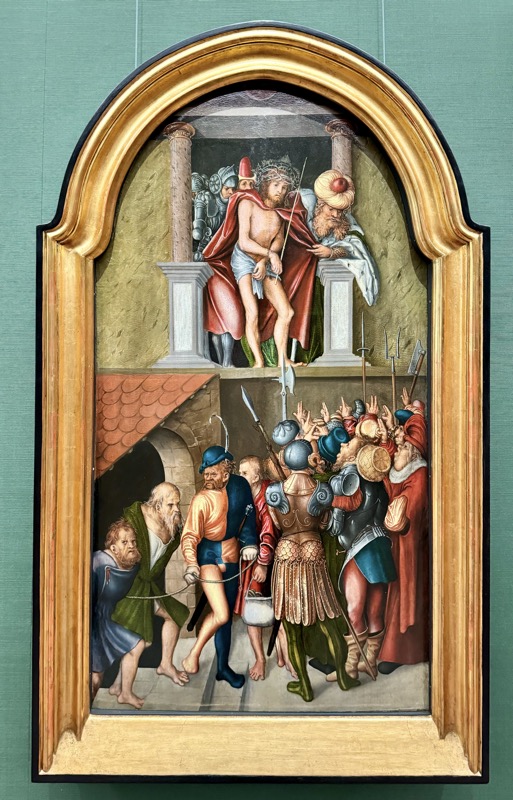
Holy Lance: Replica! Holy Hand Grenade: Replica! Holy Dagger thing: Replica!
The original objects symbolised the military strength of the head of the empire of Otto I (936-973).



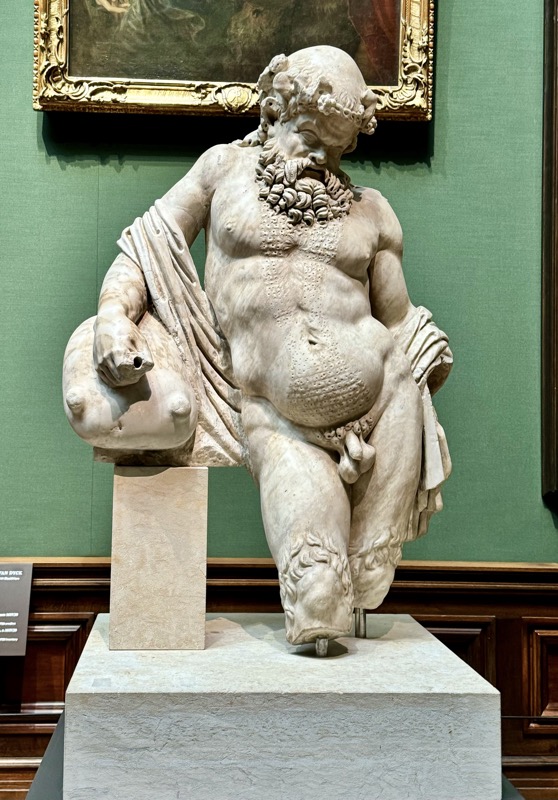
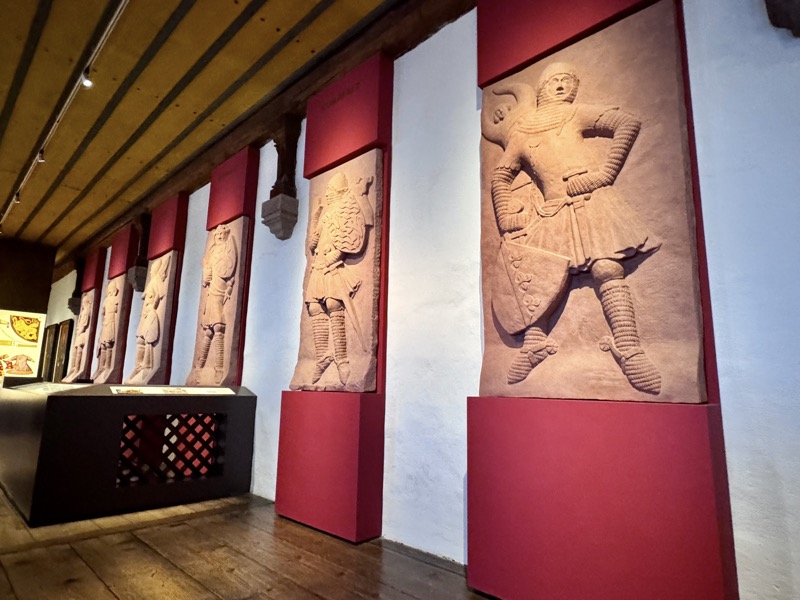
The room had these neat – but obviously modern – reliefs that depicted the famous and important houses of Nuremberg. For some reason these didn’t bother me so much, as they weren’t accompanied by an info plaque and obviously weren’t pretending to be medieval artefacts. *shrug*



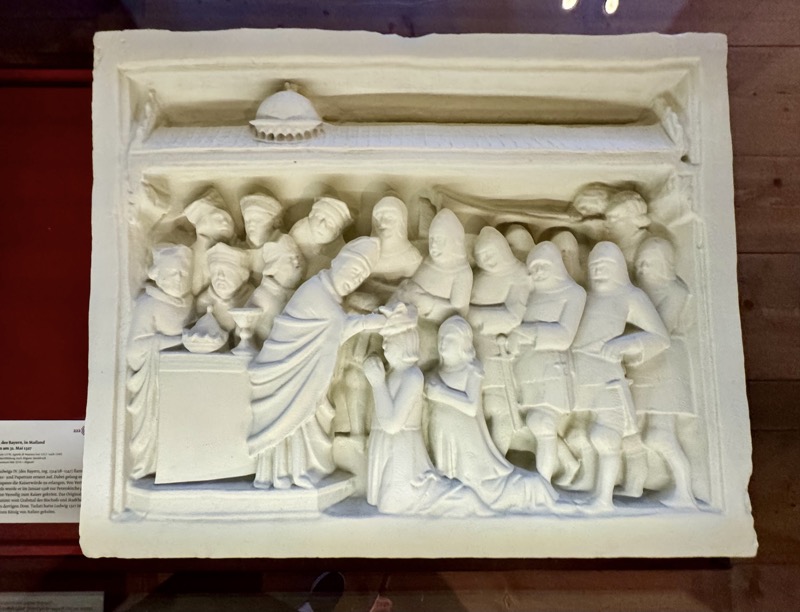
Coronation of Ludwig IV the Bavarian, in Milan as King of Italy on May 31, 1327, work attributed to Agostino Di Giovanni (c. 1310-1370)… or at least the original marble one was. This is a plaster case made in Munich.

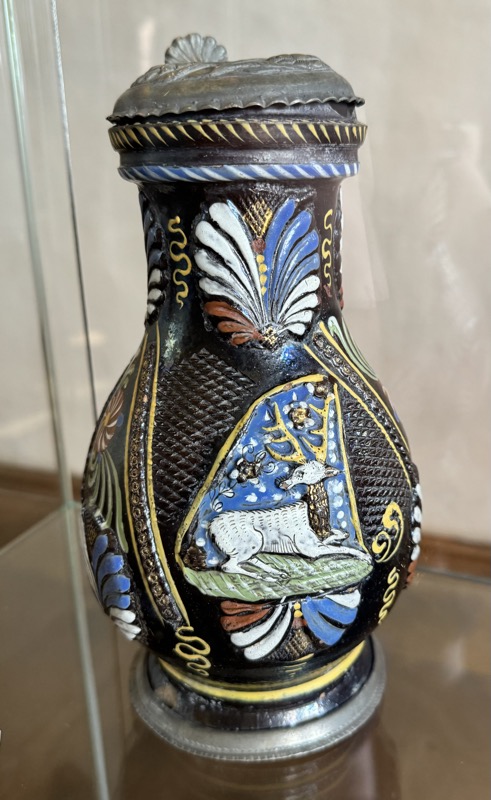
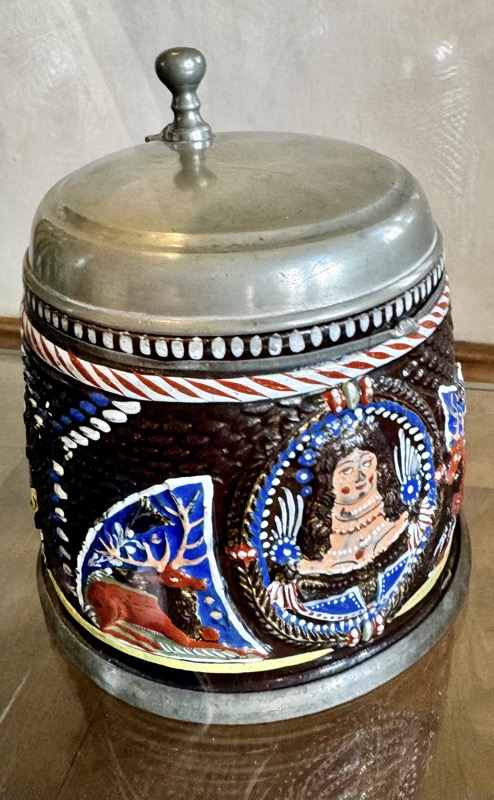
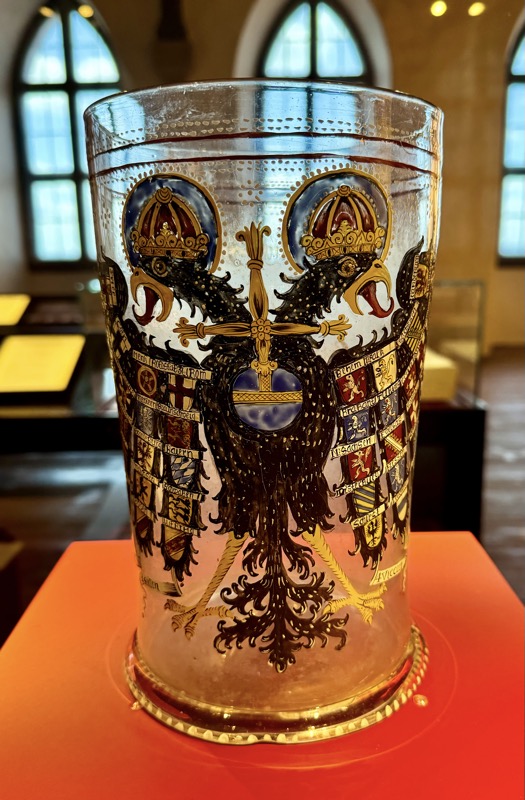
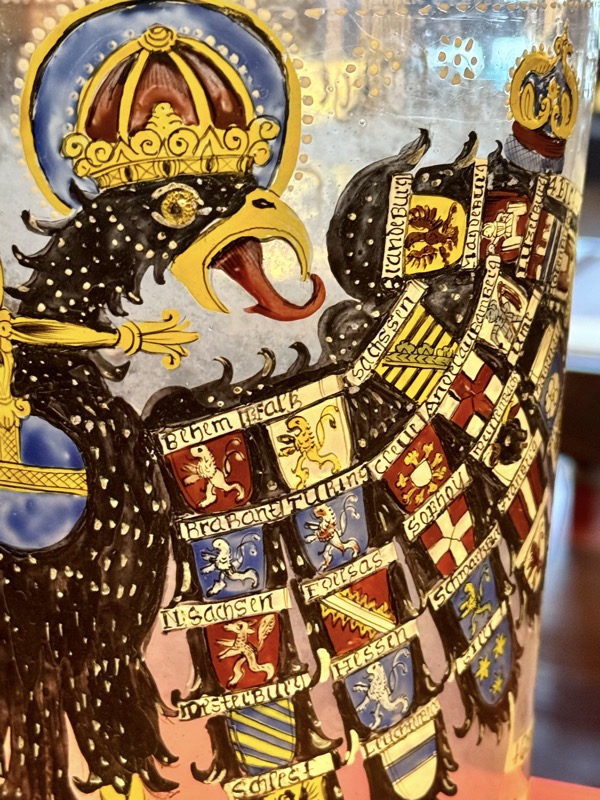
Oh thank fuck!!! I really enjoyed looking at this glass tankard, and was just now sitting here thinking, it was probably painted by some dude named Hans last week!
Imperial Eagle Tankard, 17thC glass, enamel painted, Nuremberg.
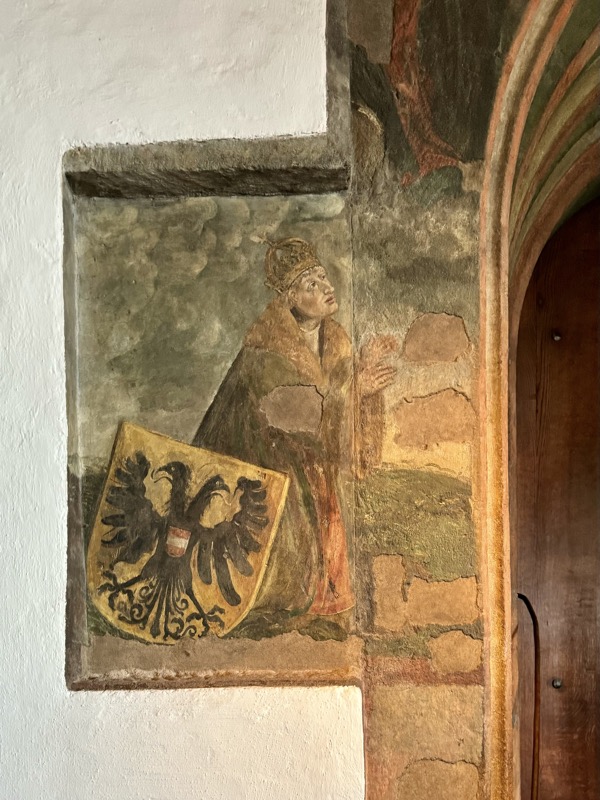
The double headed eagle was often the motif of imperial allegories and represented the structure and significant of the empire. The quaternion eagle has the individual coats of arms on its wings of the various imperial estates.


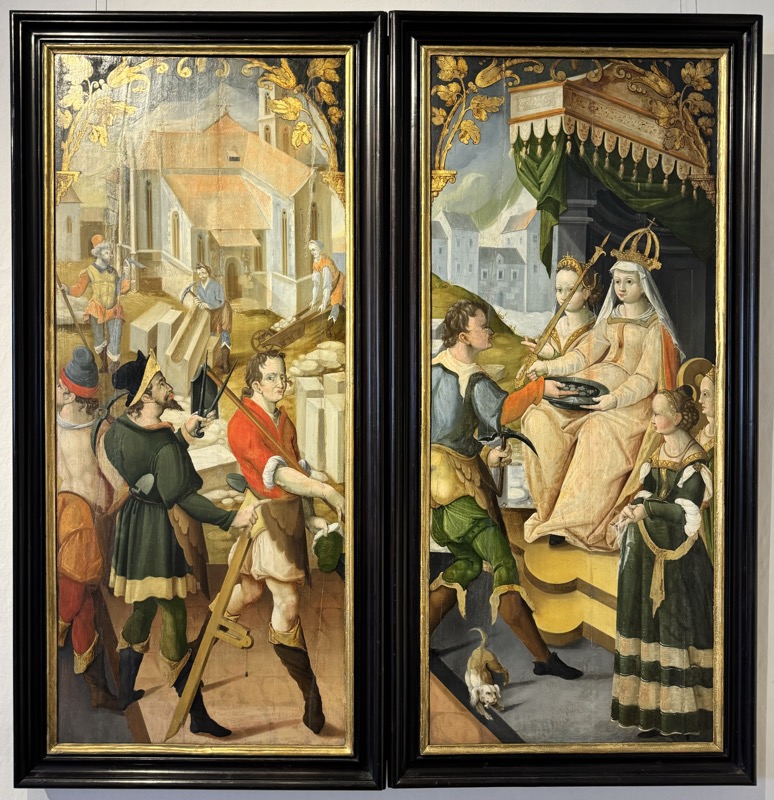
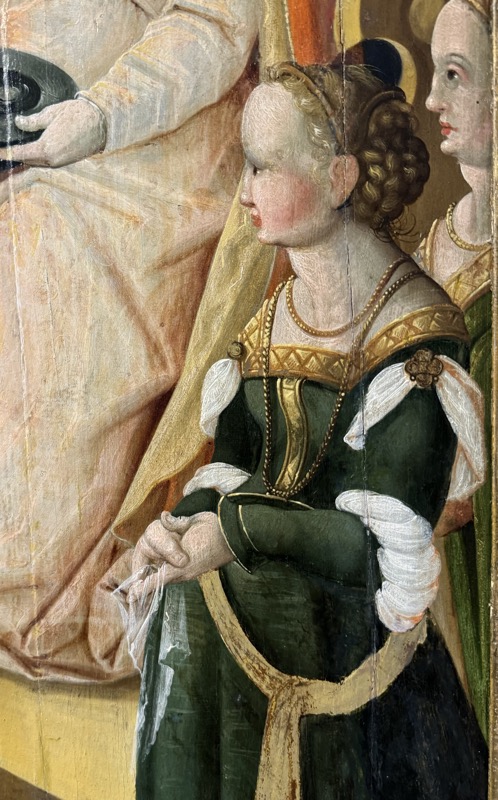
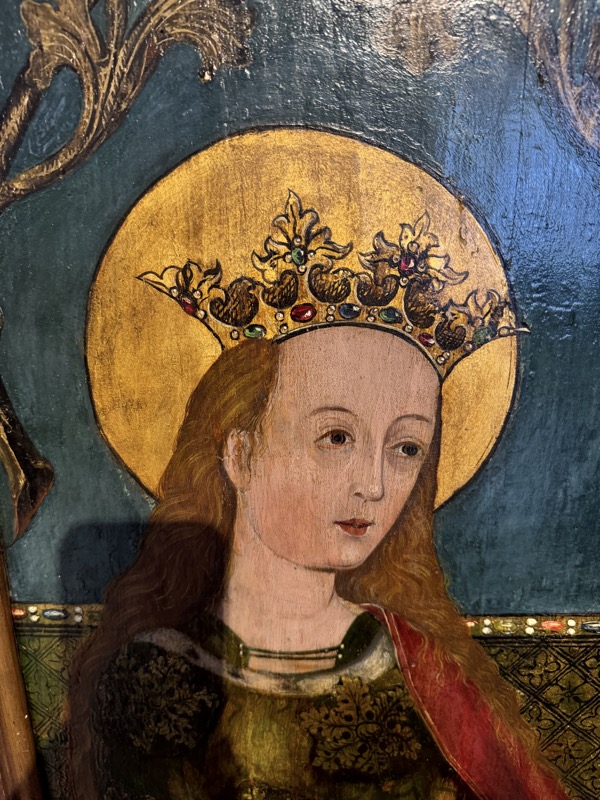
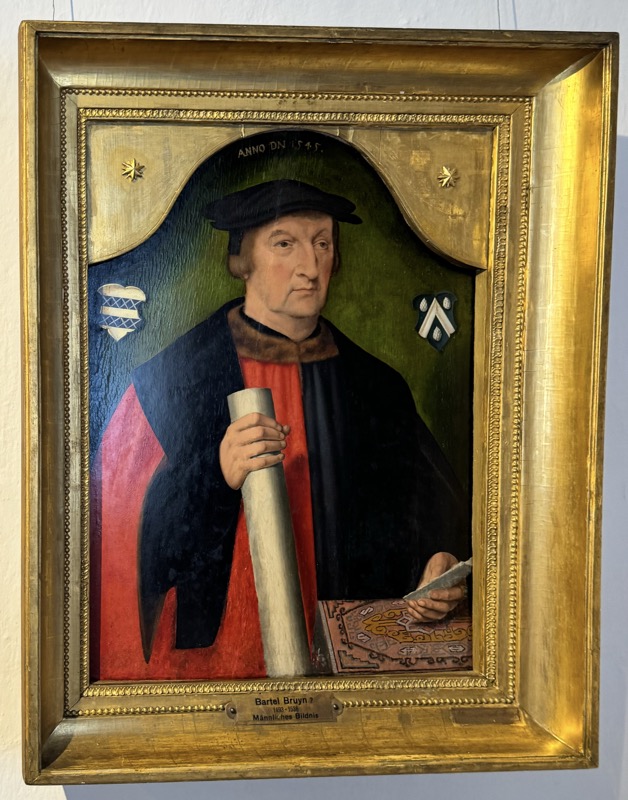
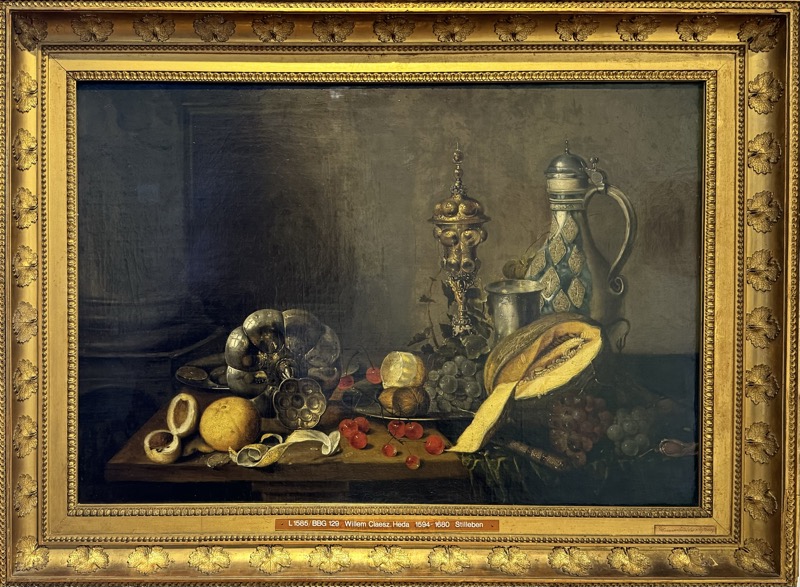
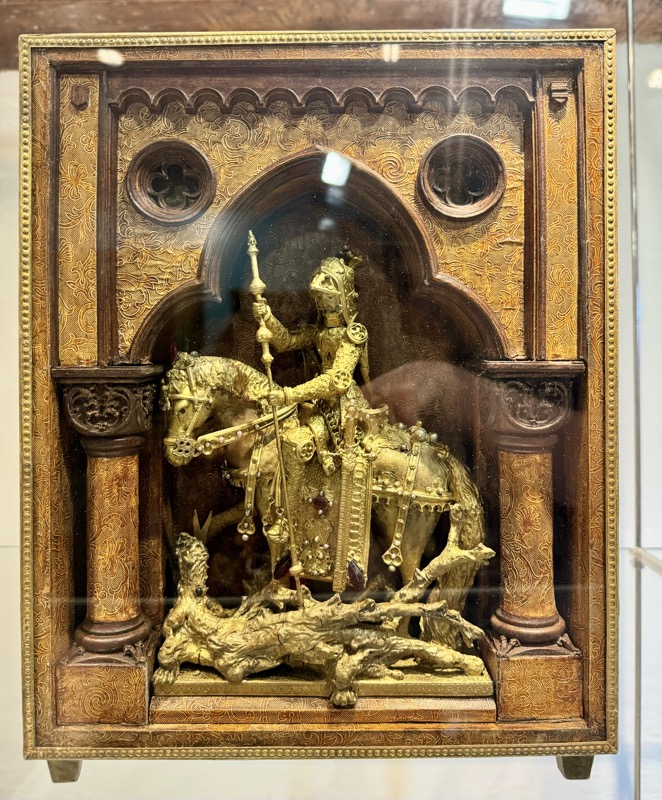
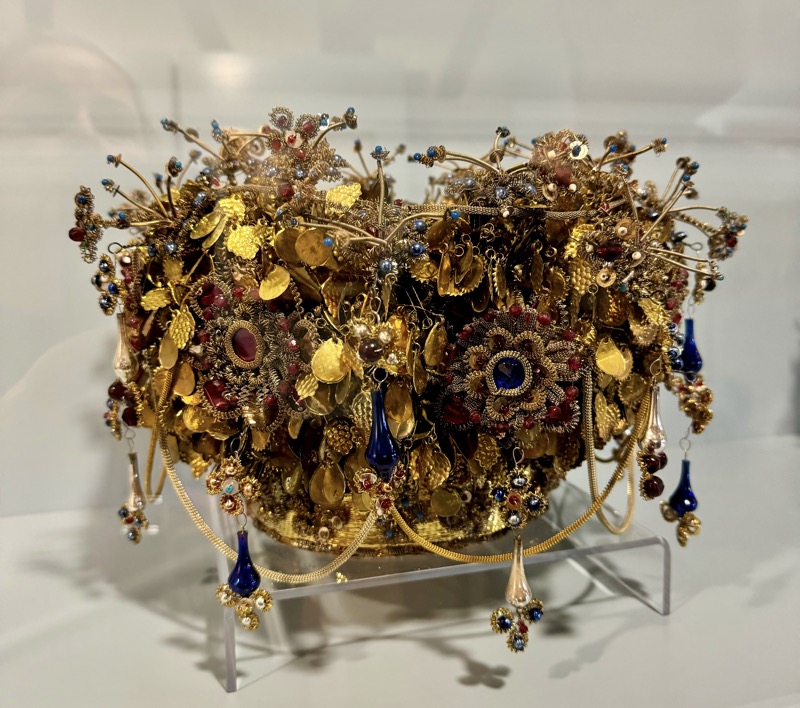
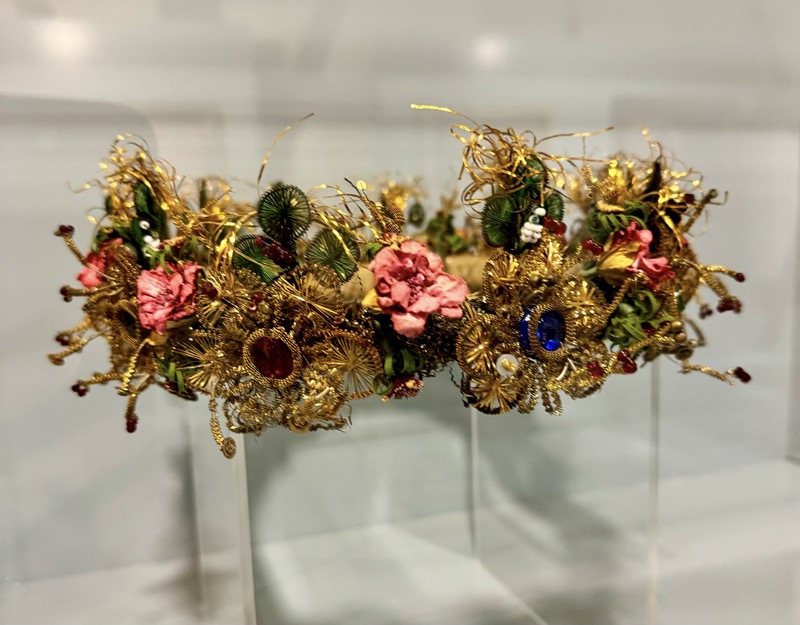
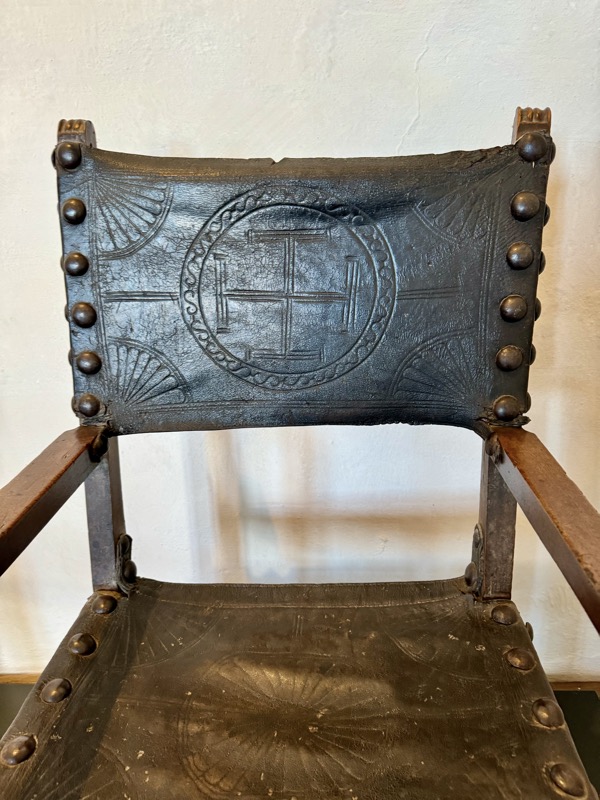
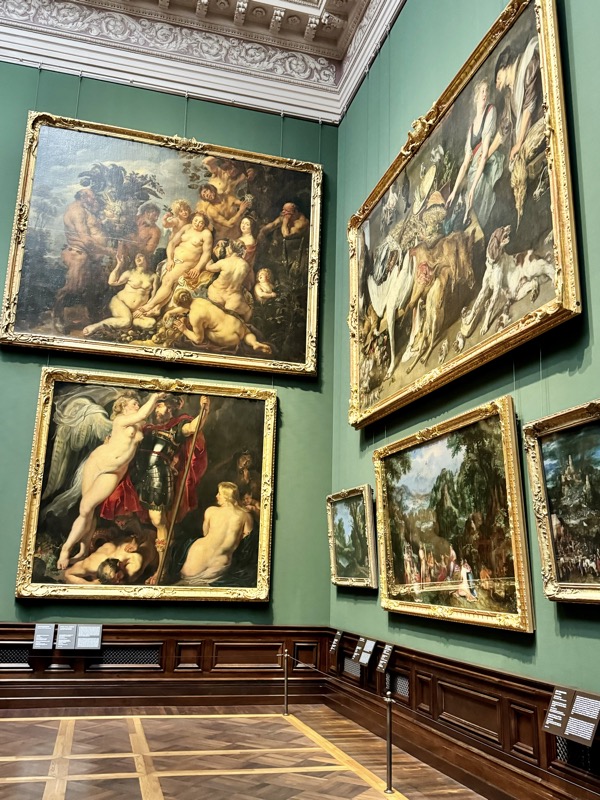
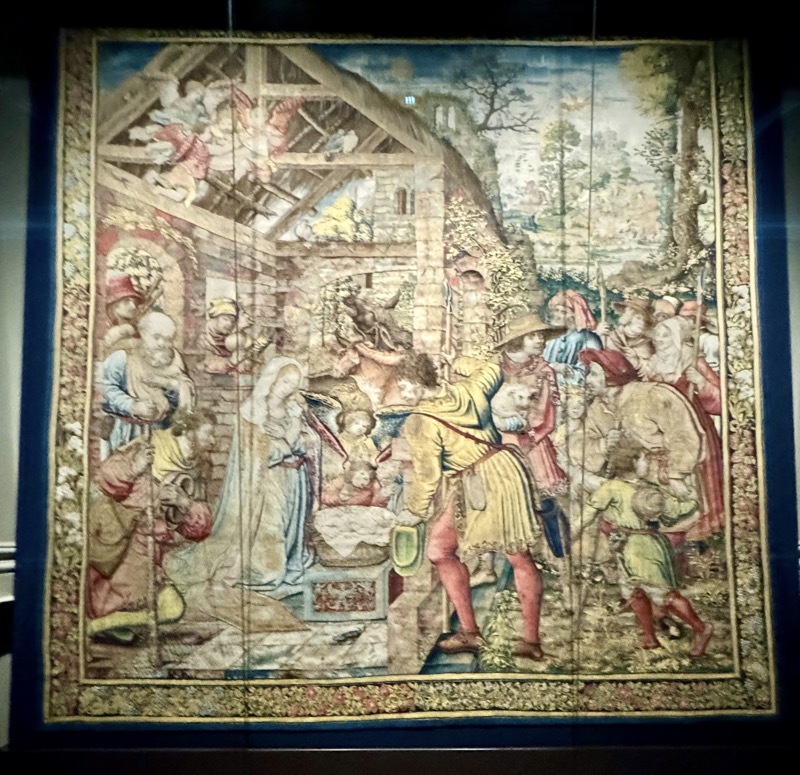
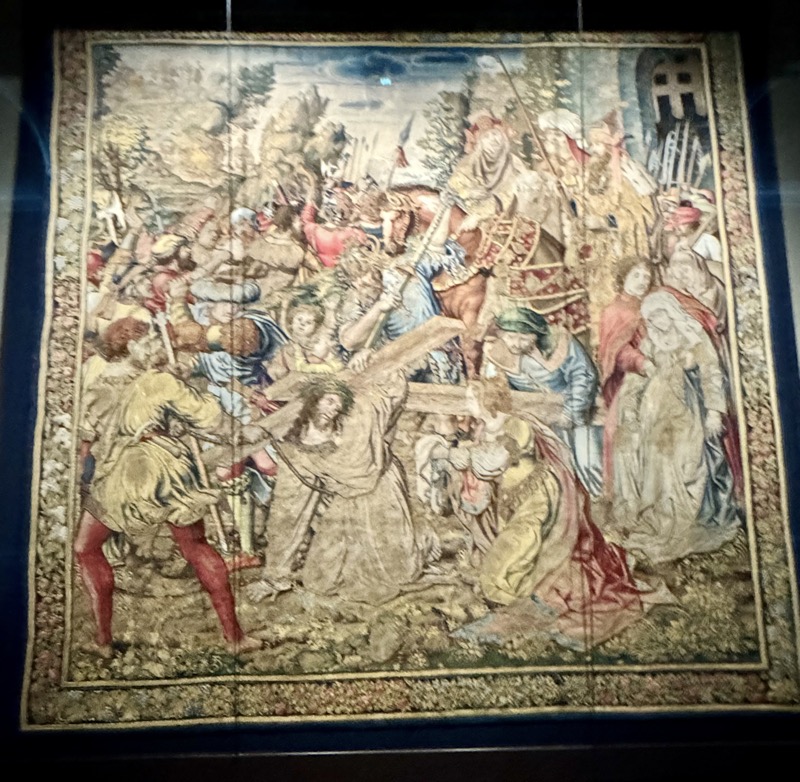
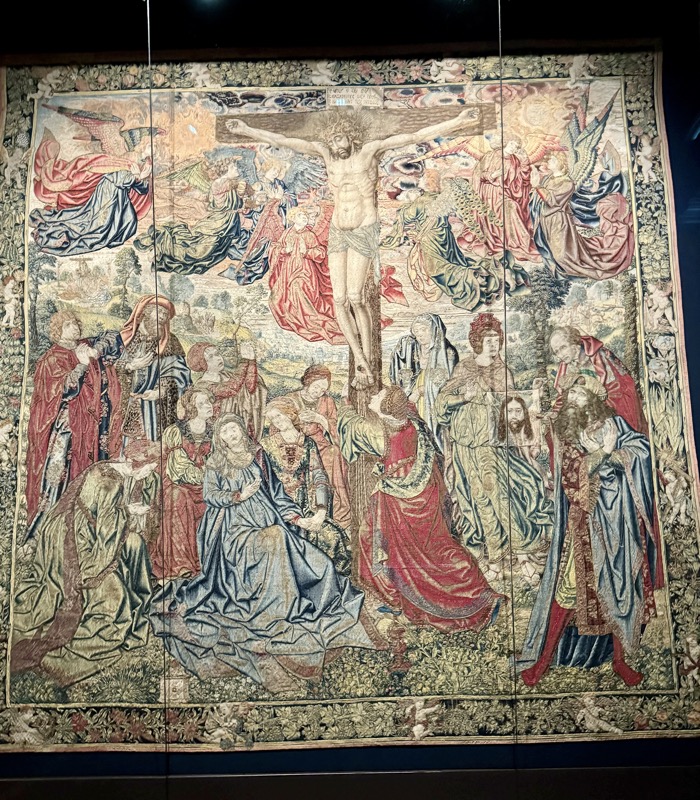
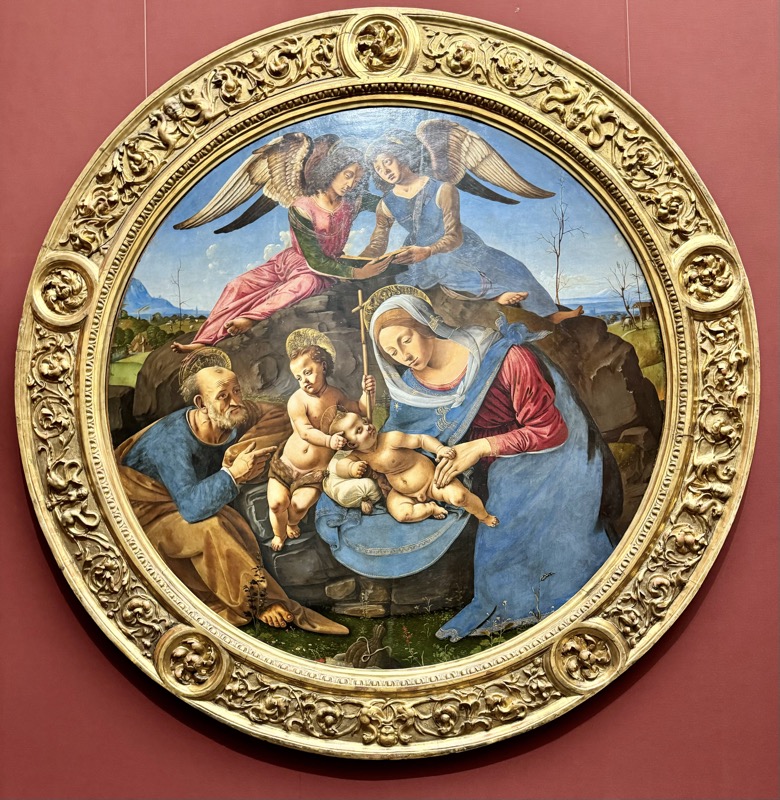
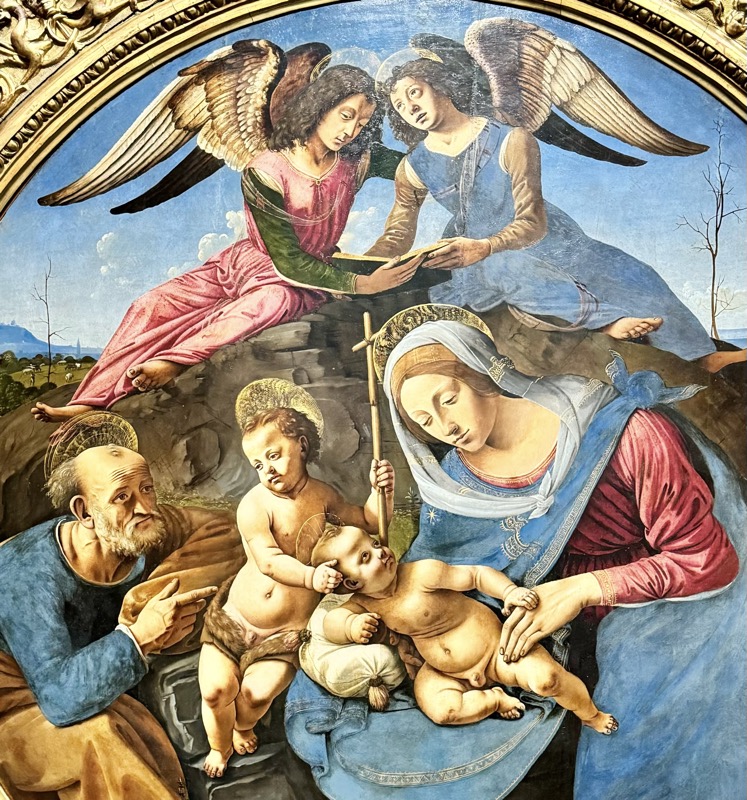
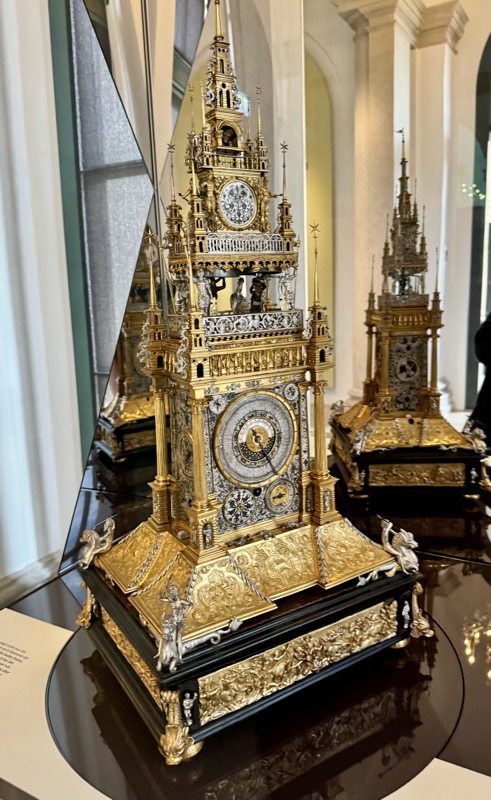
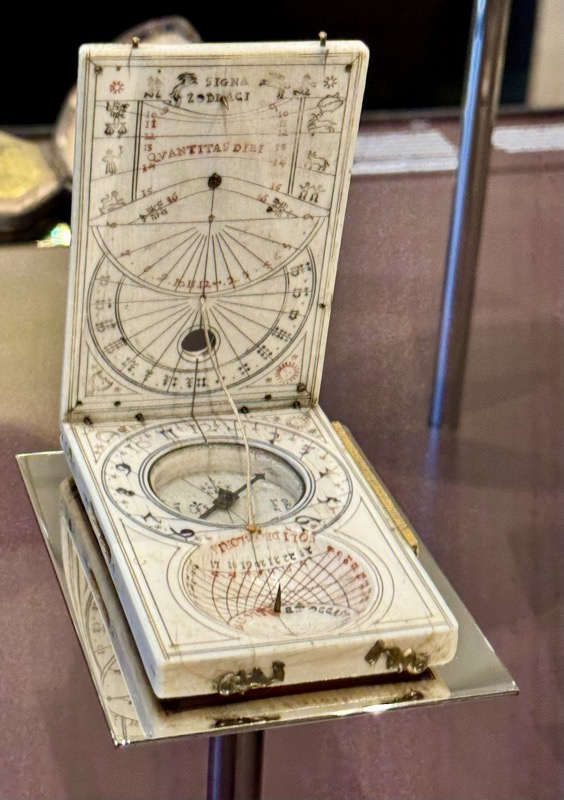
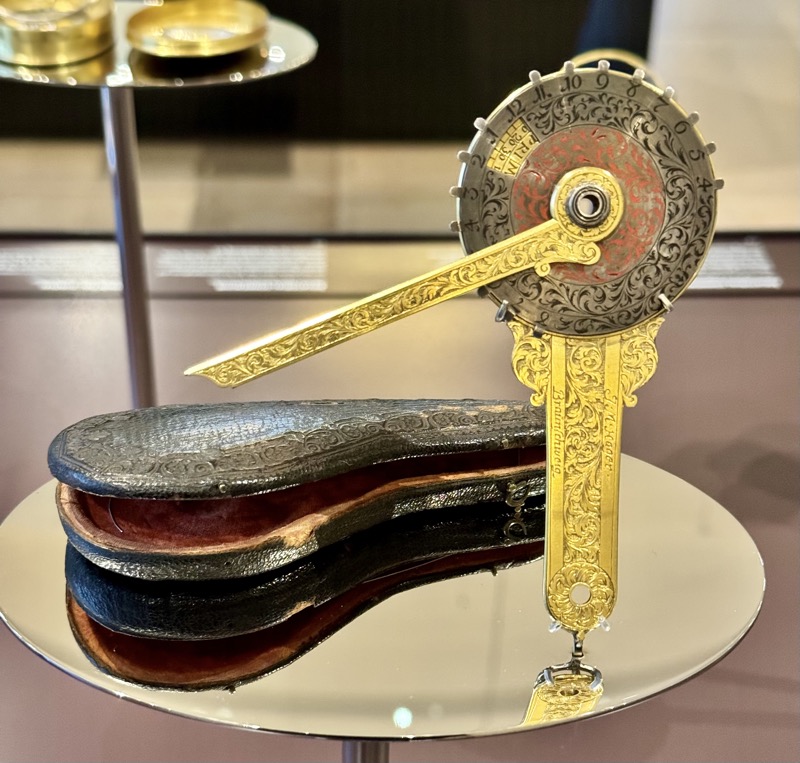
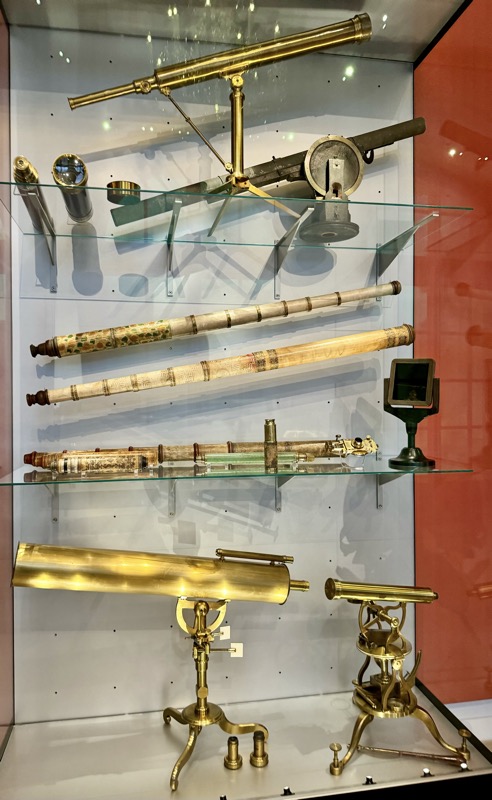
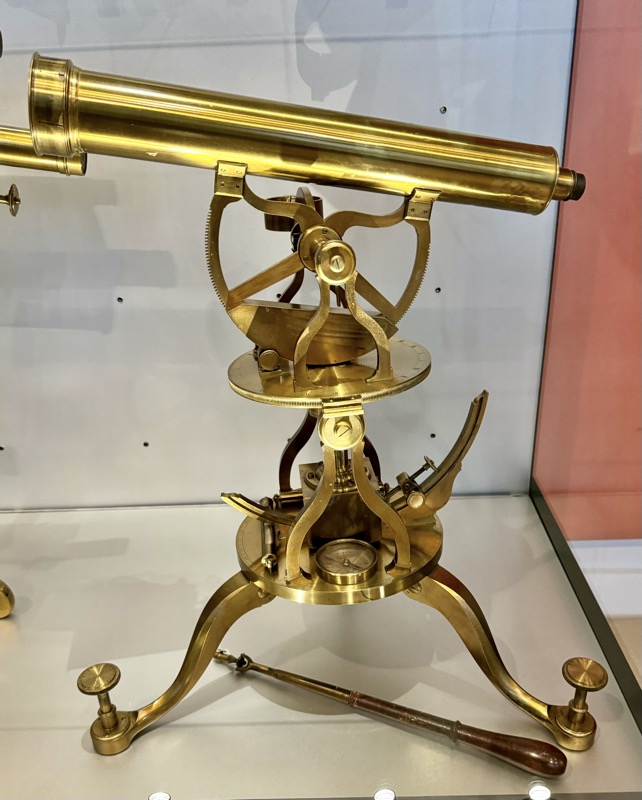
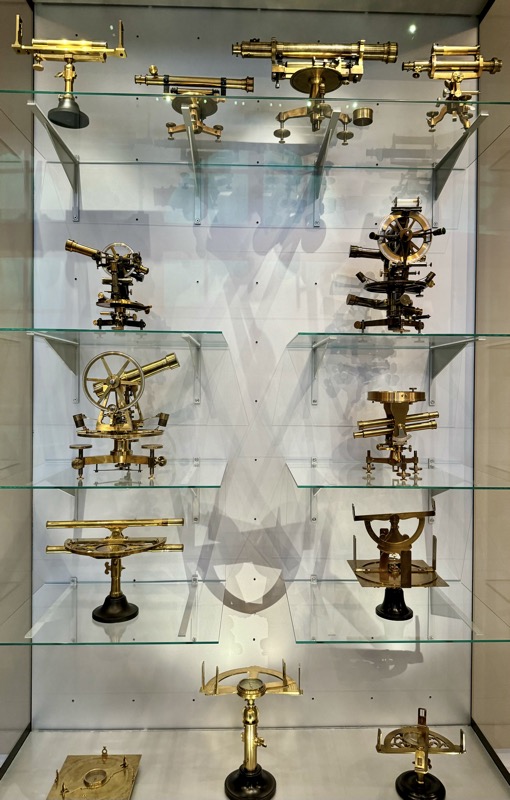
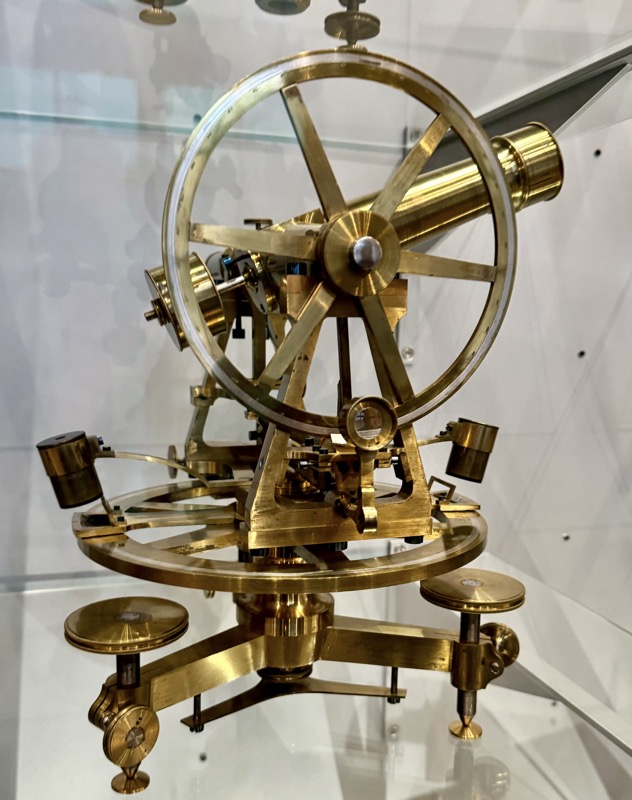
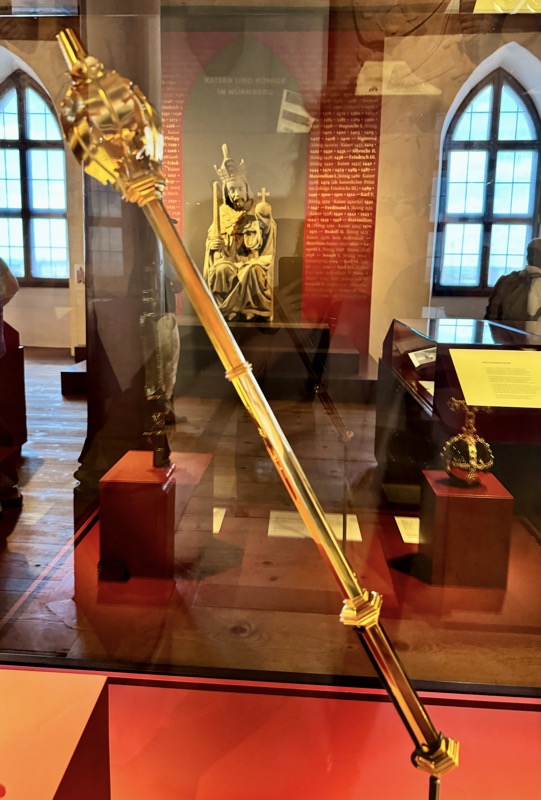
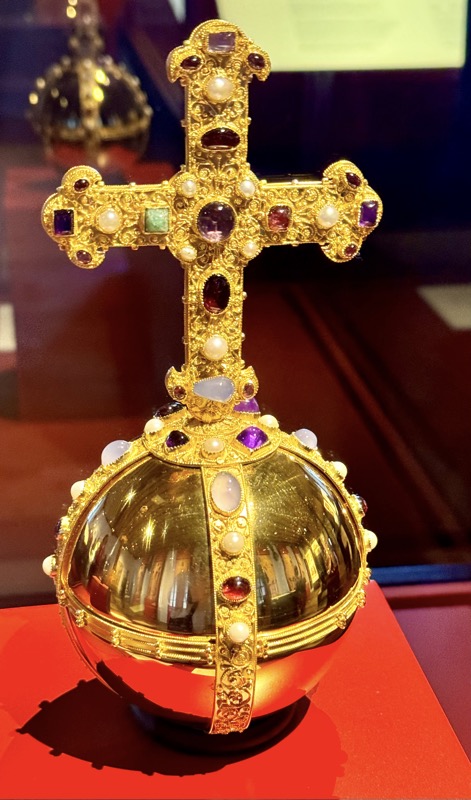
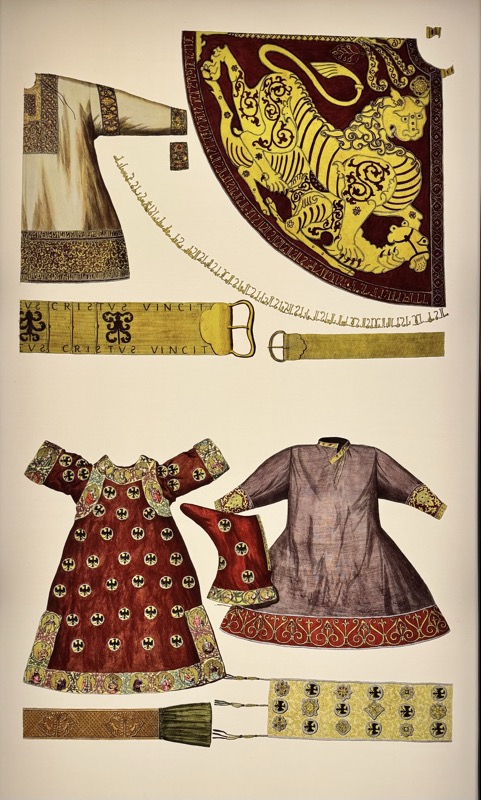
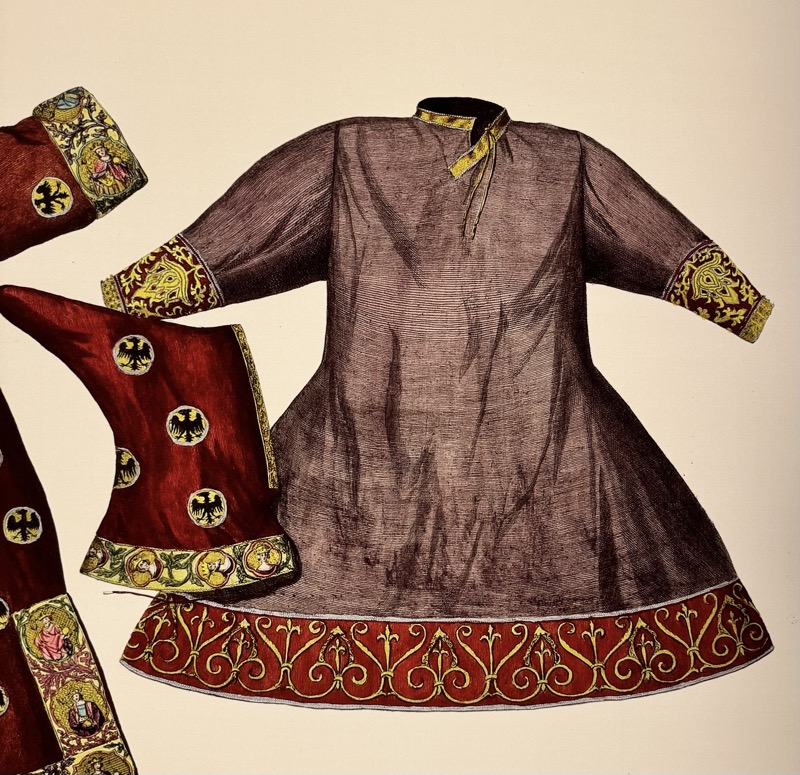
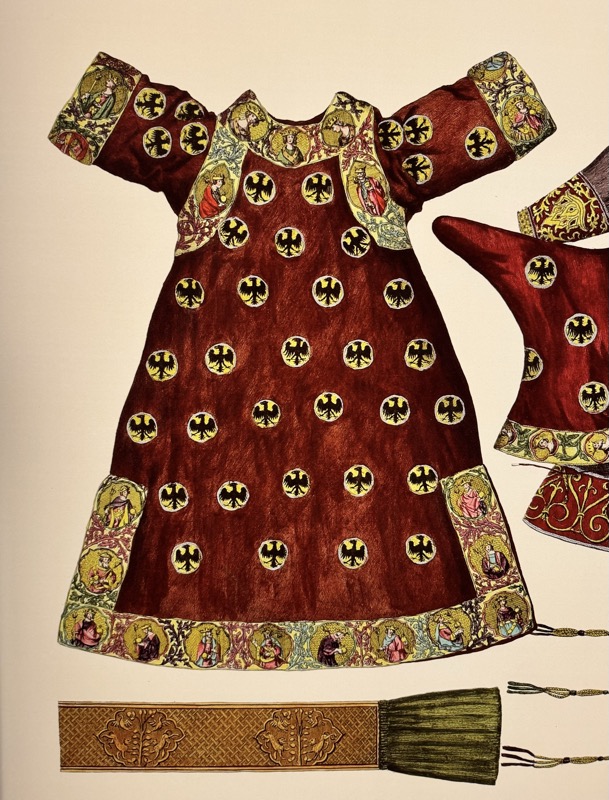
So, for the sake of representation there were some large information plaques which detailed these very famous objects associated with the Crown Treasury of Nuremberg and the Holy Roman Empire. The crown, dalmatic, and under tunic in particular are objects I am hoping to see at the Kunsthistoriches… but they’ve obviously been included here for education’s sake – and I’m really beginning to think this is a very well laid out place for school kids to come learn Stuff (which shouldn’t detract from my enjoyment of the displays – but it fucking does!).




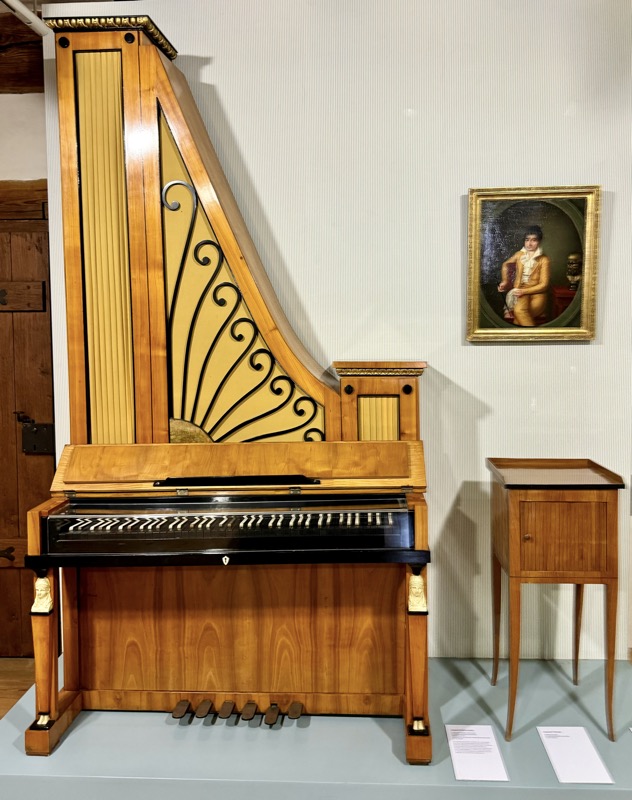
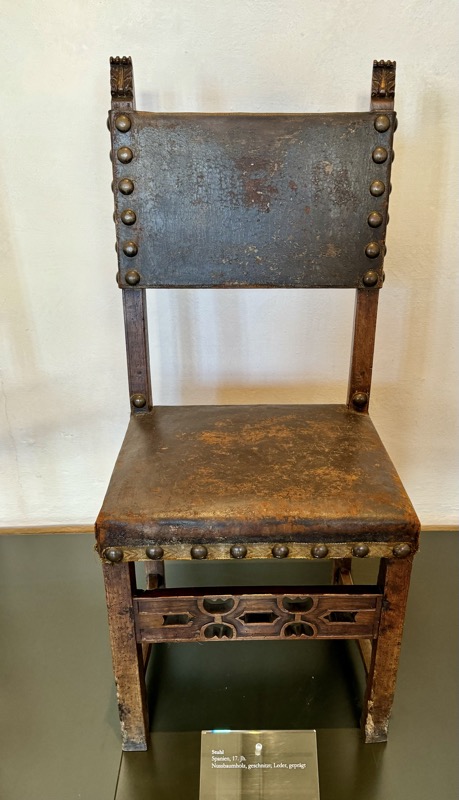
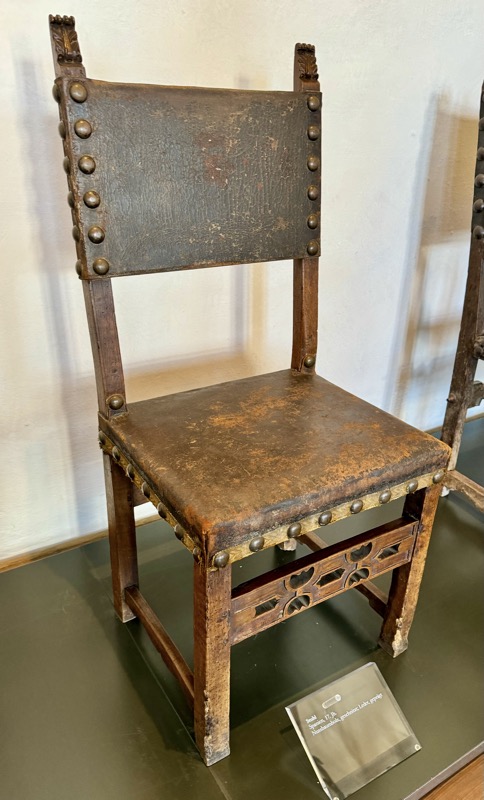
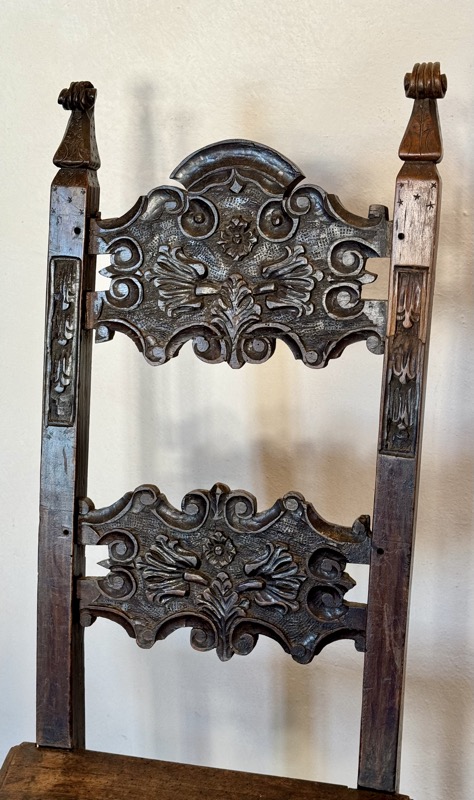
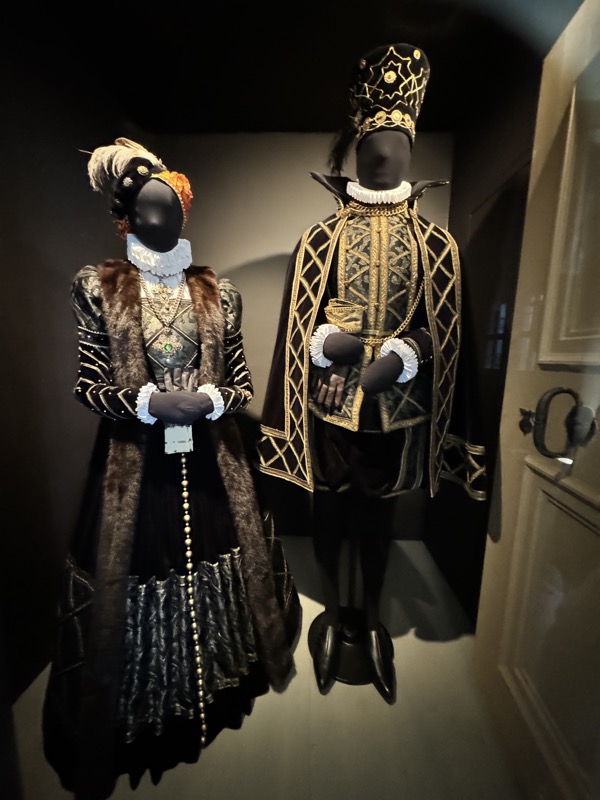
The following Palace rooms were the private chambers of the emperor/s in the upper floors of the castle; they’ve been set up post WWII to give an impression of homeliness with some furniture, portraits…
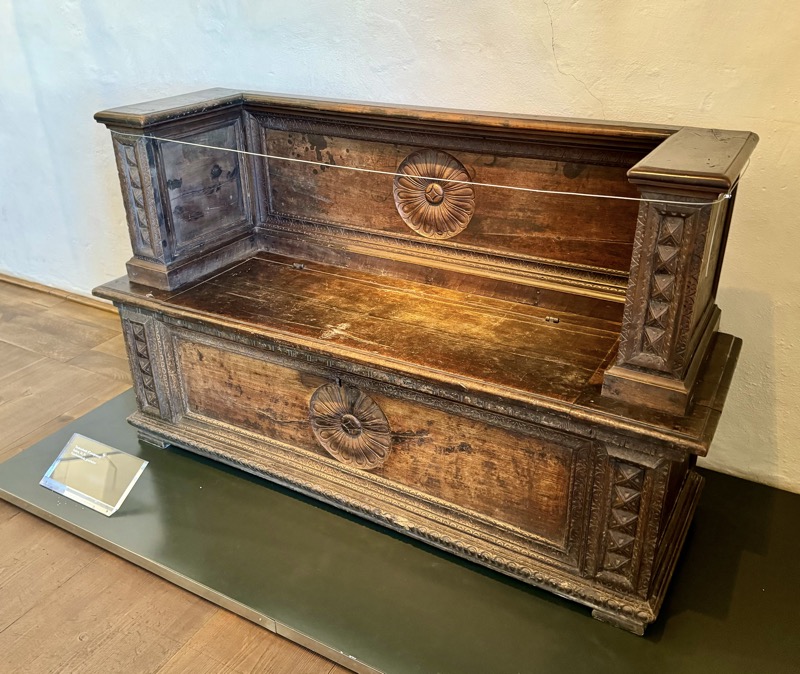
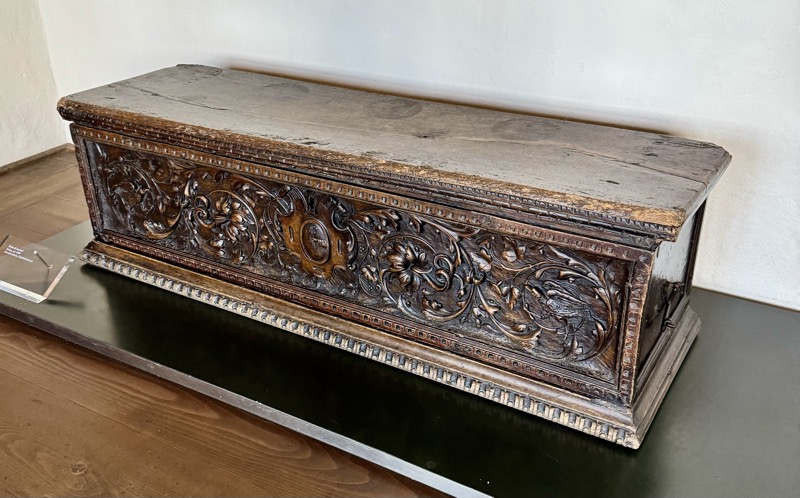
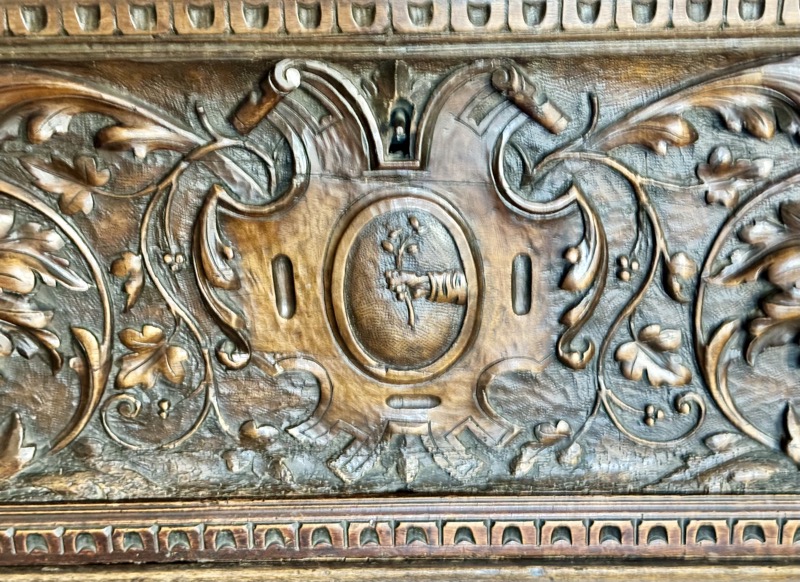
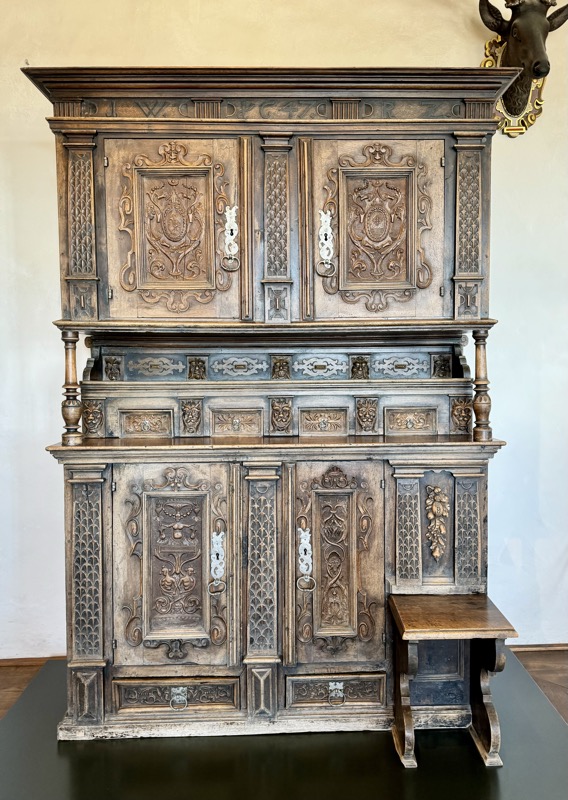
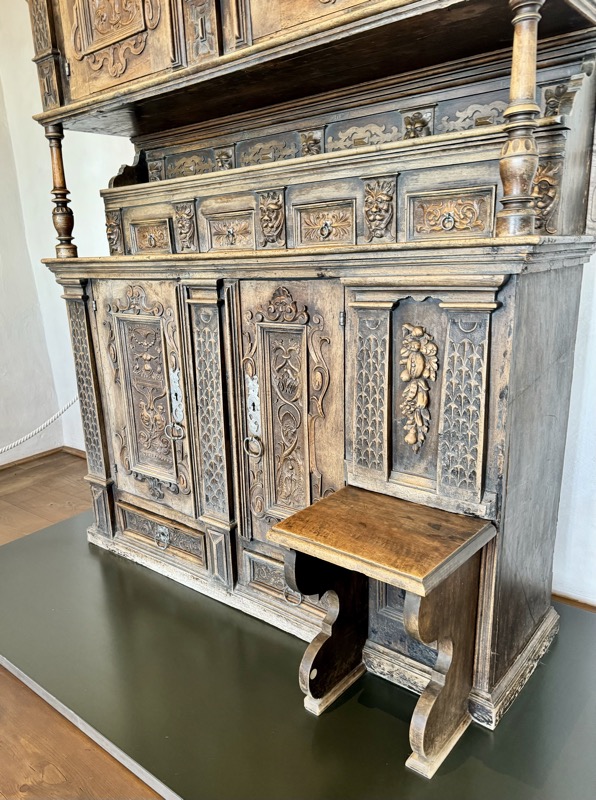
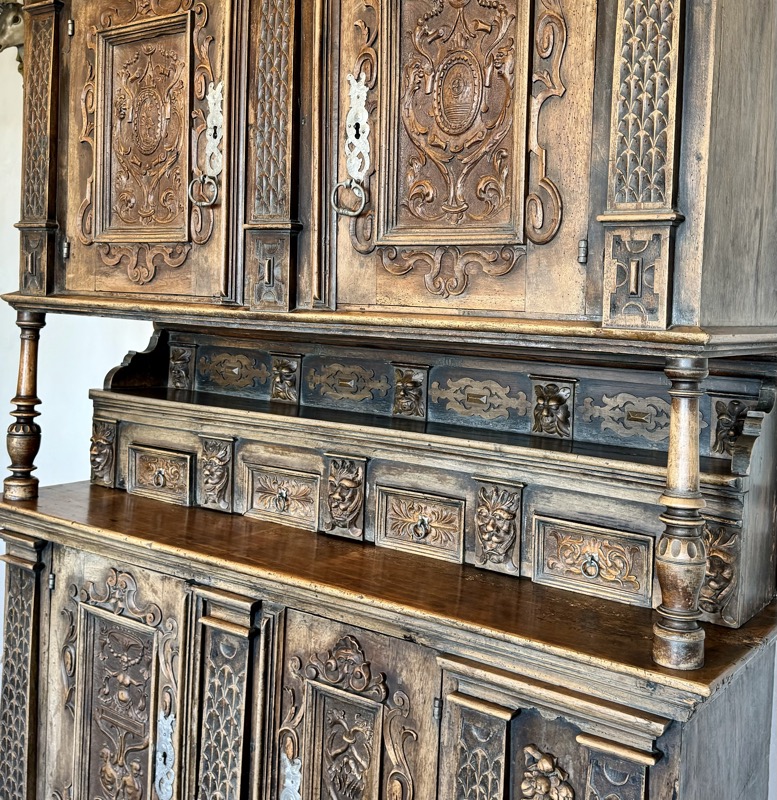
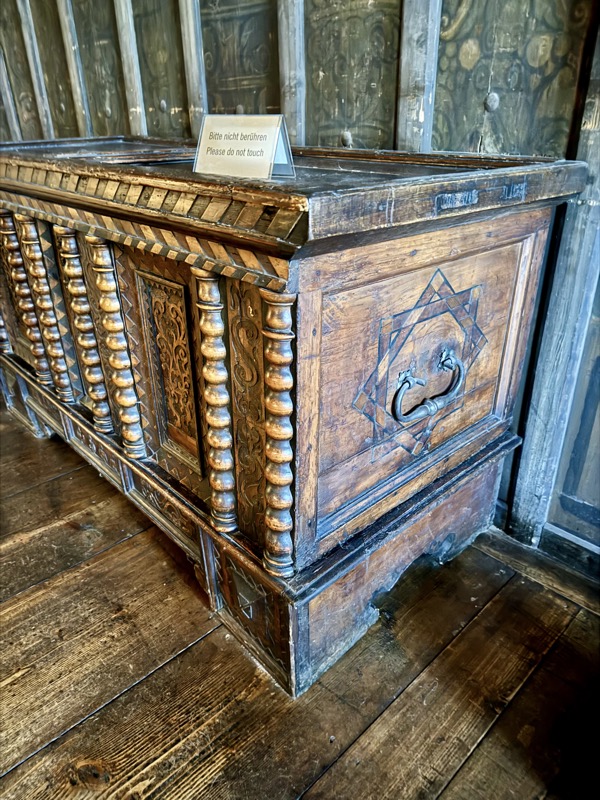
Baroque Chest, Tyrols, c.17thC.
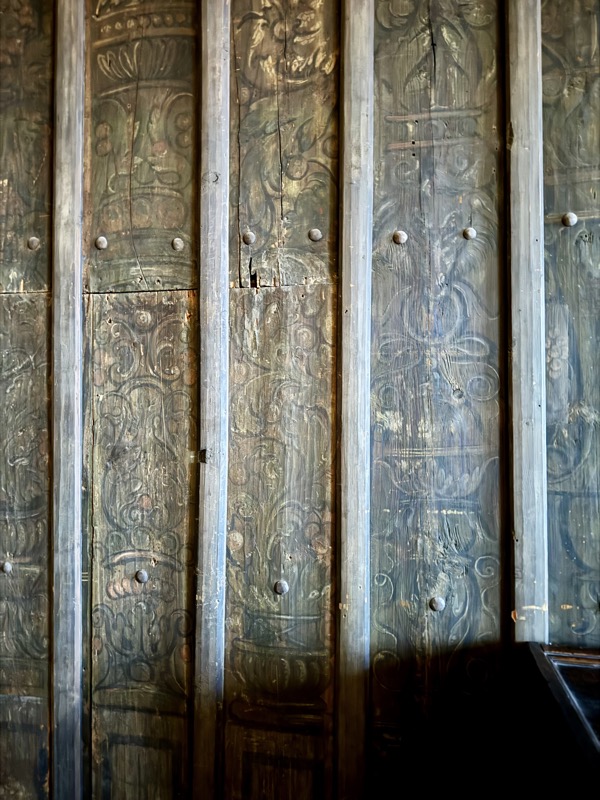



Wappendecke: Coat of arms cover, Fritz Haeberlein, Nuremberg, c.1947…?
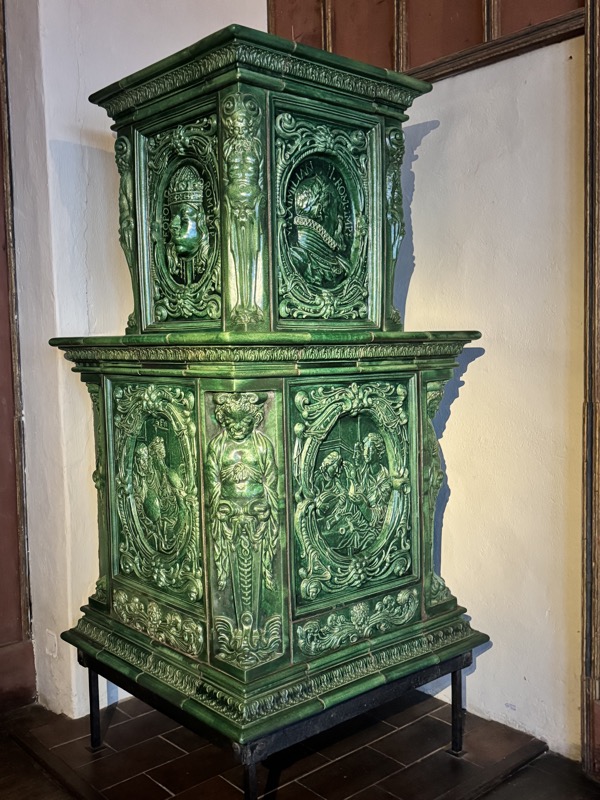
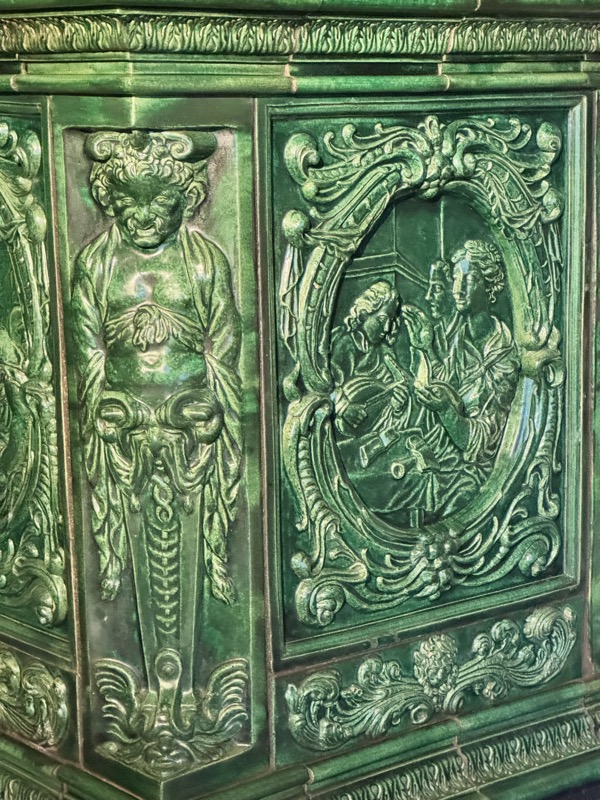



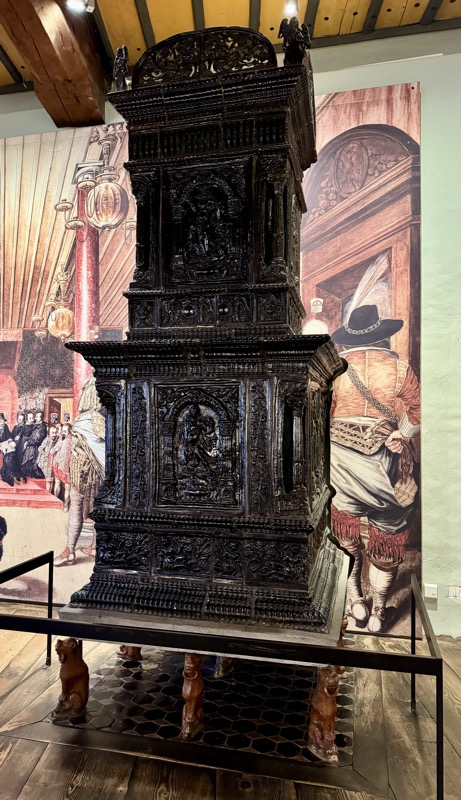
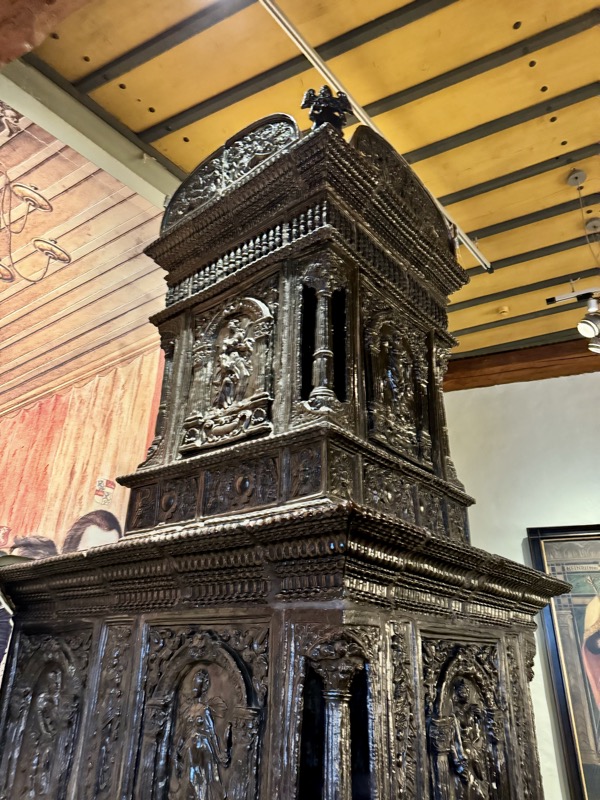
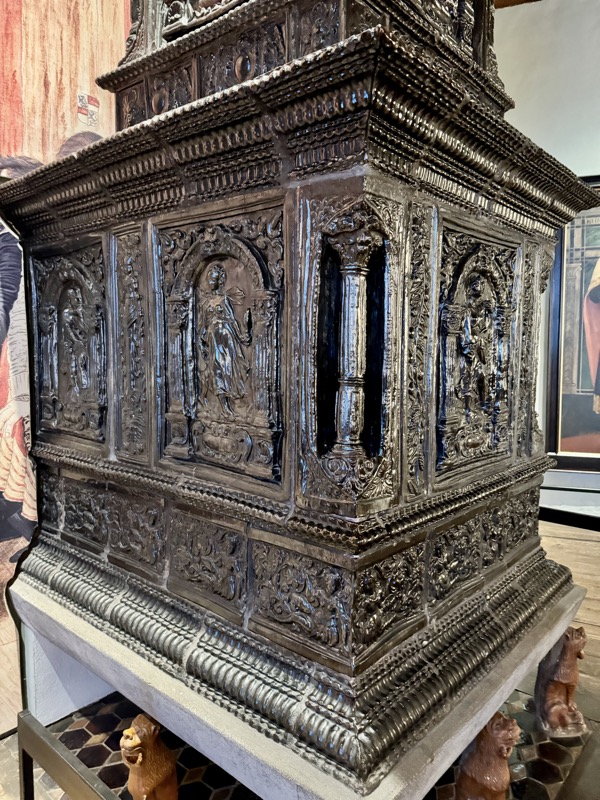
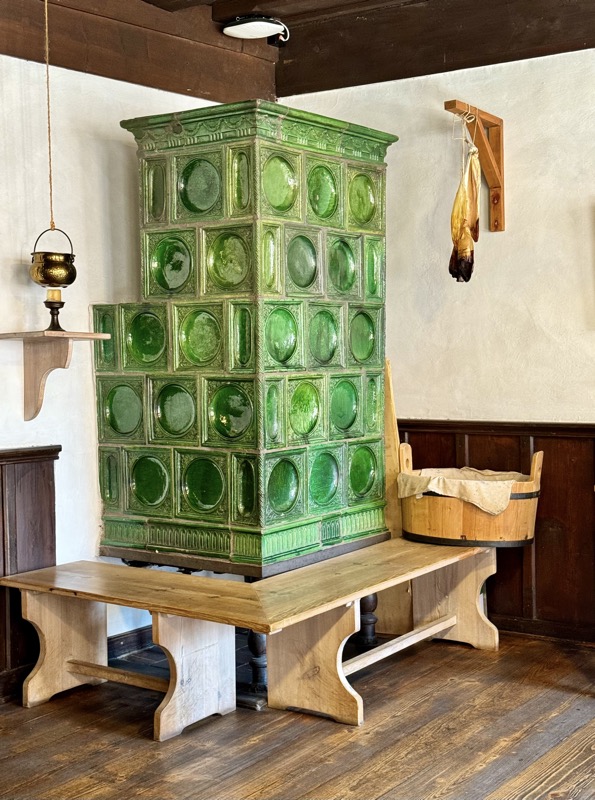
Prunkofen: a magnificent Stove, Nuremberg, c.1675. Timber exterior and tiled interior.



Four keys from the lock of the Imperial Regalia, c.16th/17thC.
In 1423, Emperor Sigmund entrusted the City of Nuremberg with the safekeeping of the Imperial Regalia. The relics were kept safely locked in a shrine, in the church of the Holy Spirit Hospital, which was under the city council jurisdiction. Access to the chapel vault was secured by multiple persons holding different keys.


The views out to the courtyard… while walking through these rooms today, I was wondering what it must have been like for the high born womenfolk who inhabited these walls. Now, I reckon these windows were probably installed after WWII and no medieval women looked out these windows.

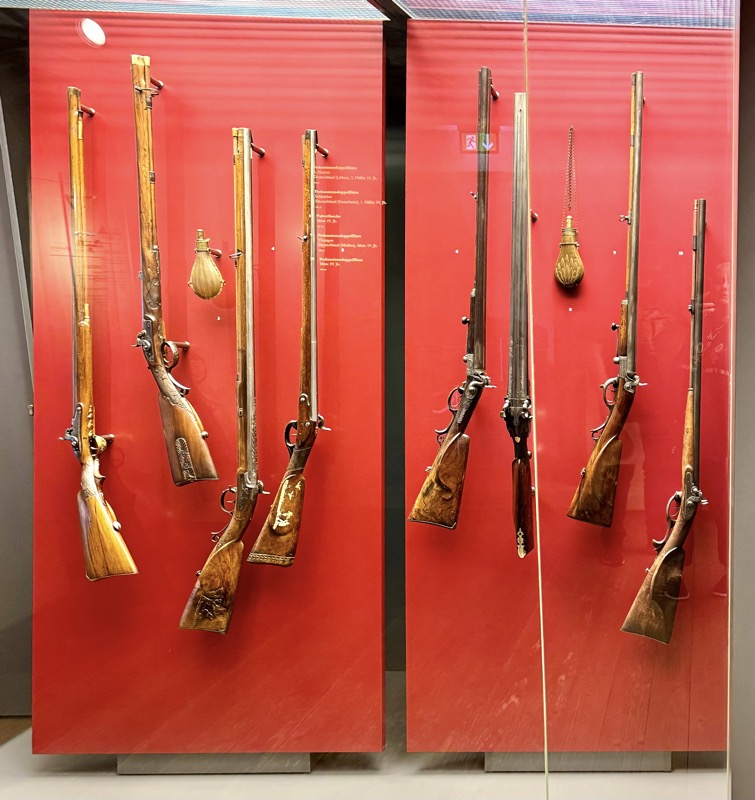
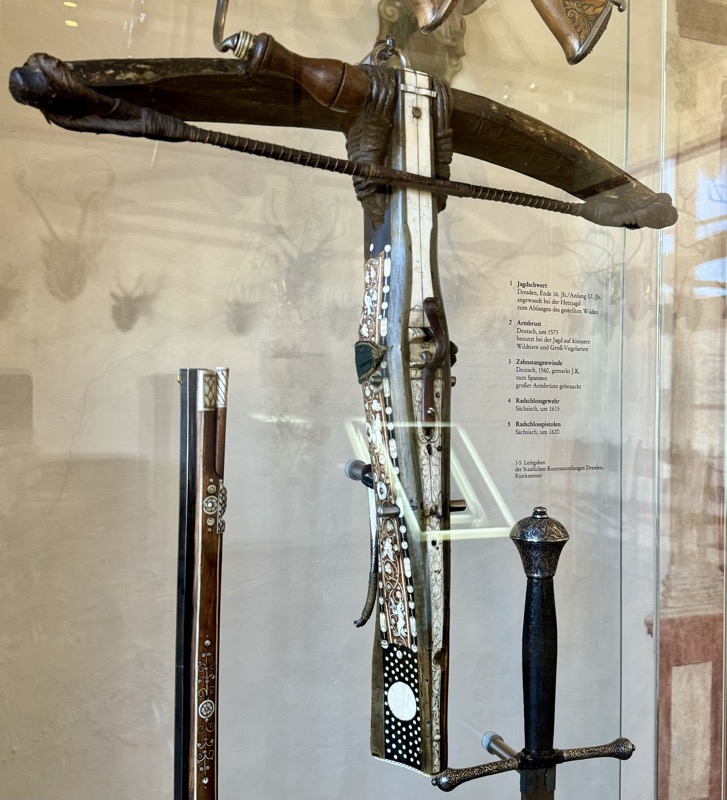
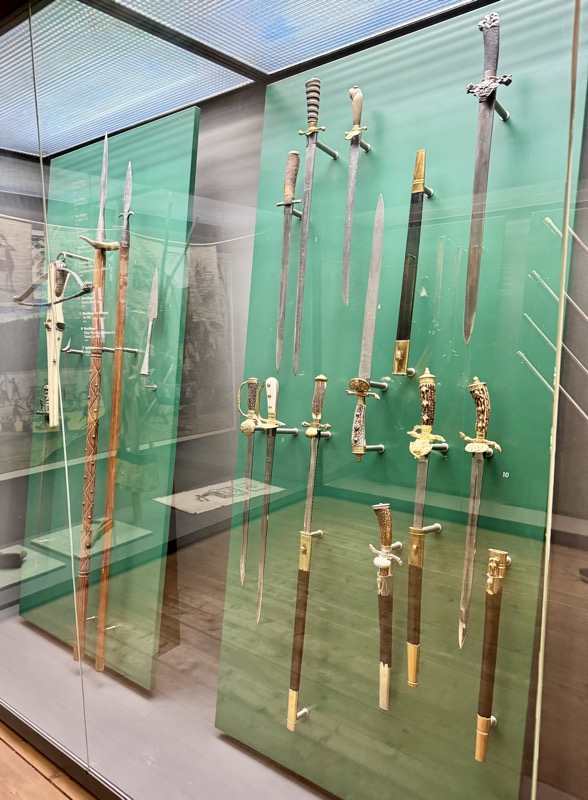
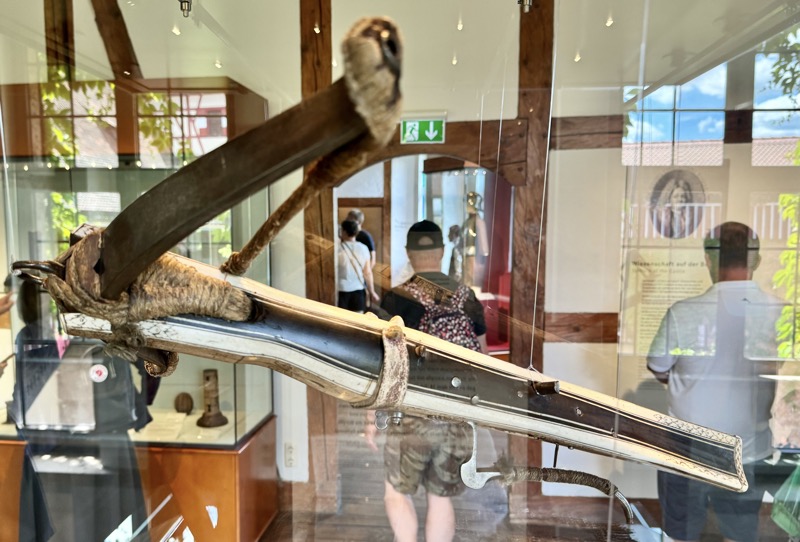
Armbrut: Cross bow, Nurember, c.16thC,. Bow: steel. String: hemp. Column: wood, black horn and white etched horn inlay.


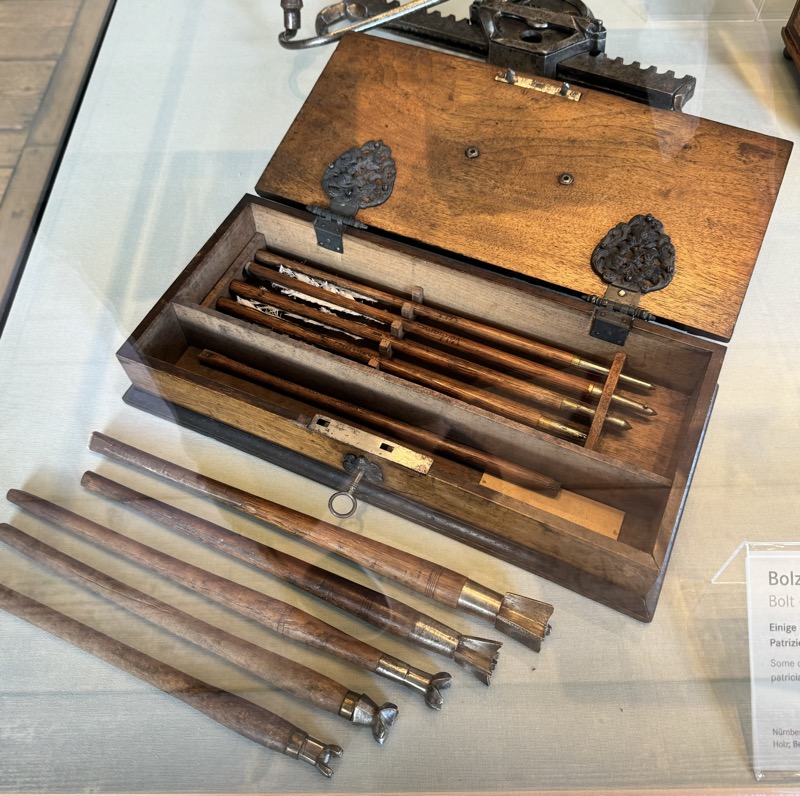
LEFT: Bolt case, some labeled with the name of the Nurember patrician family, “Volckamer”, c.1595. Wood, fittings of iron, partly tinned, handle of brass.
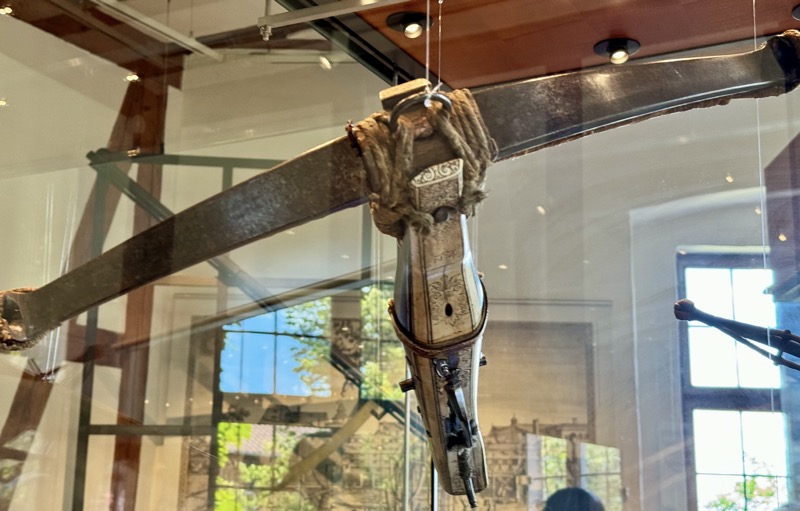
RIGHT: German crossbow crankequin. Heavy craniquins like this one were indispensable for drawing the bow-string on a robust steeel bow.
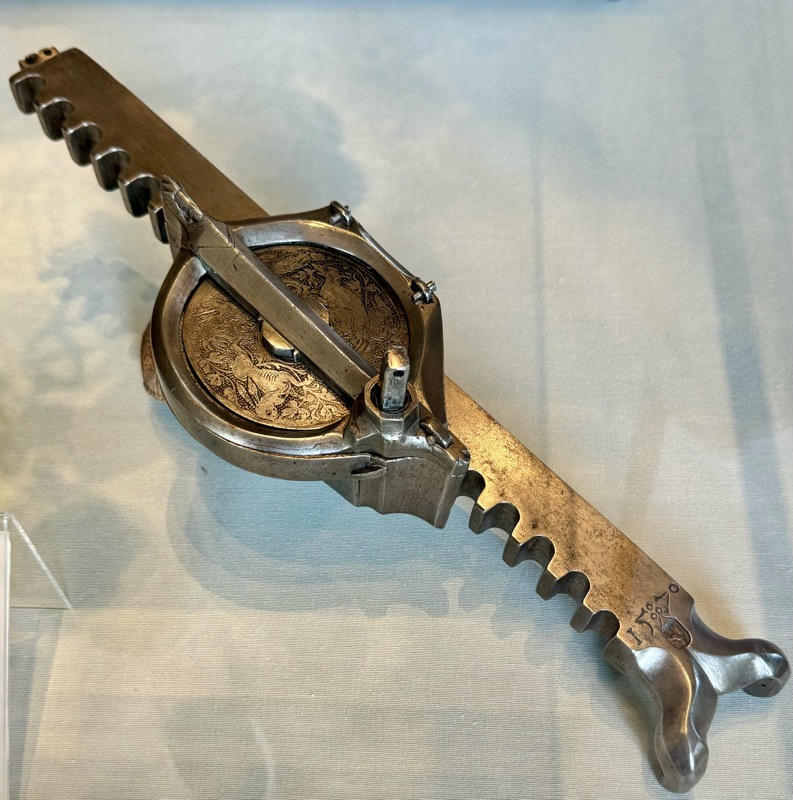


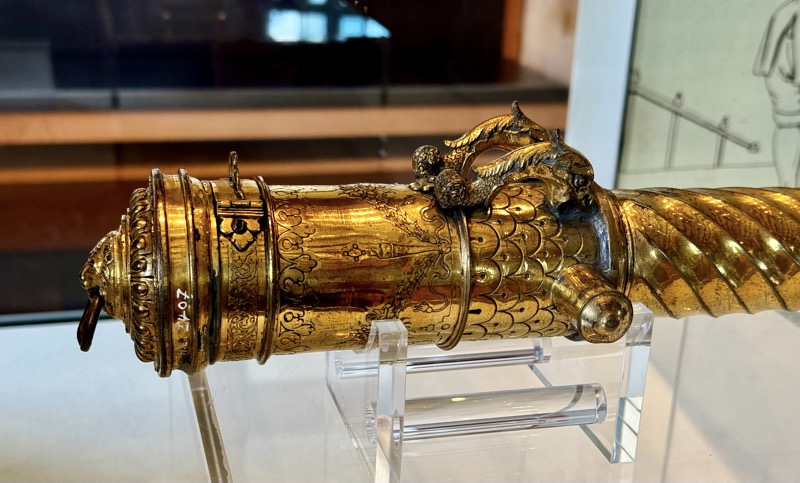
Drinking vessel in the shape of a richly ornamented cannon. When the cover is opened, it becomes apparent it is for dining. Citizen’s Artillery of Nuremberg, c.15thC.


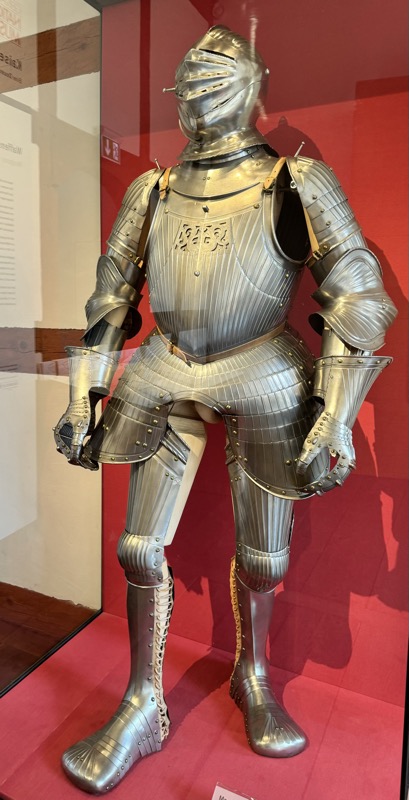
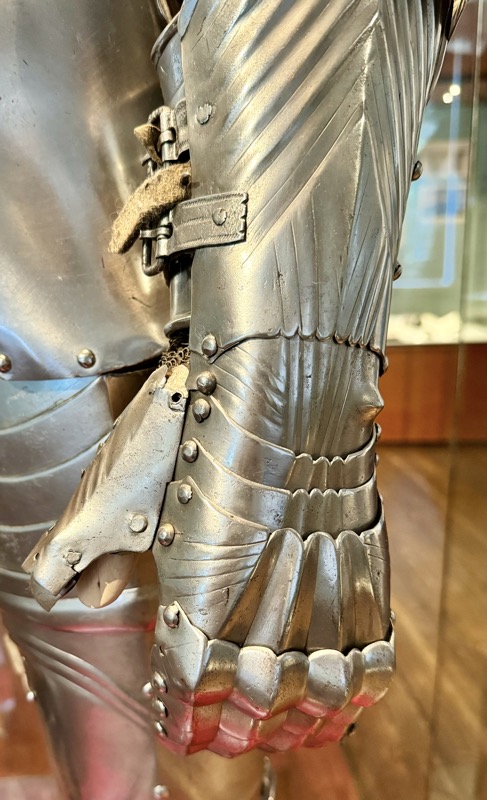
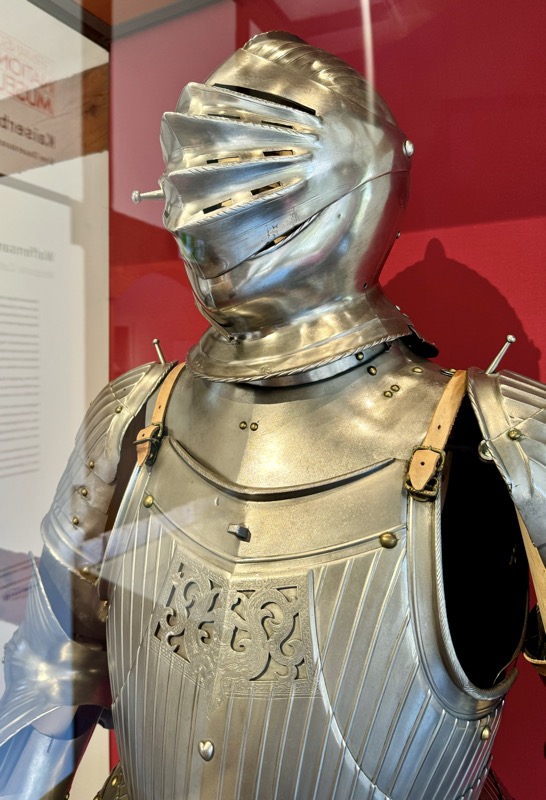
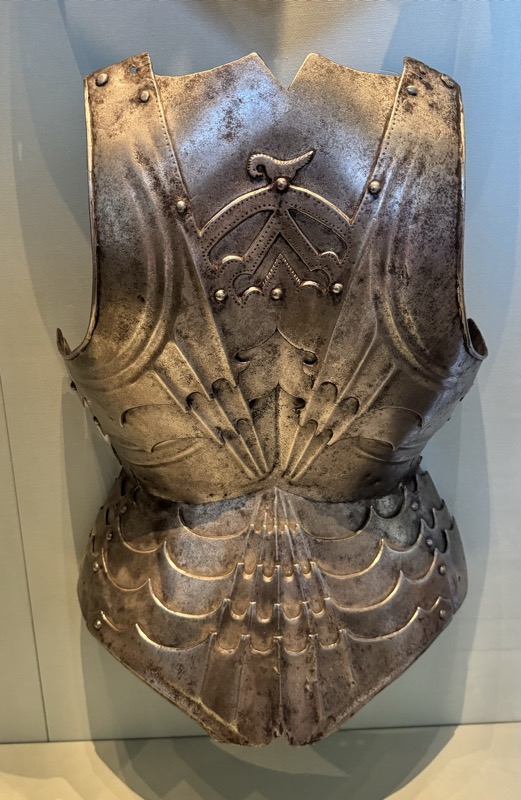
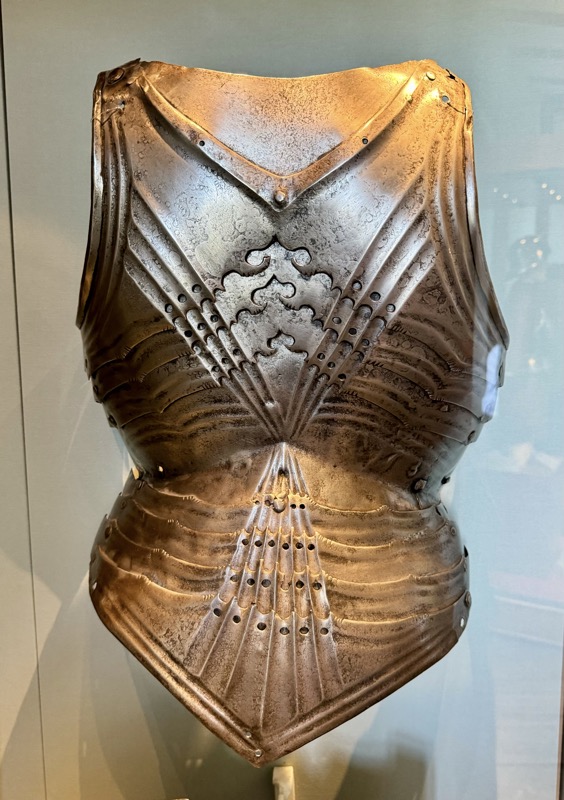
Maximilian style armour.
“The suit of plate armor is a complex artistic and technological masterpiece. In development since around 1300, full body armor made up of many different parts had reached its highest level of complexity by 1500. In principle, the individual parts had to be adapted to the individual wearer if the armor was to be fully functional. Not everyone could afford such tailor-made armor, however. Many fighters put together their protective equipment from parts that were already available. In order to increase mobility, individual parts of the armor could be left out at any time.
A suit of plate armor is a complex artistic and technological masterpiece. It was developed from ca. 1300 on and reached its highest complexity around 1500. Generally, each part had to be fitted to the individual wearer, if the armour was to function properly. However, not every fighting man could afford customised armour. Protection often had to be improvised and adapted from available parts. In order to increase mobility, parts would be left off.” Sounds familiar…



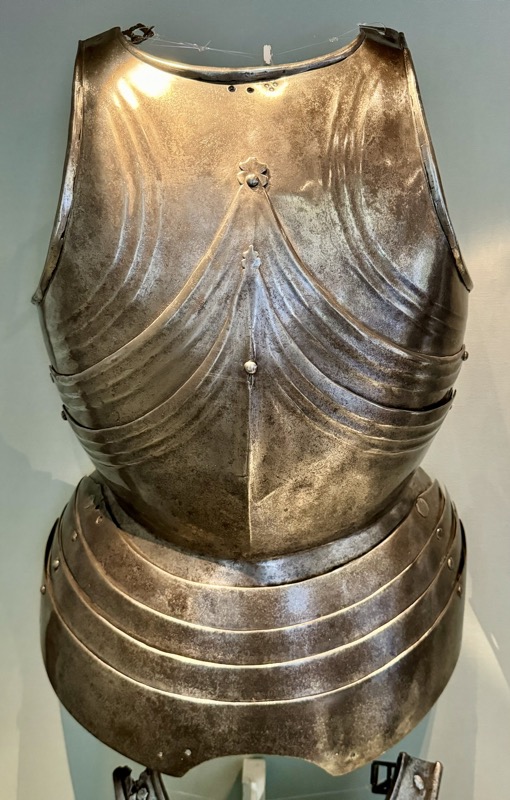
Two breastplates of late Gothic Armour; from the town hall in Spittal, Carinthia, Austria. C.1450-1500.
Iron, forged, steeled, filed, and originally polished.


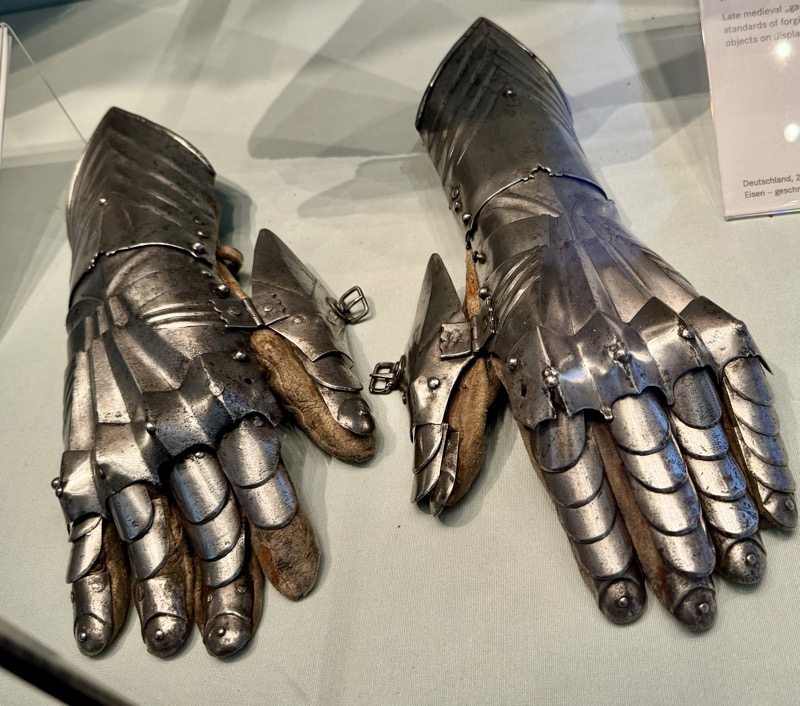
Late Gothic armoured gloves.
Germany, iron, forged, steeled, ground, polished, leather later addition, c.1450.

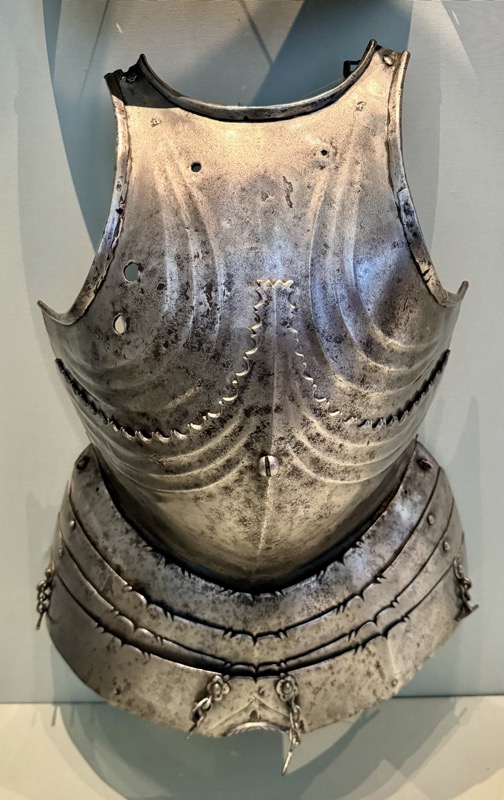
Two backplates of Late Gothic armour from the town hall in Spittal, Carinthia, Austria. C.1450-1500.
Iron – forged, steeled, filed and originally polished.


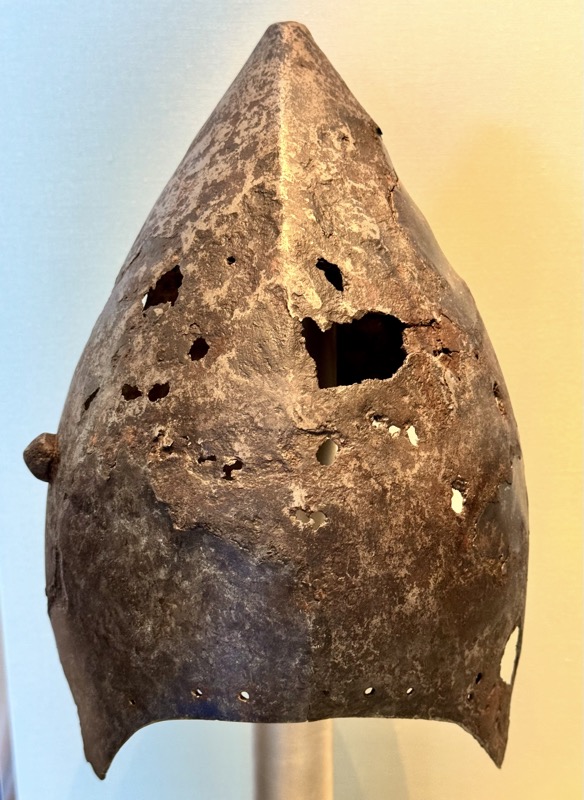
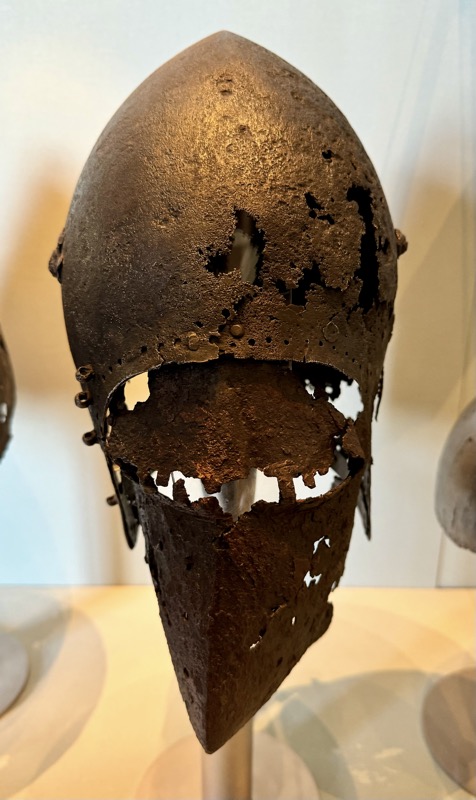
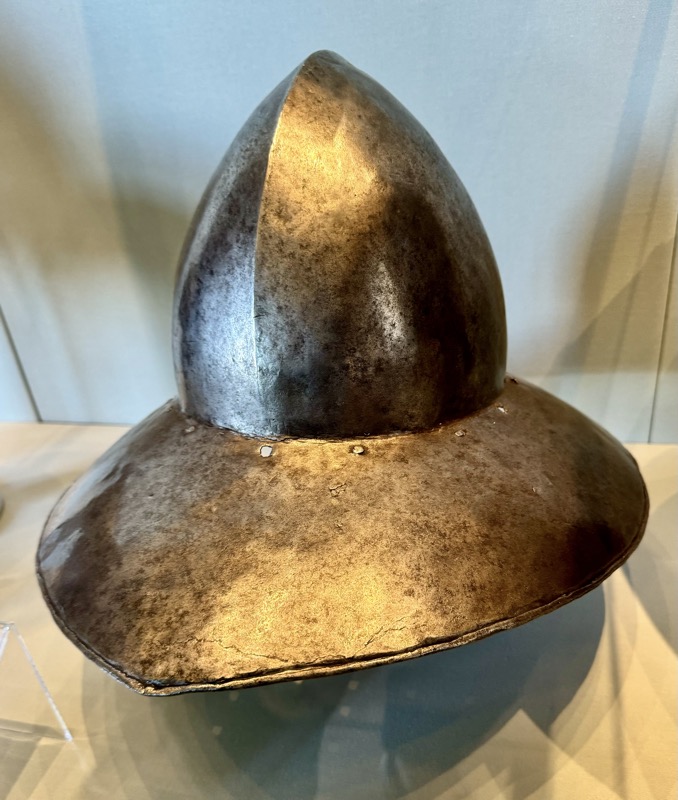
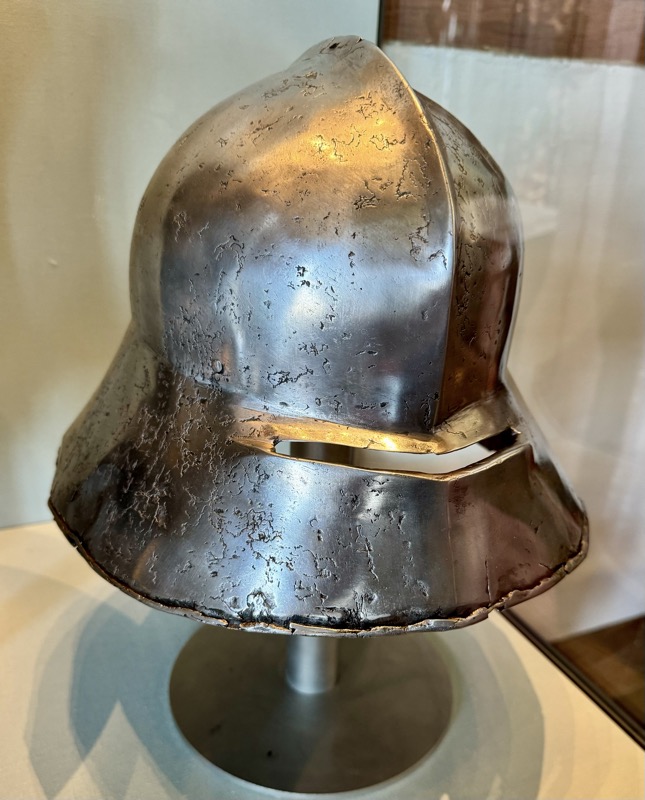
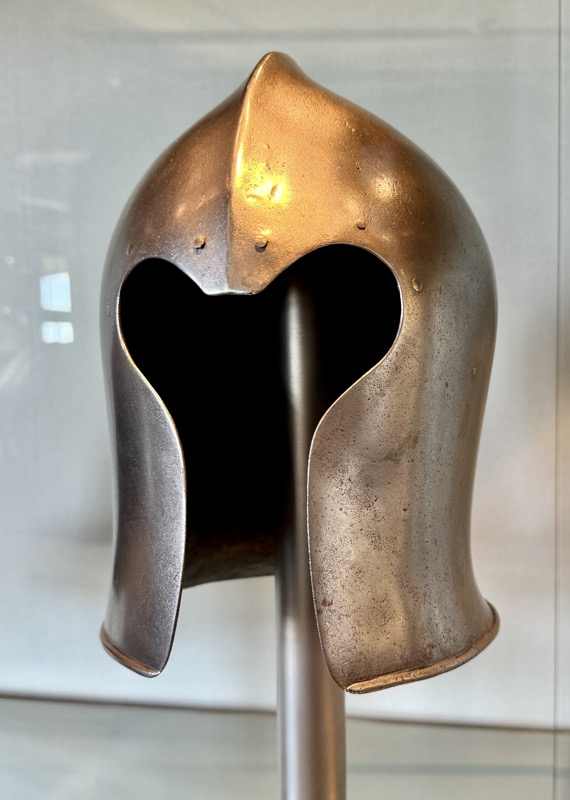
Helms: 1) Bascine, 14thC. 2) Bascinet, German, late 14thC. 3) Kettle hat or Chapel-de fer, Tirol c1400.
4) Jousing helm, Tyrol, late 15thC. 5) Sallet, Frankie, c.1450/60. 6) Italian bascinet, Northern Italian late 15thC.
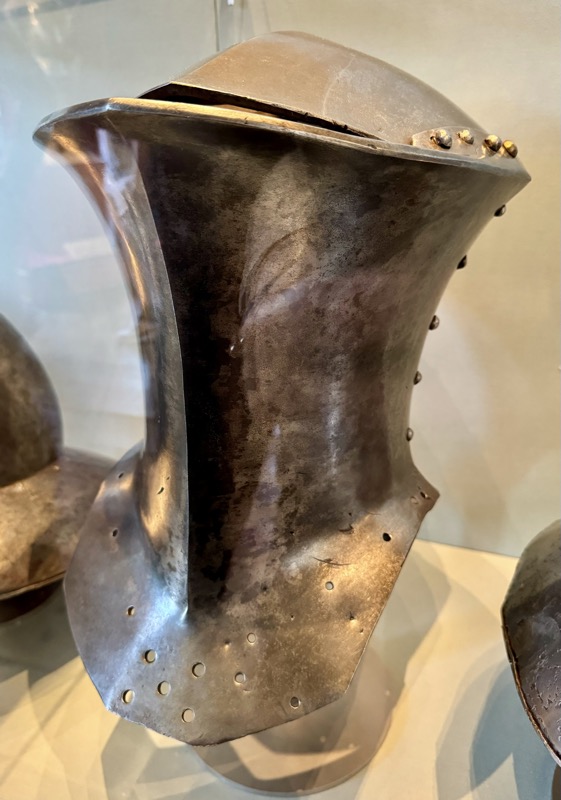






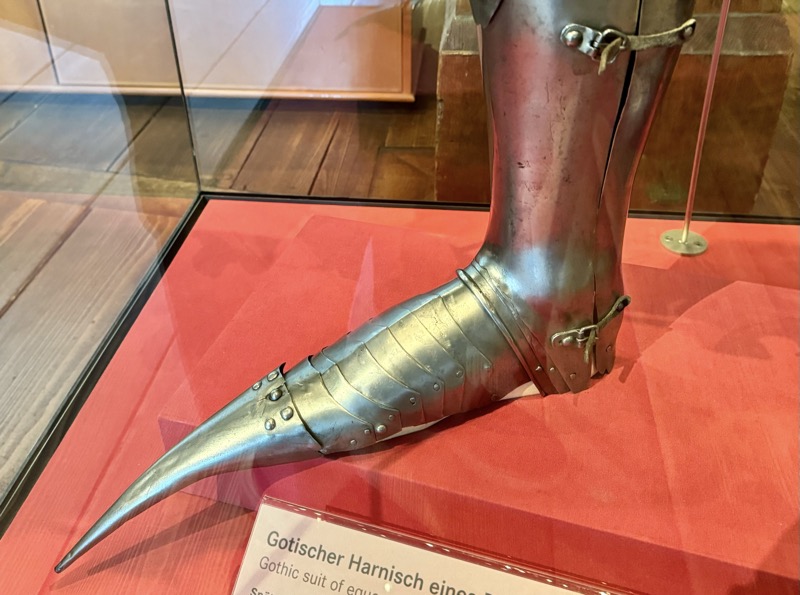
Gothic suit of equestrian armour – almost complete condition which is extremely rare apparently. Nuremberg armoury, the fancy shoe tips made it unsuitable for combat. It could have Ben worn only be a rider. The help is not original to this suit.
Nuremberg, c.1470/80. Iron – steeled, ground and originally polished to a high sheen.

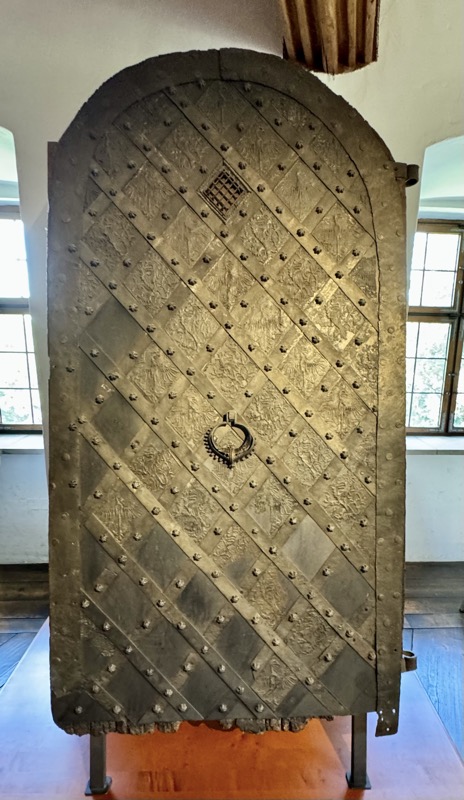
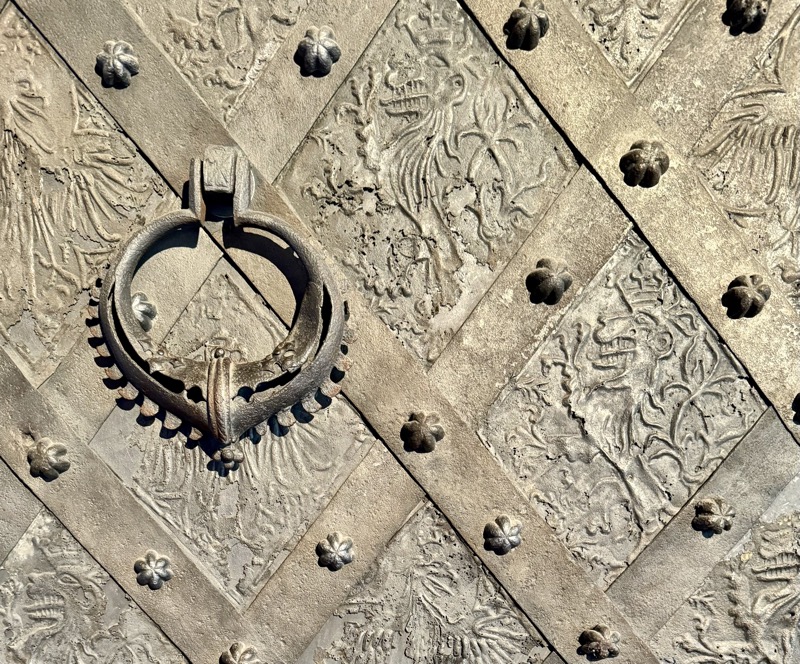
Iron-clad door with iron fittings. . Dates from the reign on fate Bohemian and German Kings Charles IV or his son Wenceslas. 2nd half 14thC.


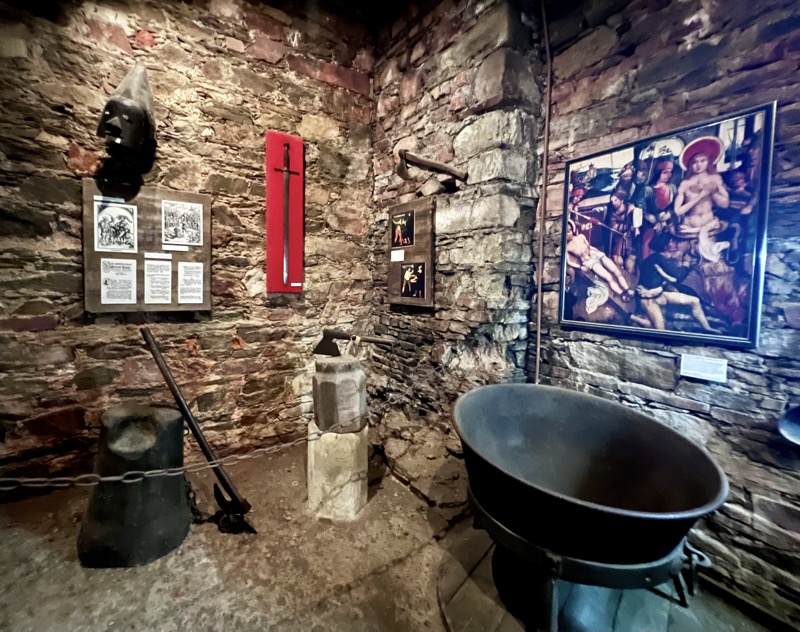
There was a very small section that dealt with the history of Nuremberg after the period of theHoly Roman Empire and glossed over WWII fairly quickly.


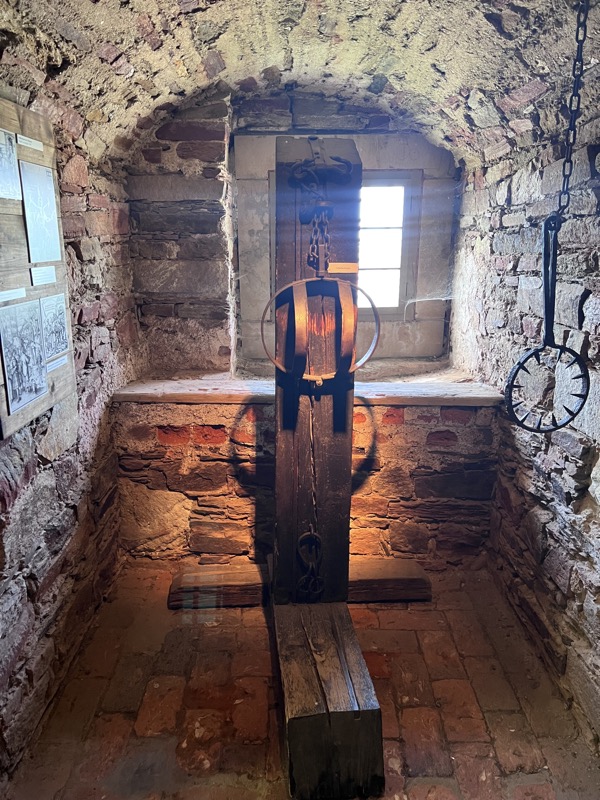
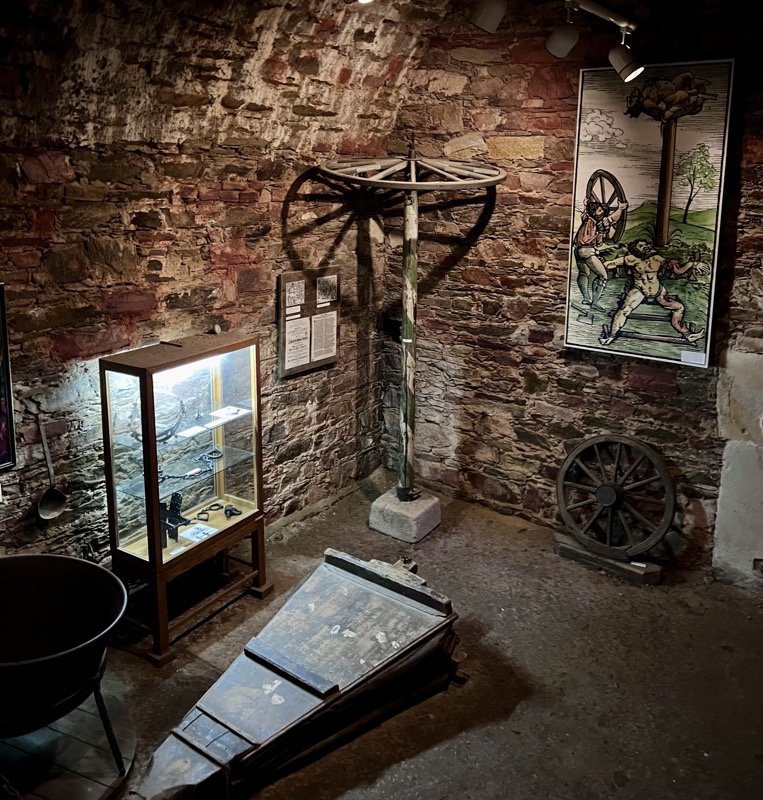
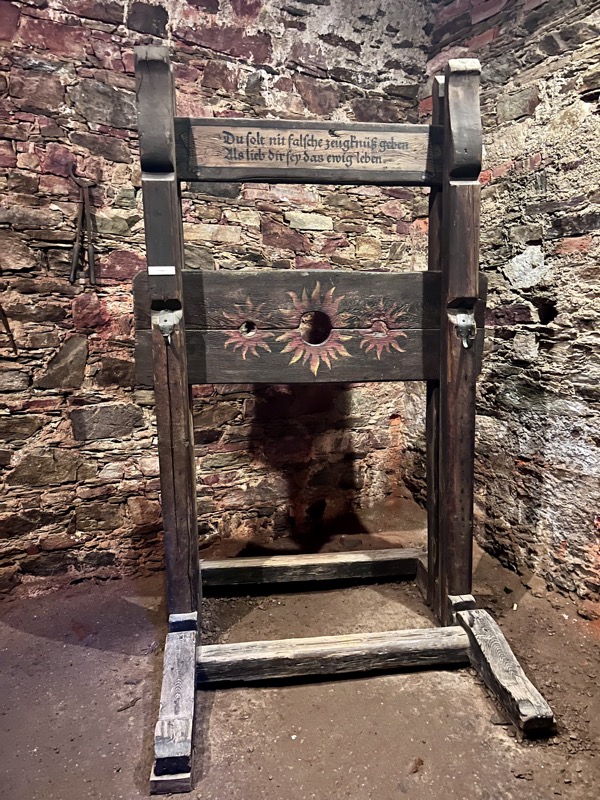
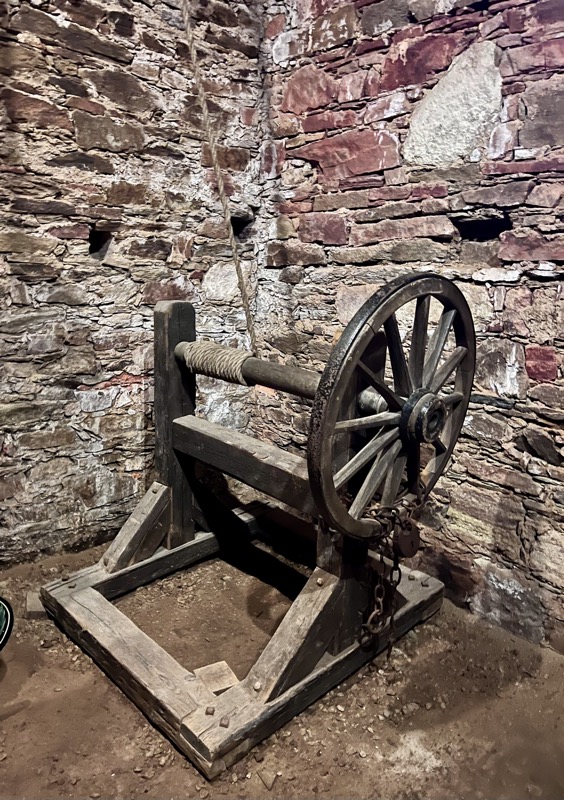
Ok… the Castle was very cool and I really enjoyed seeing the buildings a the layout of the fortress complex… but fuck me, I was so dirty when I discovered how many of the artefacts were just bloody modern replicas. I know it shouldn’t detract from the enjoyment of seeing these things in this context, but it fucking does! I walked up (and back down – which is sometimes even more painful) four storeys of stairs with a severely torn meniscus to see stupid copies of things? My heart rate was up around 150bpm the whole time, and I was overheating due to the excessive pain from my knee joint (and an involuntary habit of holding my breath inappropriately while in pain) and for what? To see shit that I would have been better off looking up high res images of the originals, online? It was so deflating.

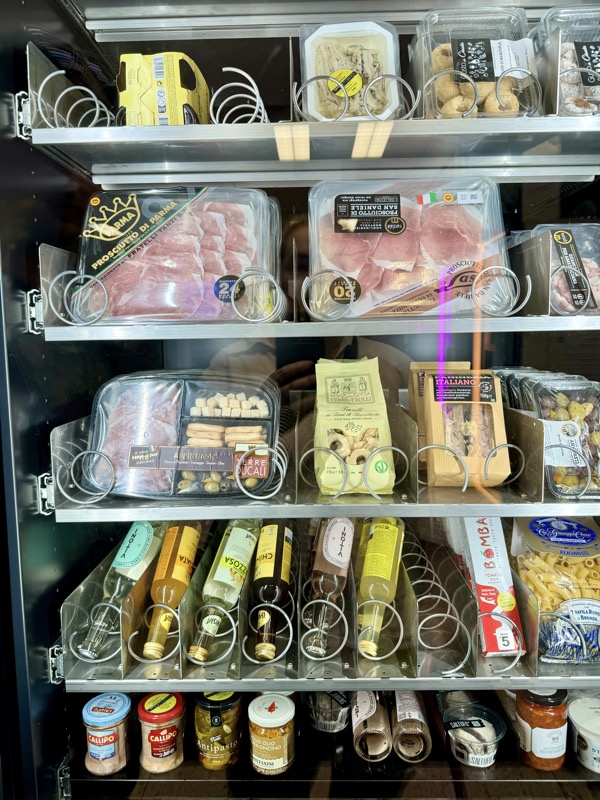
Encountered this amazing vending machine in a shopping centre car park of all places – full of cheese and charcuterie! And here’s me thinking Japan has the best vending machines.


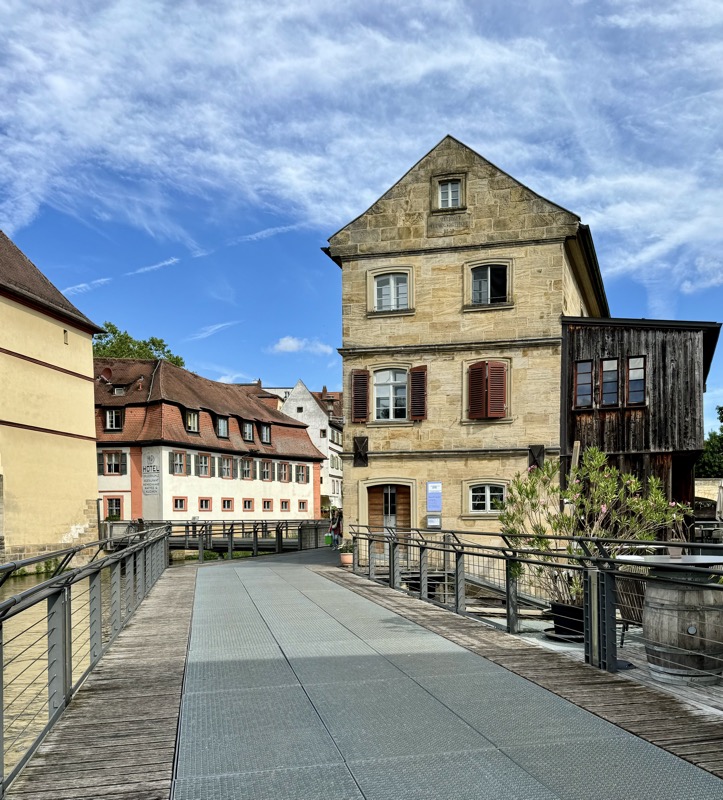
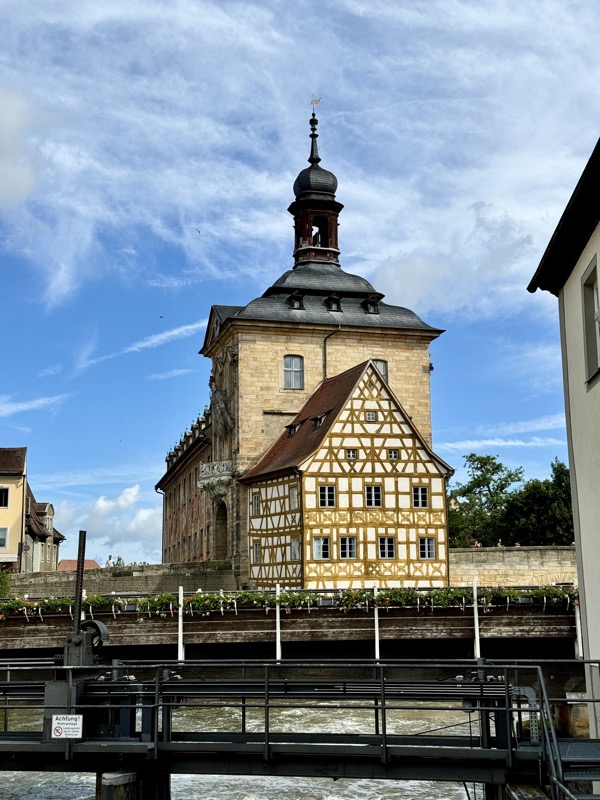
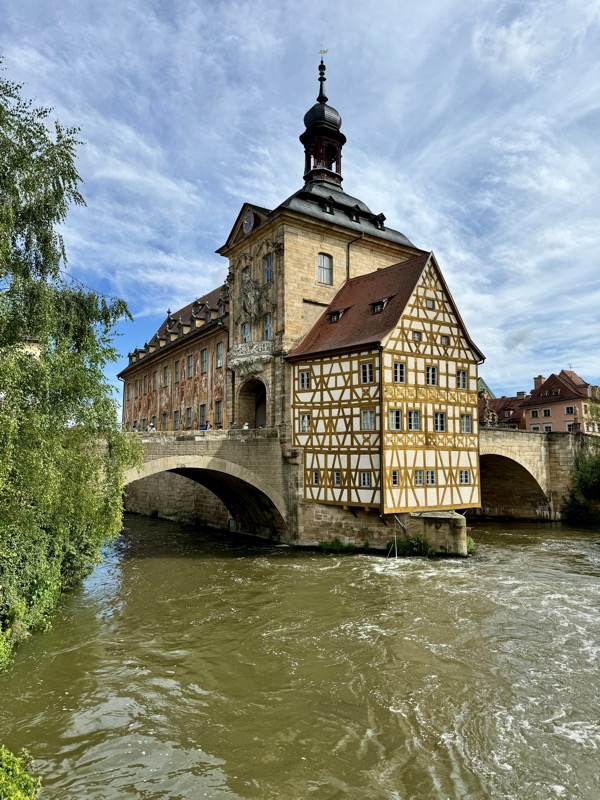
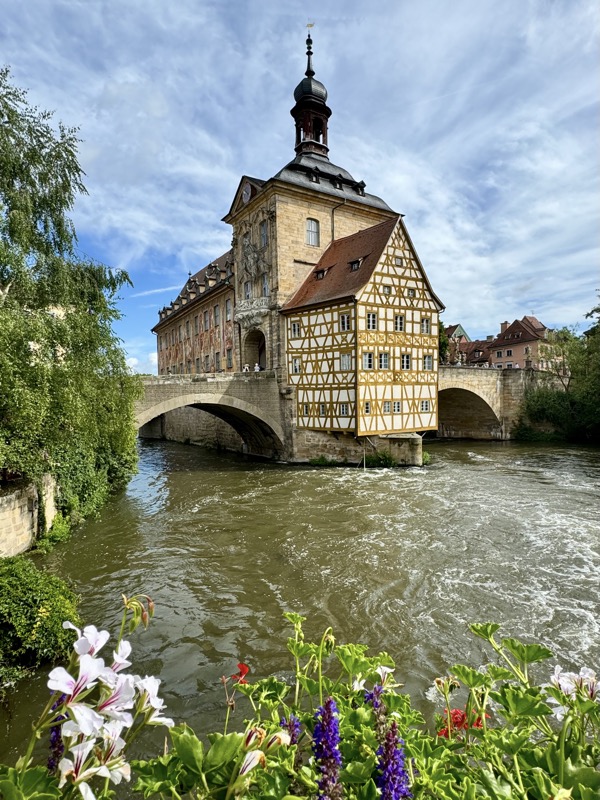
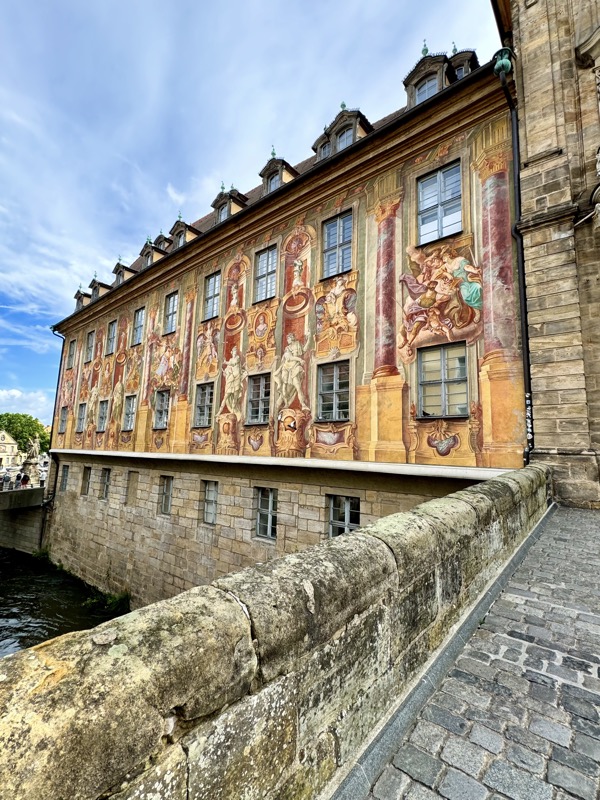
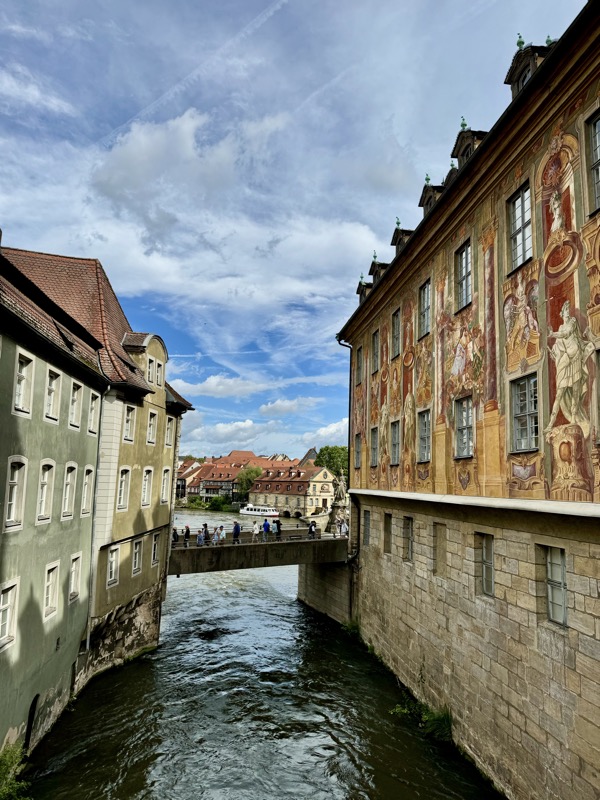
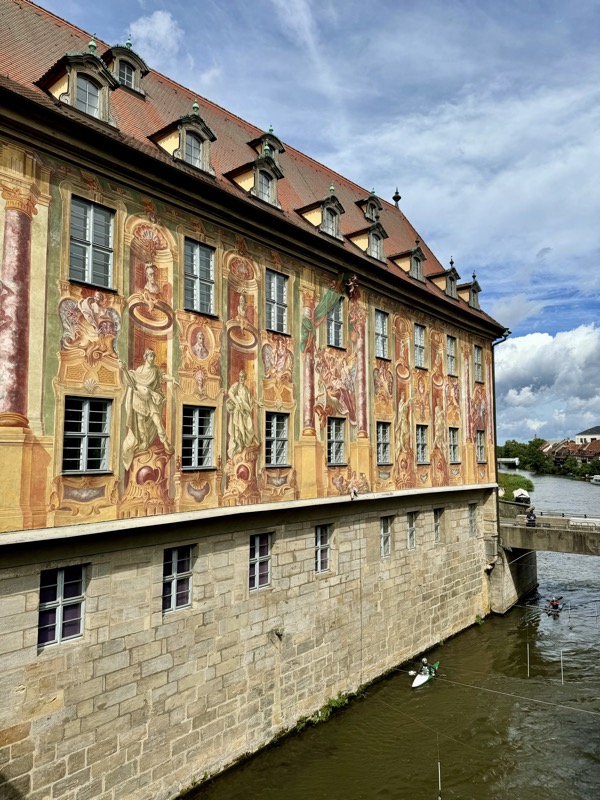
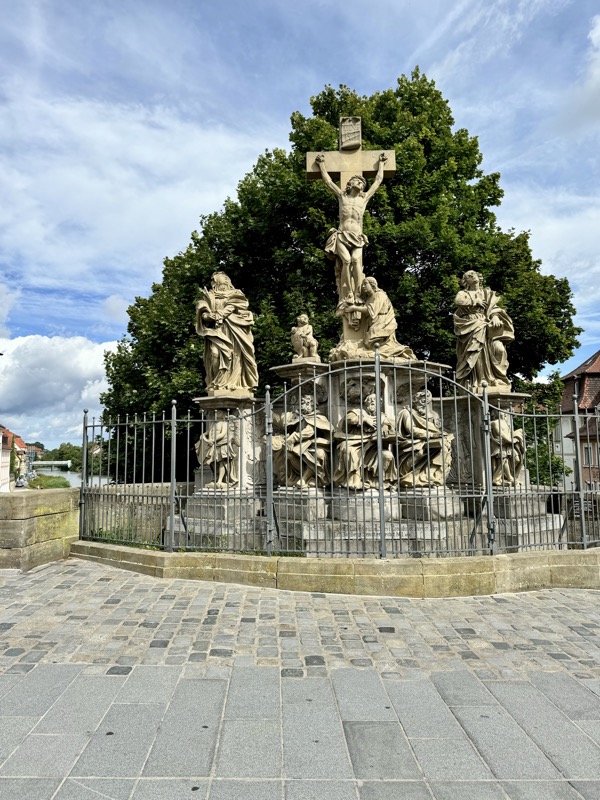
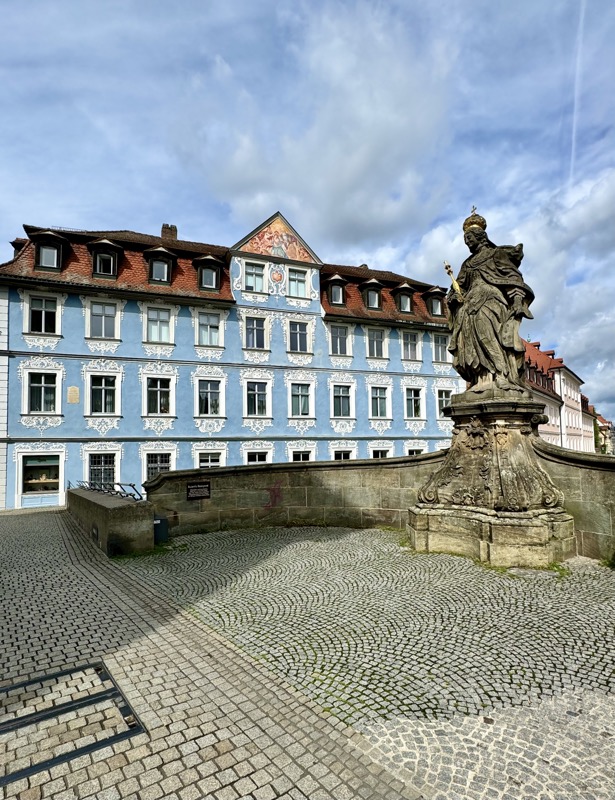
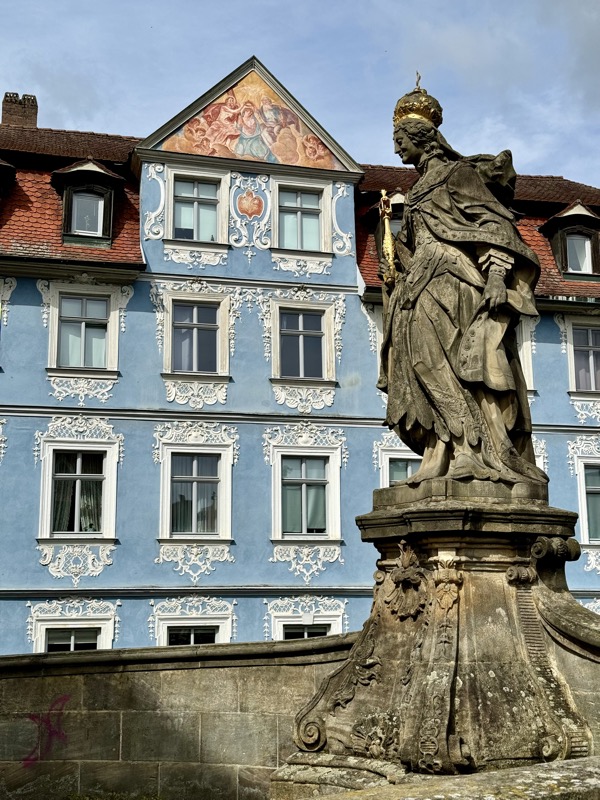
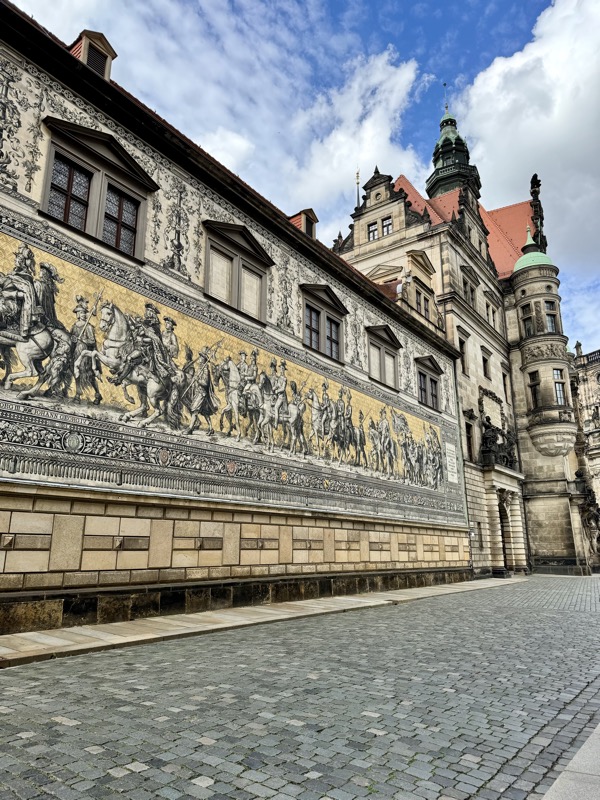
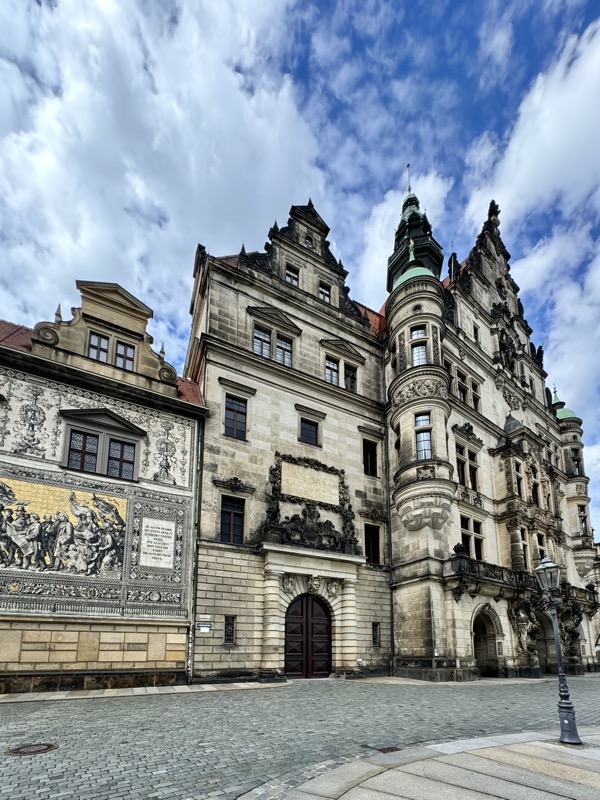
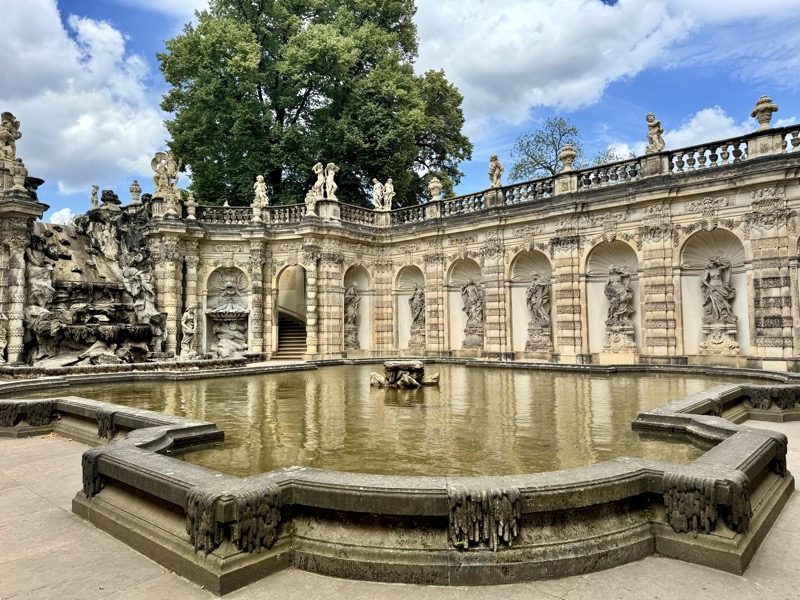
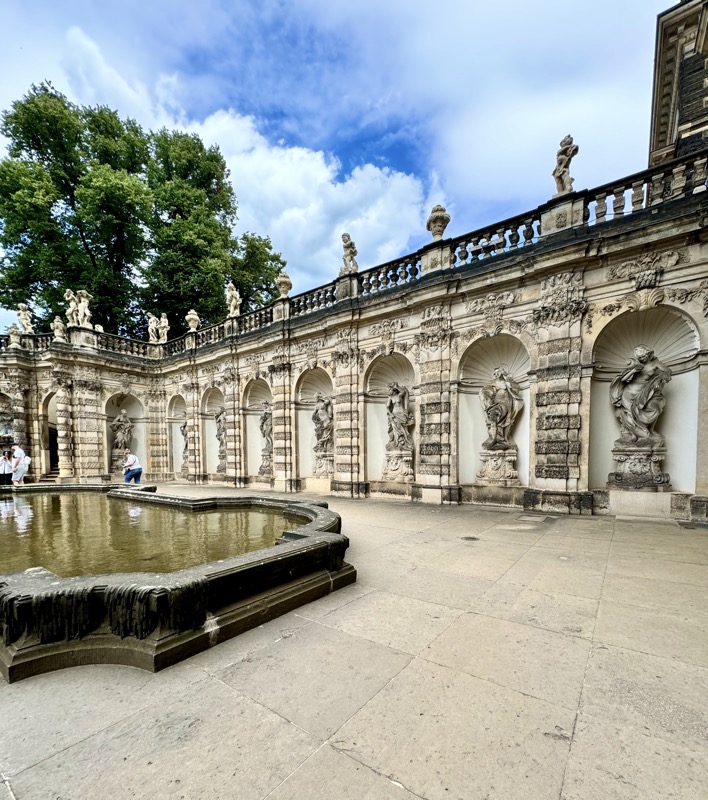
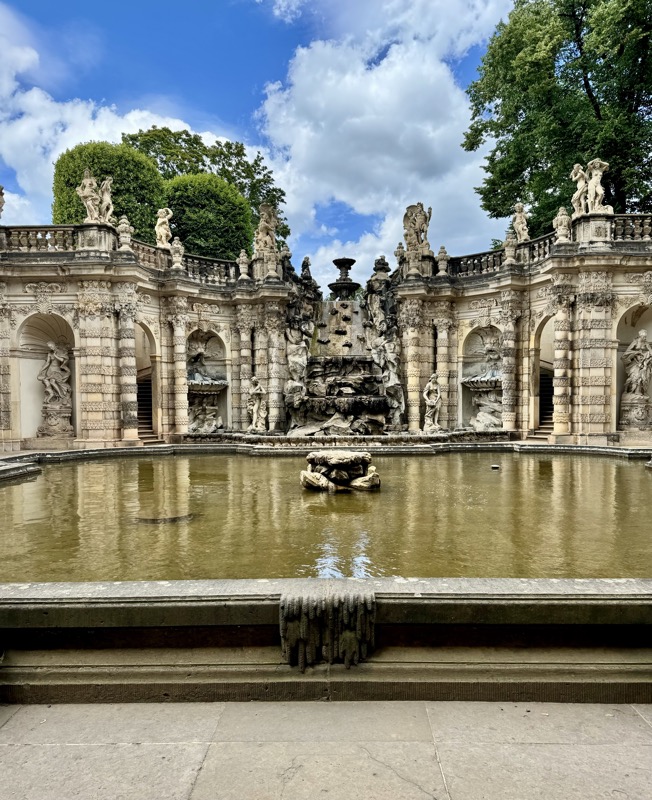
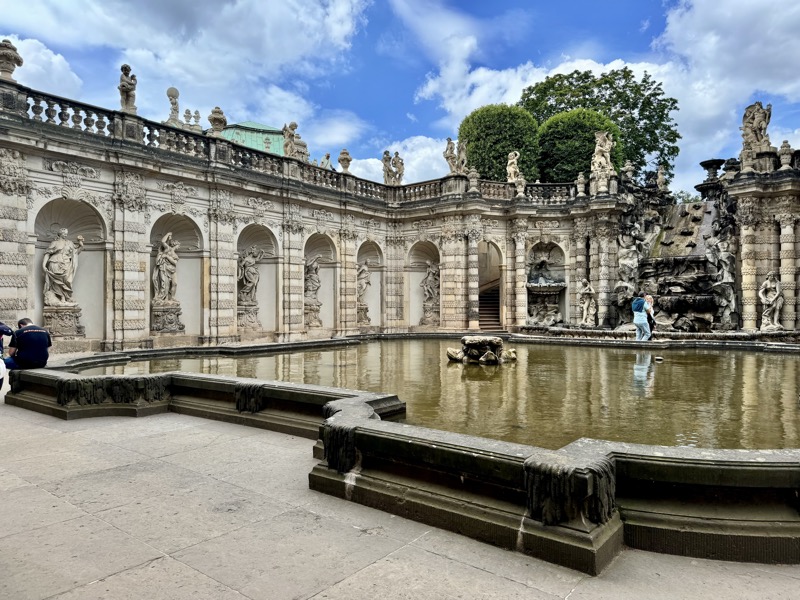
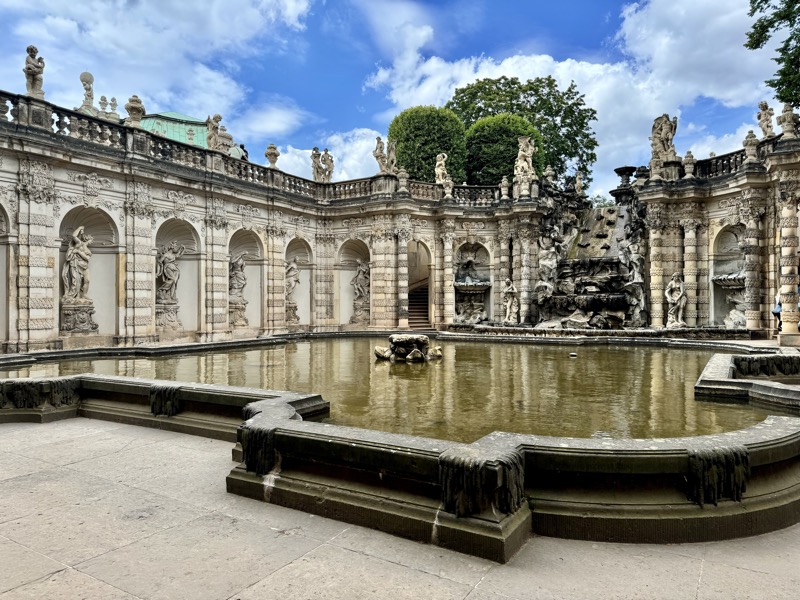
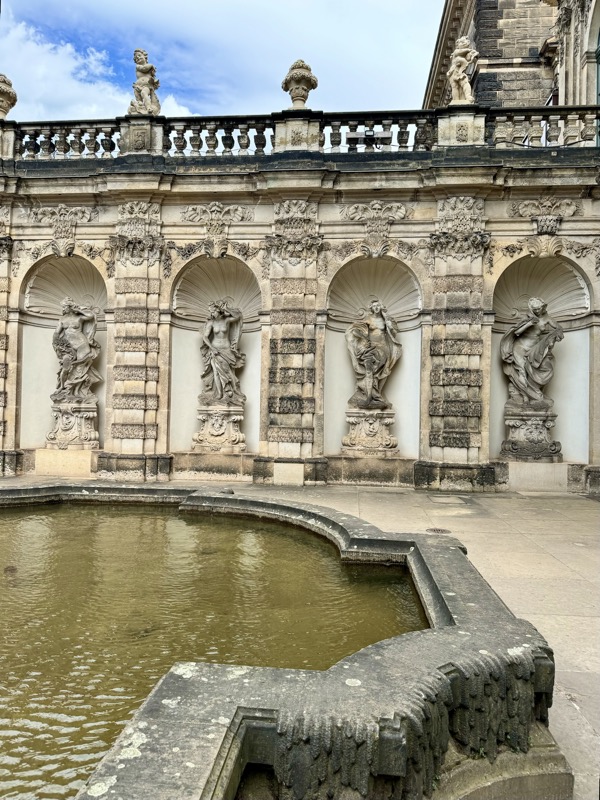
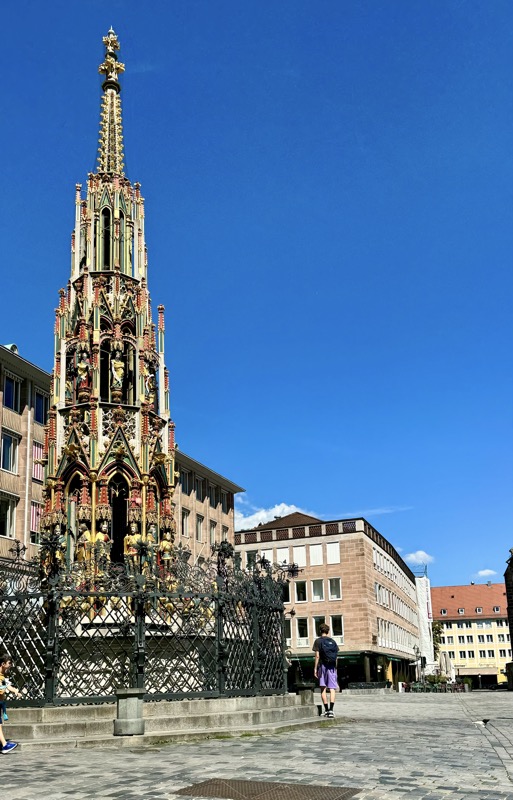
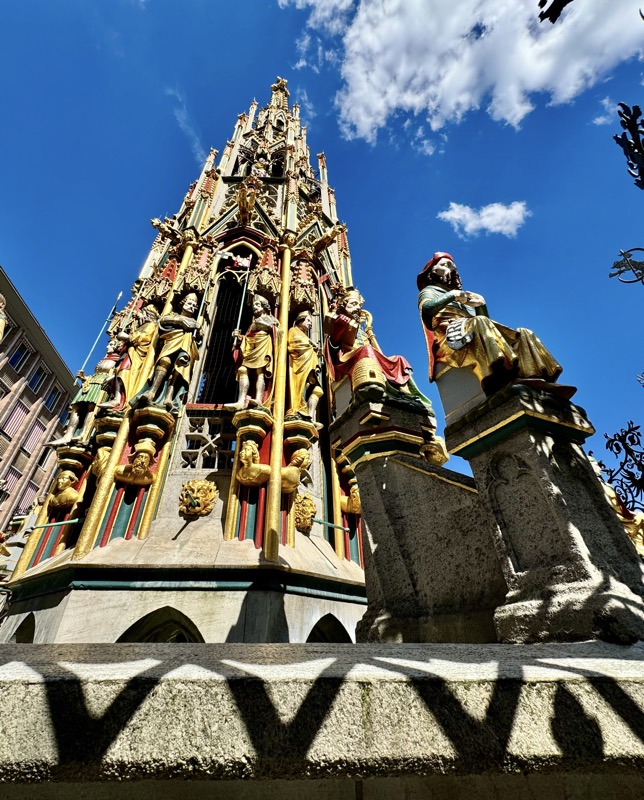
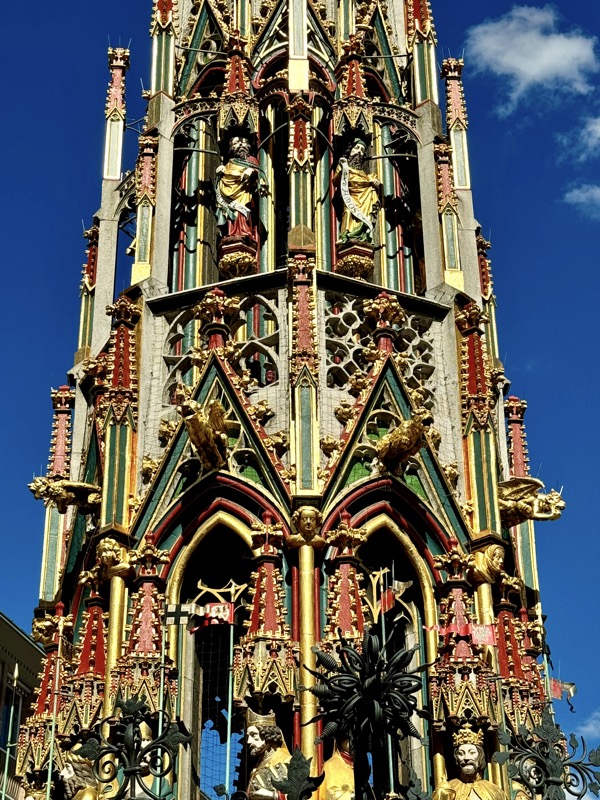
After the castle, we made our way to Haupmarkt to see the famous Schöner Brunnen fountain, a 14thC Gothic fountain locate next to Nuremberg’s main markets and the town hall. It is 19m high and in the shape of a church spire. It was built by Heinrich Beheim in 1385.



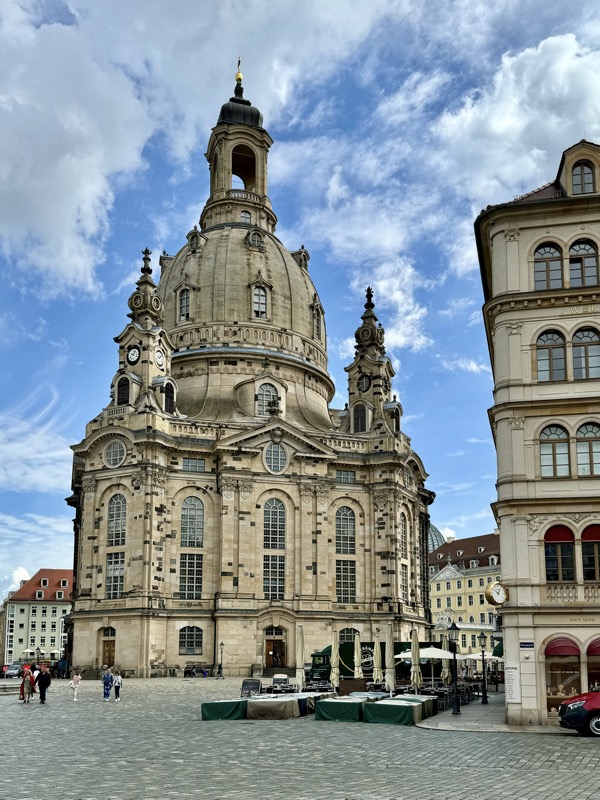
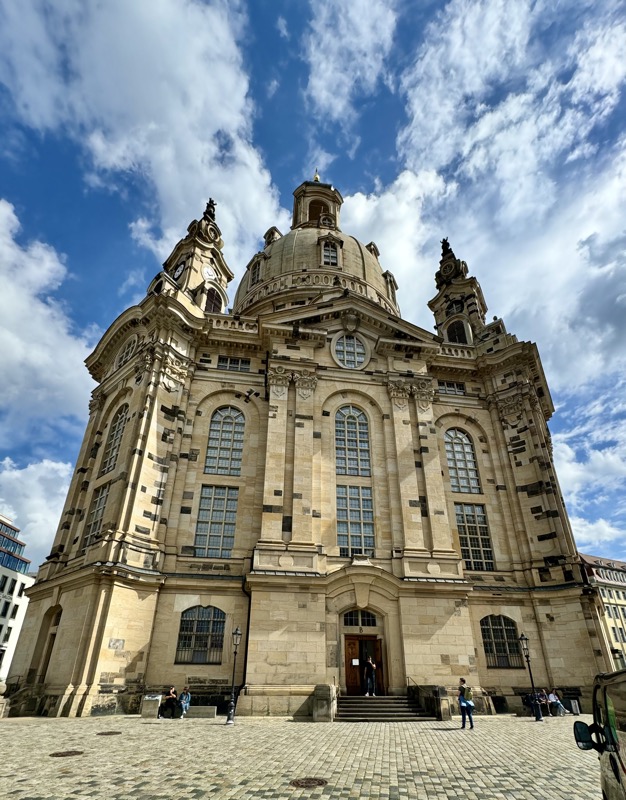
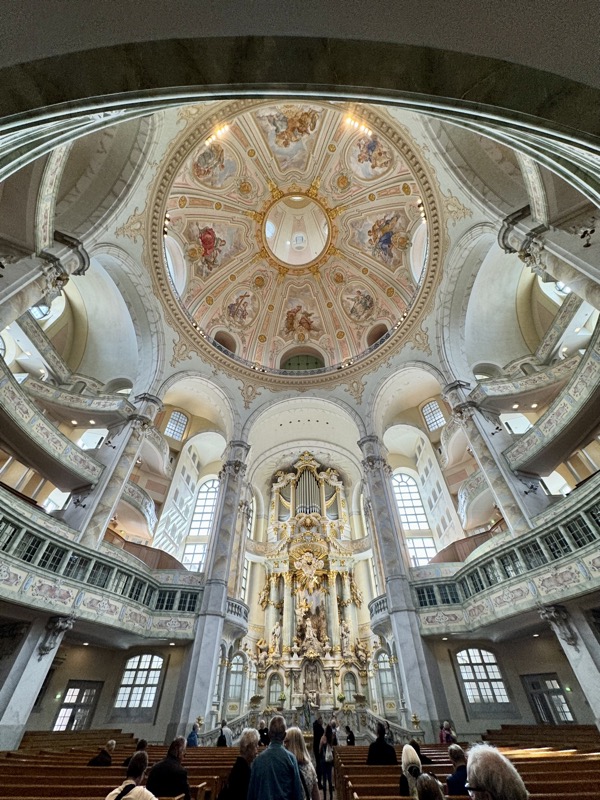
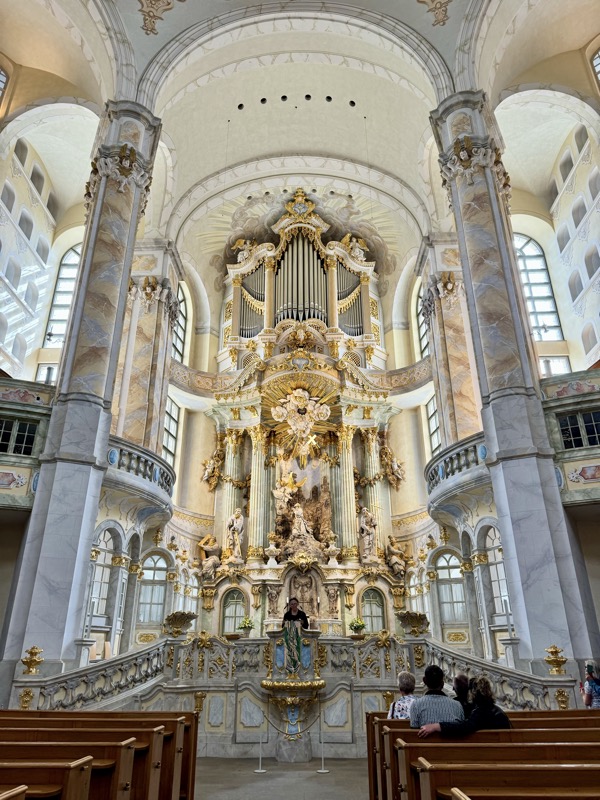
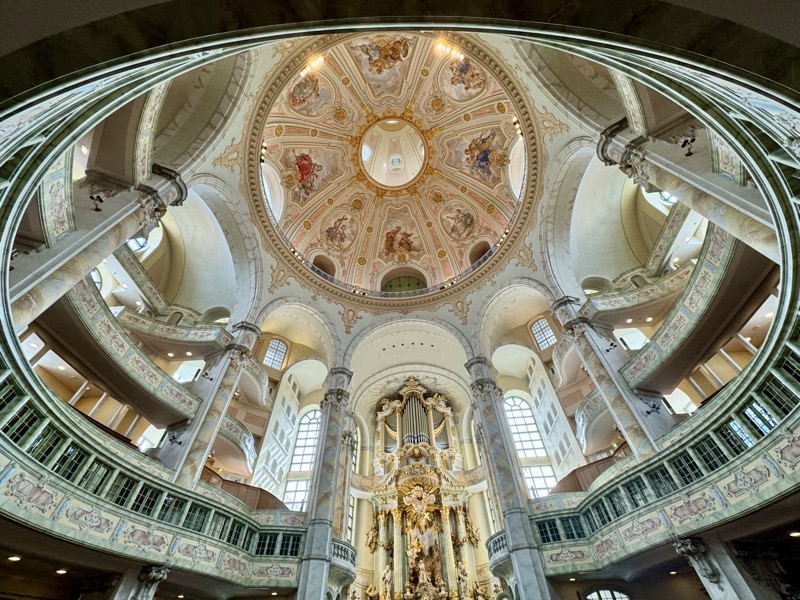
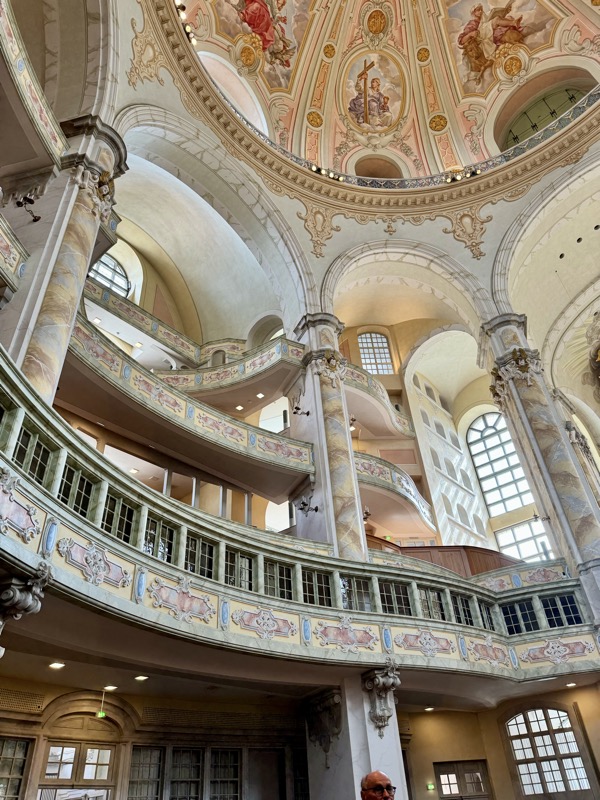
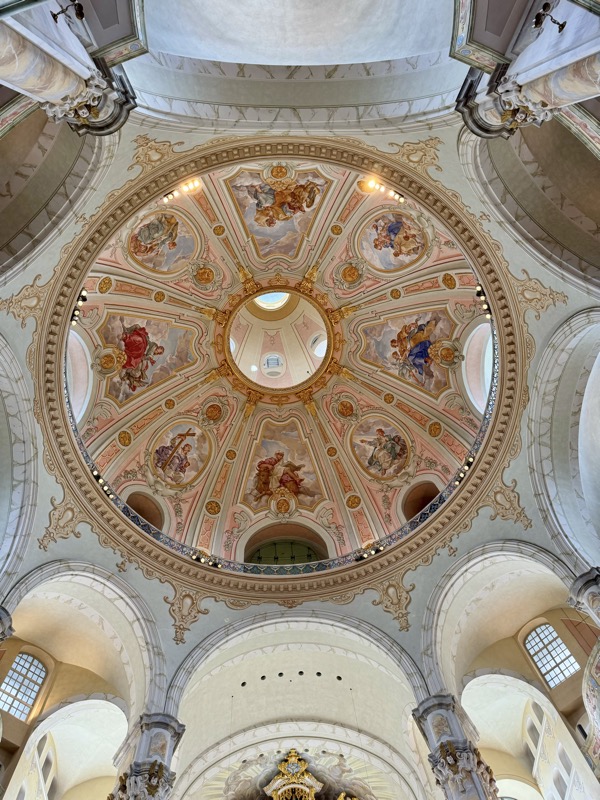
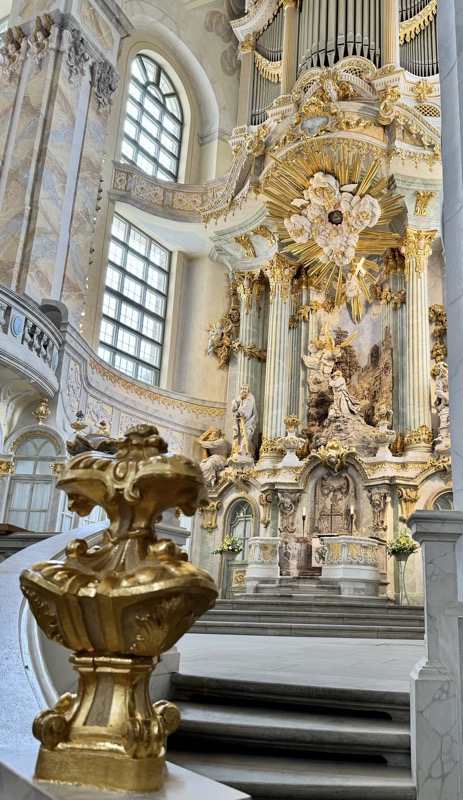
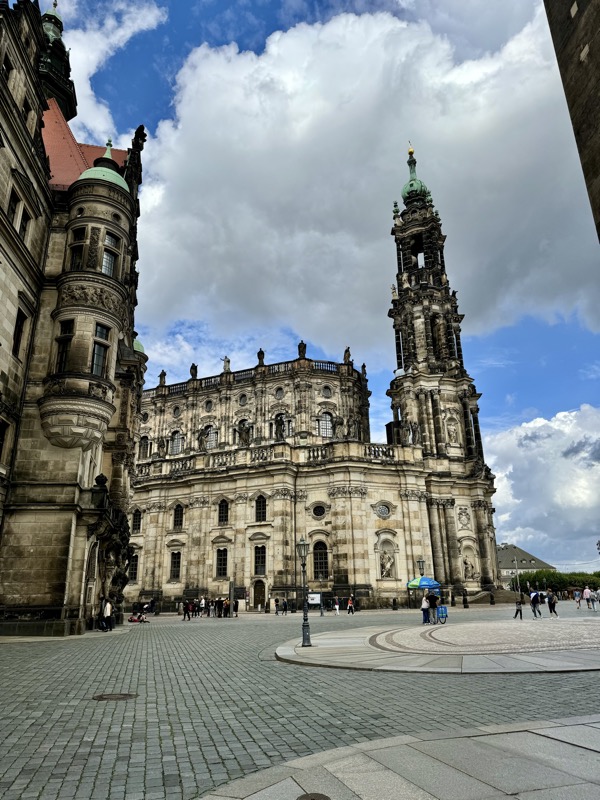
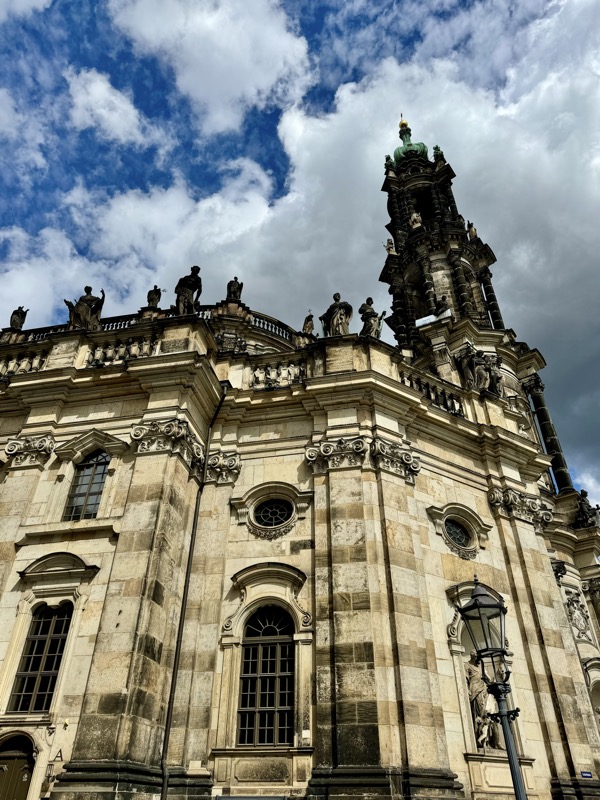
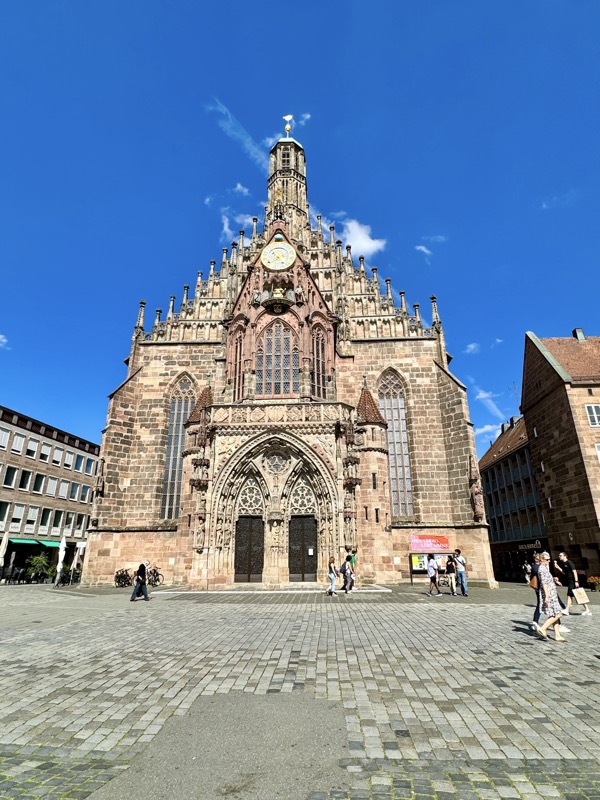
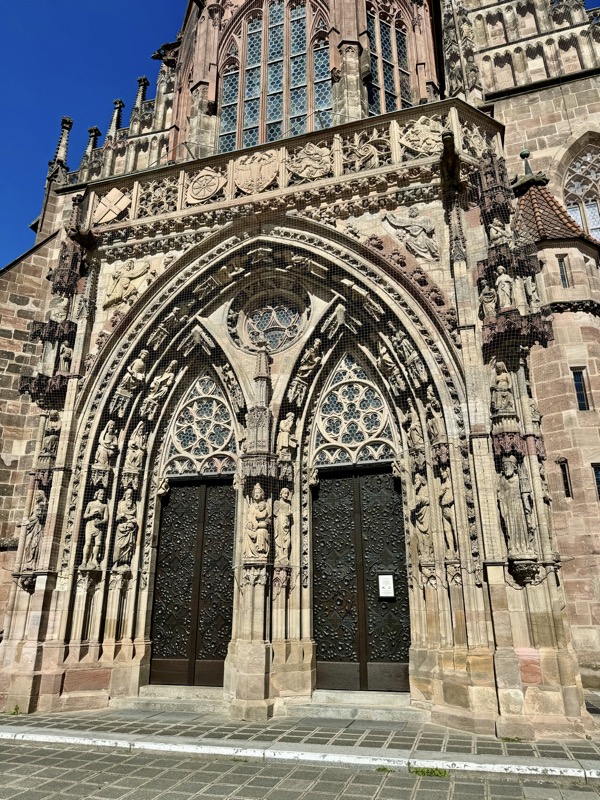
The Frauenkirche is not far away and is the Roman Catholic parish church of Nuremberg. It was built at the commission of Emperor Charles VI from 1352-1362 as a hall church. It is full of sculptures, many of them have been preserved from around the time of construction, so they are c.1360 also. There wasn’t a lot of information available in the church, an it was smaller than I expected.


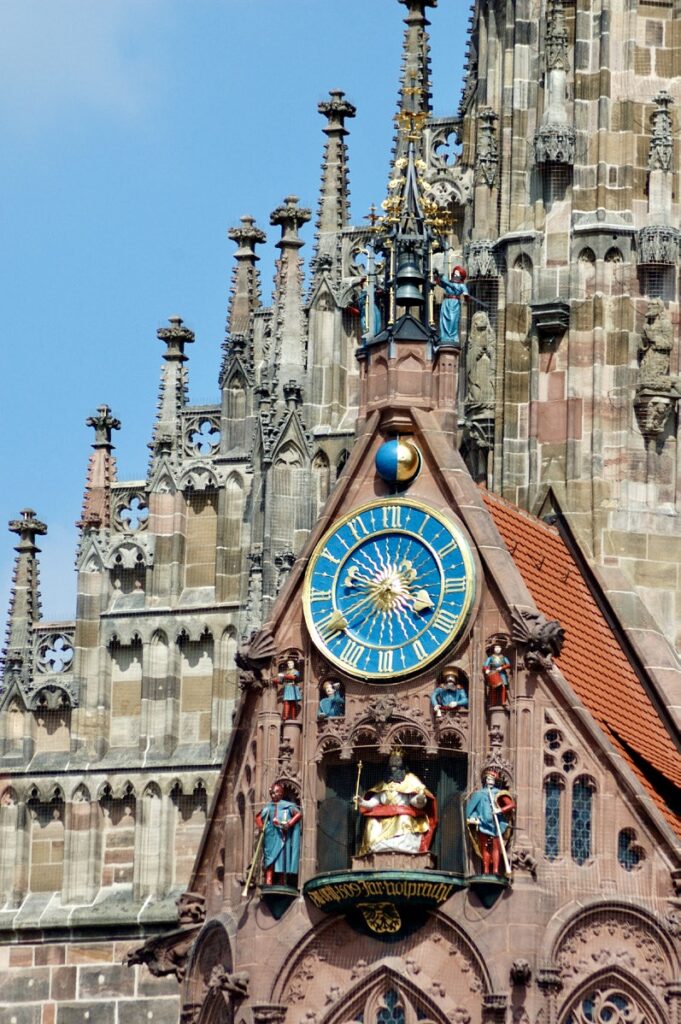
The facade of the Frauenkirche has as clock called the ‘Männleinlaufen’ (Little Men Running) which is activated at noon, and has seven little men – representing electors of Nuremberg – that move with chimes. It was built/ordered by Charles IV in 1356 to commemorate the Nuremberg code of Laws, the Golden Bull. The clock was removed during WWII and stored in a Nuremberg Art Bunker.

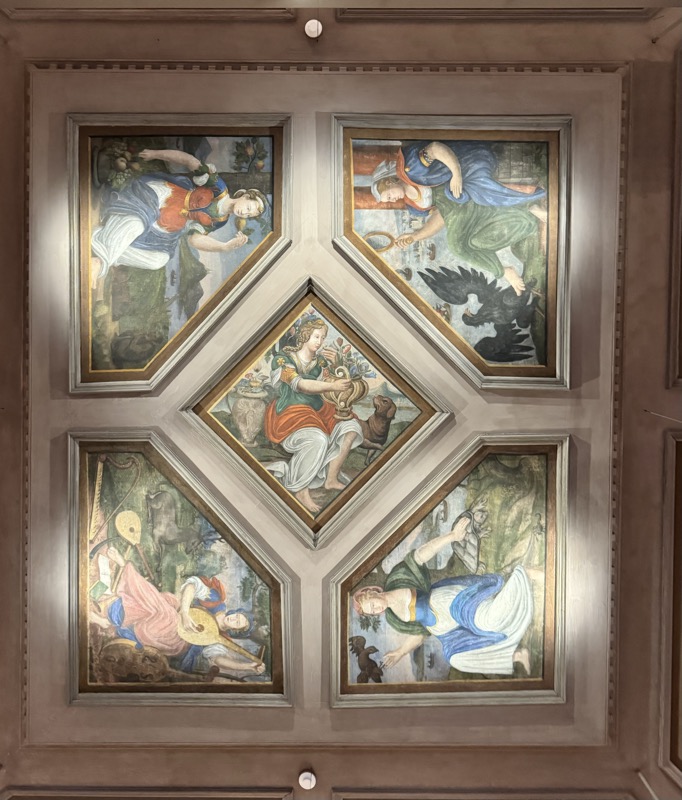
The inner vestibule was full of brightly painted relief art work – I imagine this is what a lot of the old cathedrals looked like but haven’t been restored over the centuries.
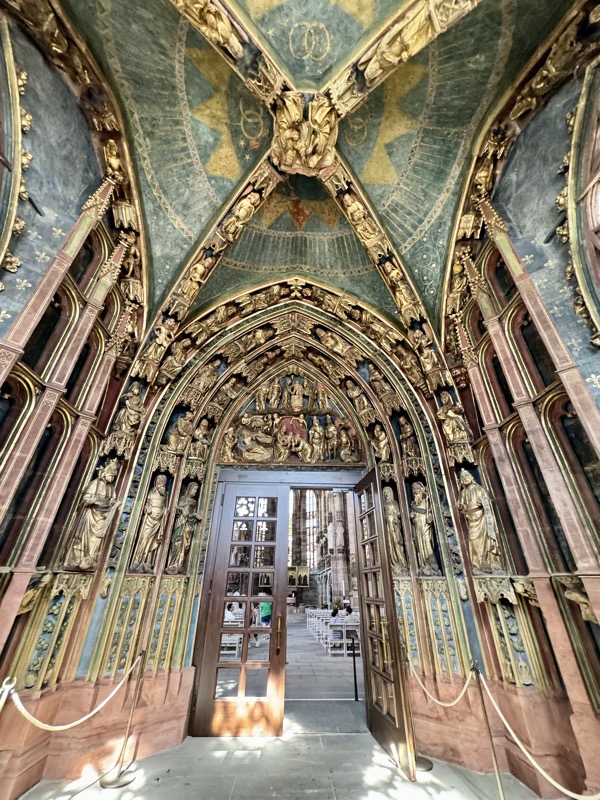
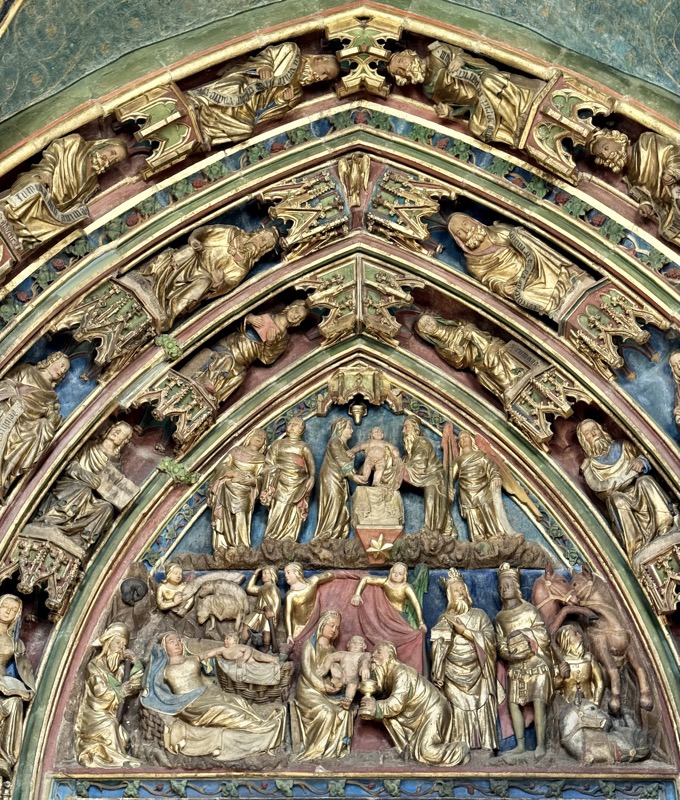
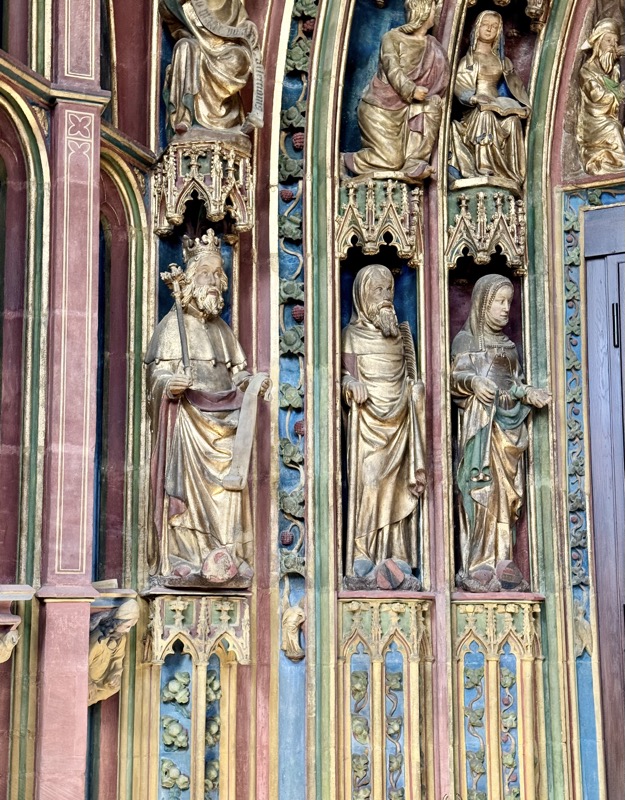
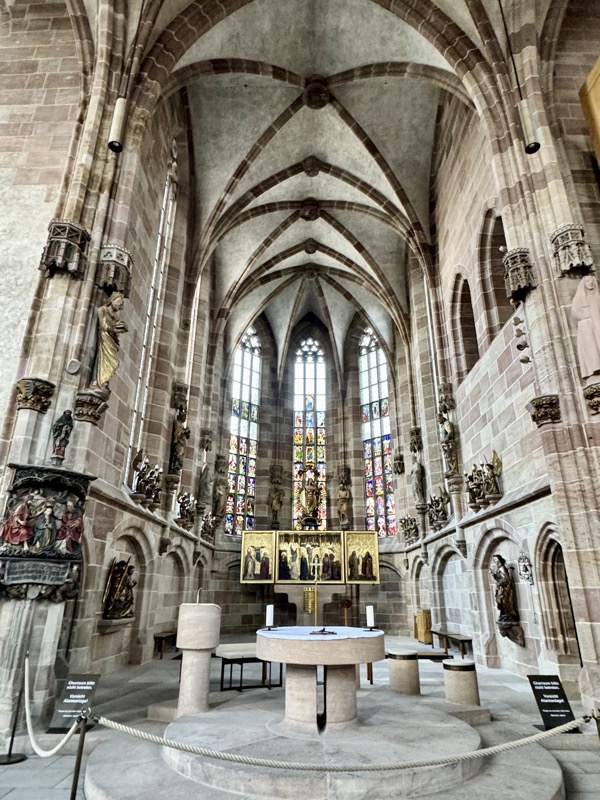




The Tucher Alter c.1440/50 came from a demolished Augustinian Church – the Frauenkirche was used as a Protestant church for several centuries and much of the art and sculpture came back into he church when it was redesignated? reconsecrated? by the Catholic Church.
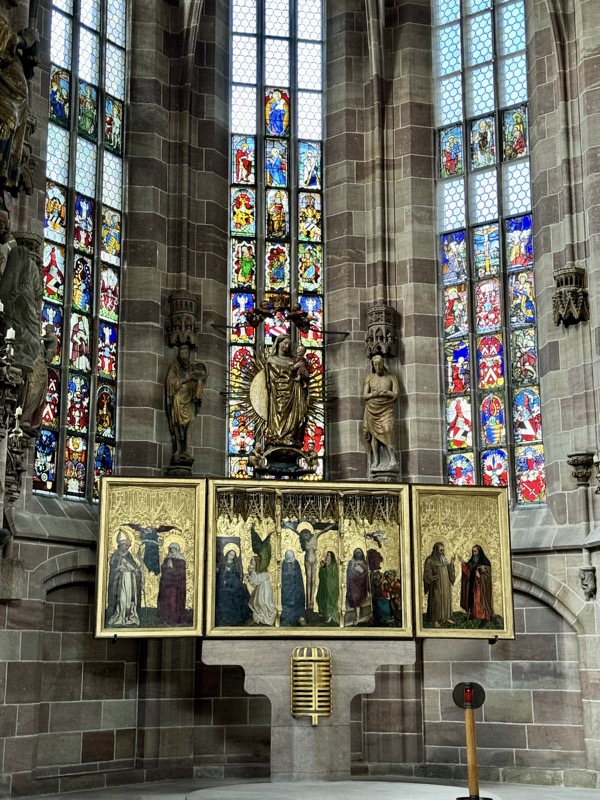


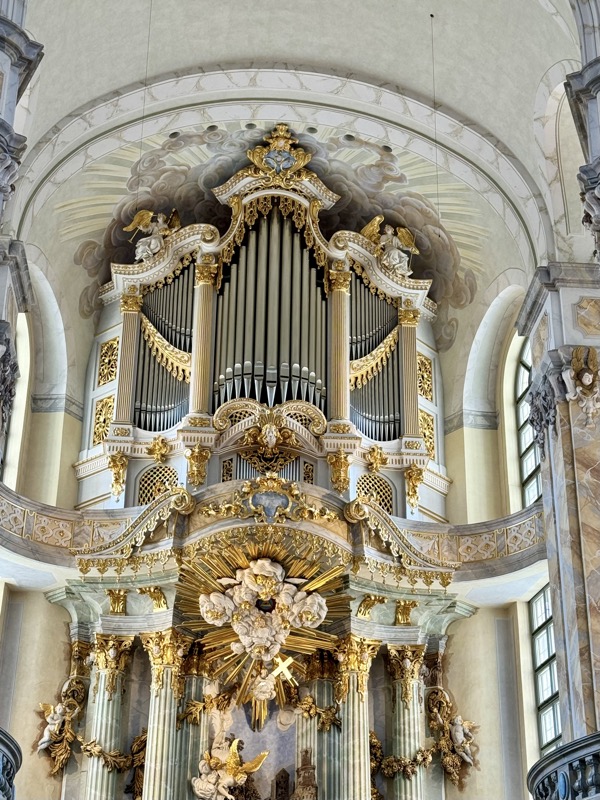
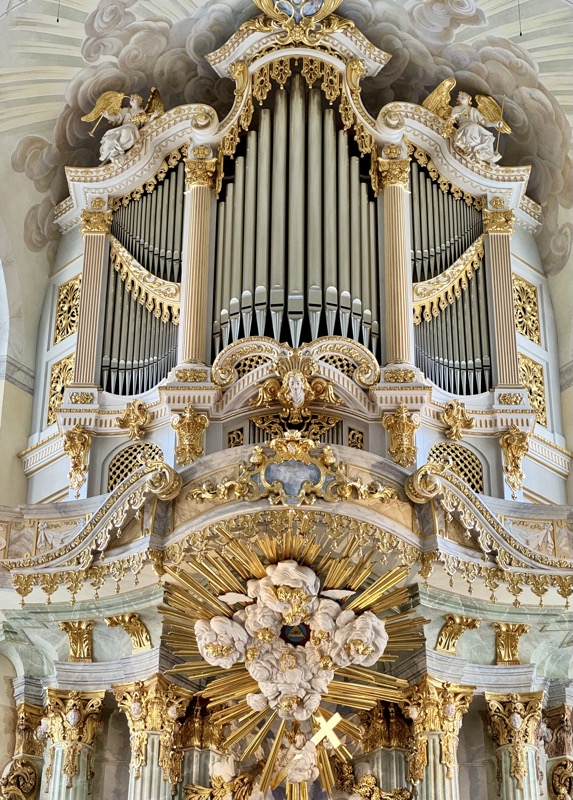
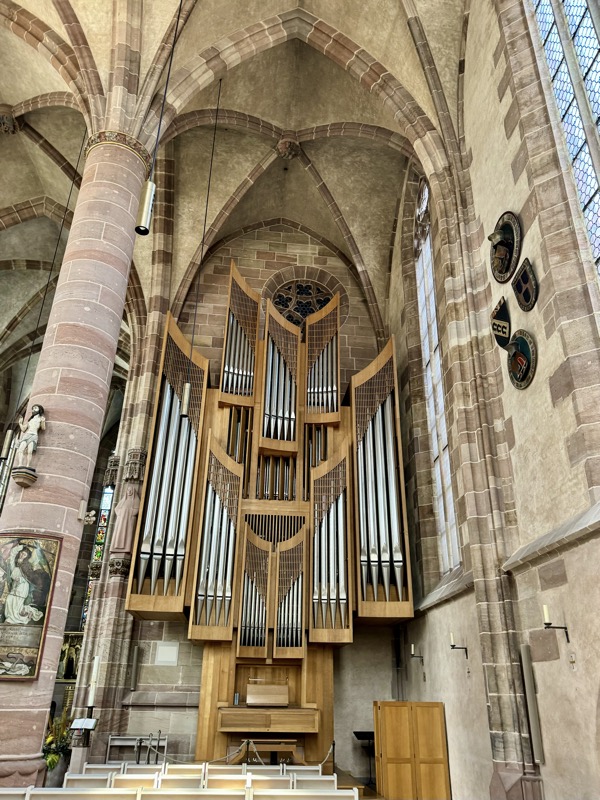
There has been an organ in this church since 1492, however this one is from the 1950s.
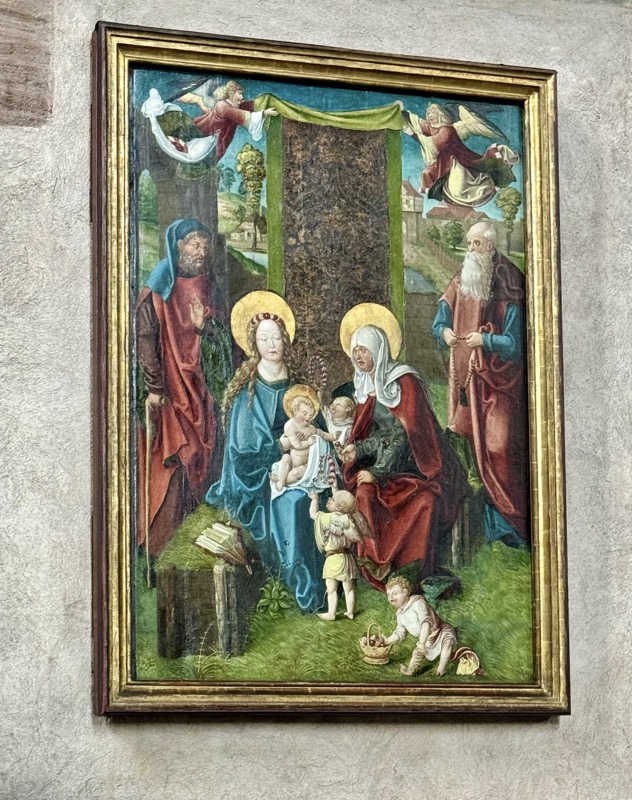


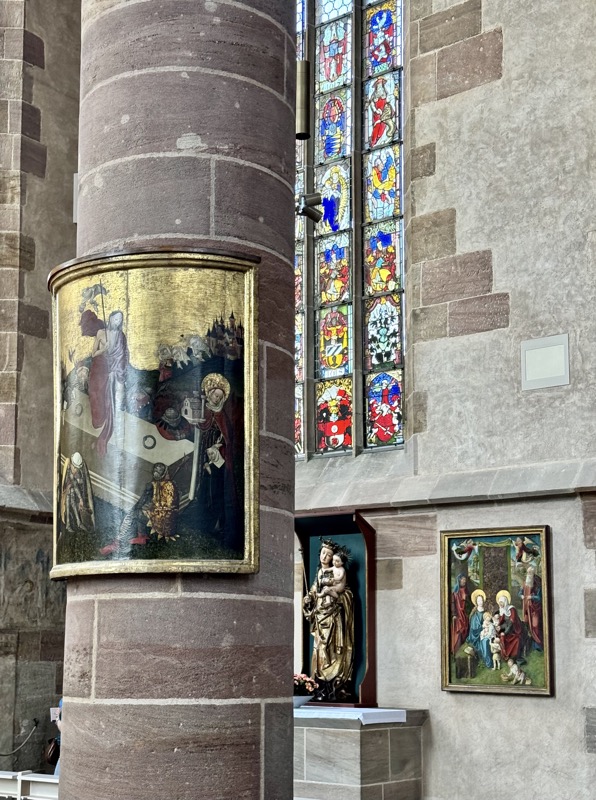
I got nothing on this sculpture, other than that Baby Jee looks stoned.
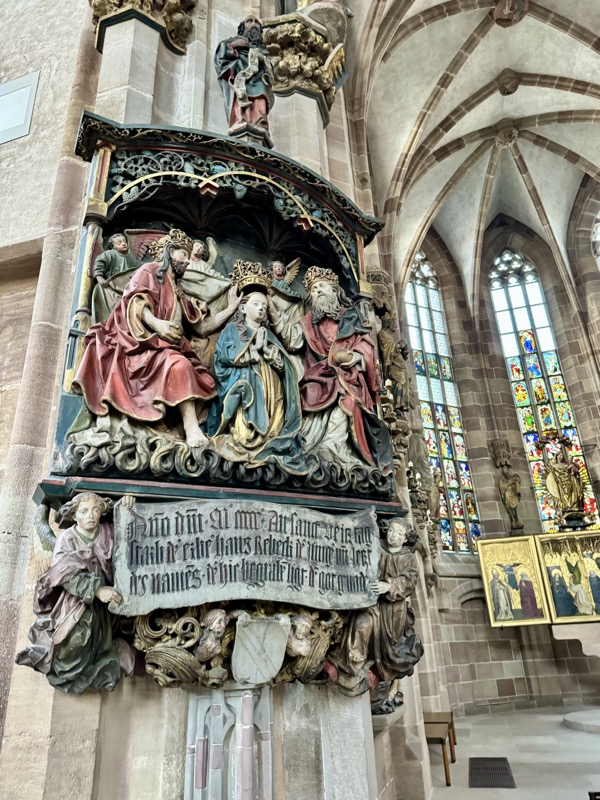



Pergenstorfer Epitaph.

Stopped by a bookshop, having decided to acquire a couple of well known books to try to read in German. I figure this immersion stuff has to help at some point. It’s sure not helping here; every time I try to speak with people in German they can tell I’m not a native speaker immediately and they switch to English. How are you supposed to get any better if people won’t talk to you? :/


St Seibald’s Church apparently began with a grave in 1070, and not long afterwards reports of healing miracles occurring at his grave are documented.
The Chruch that is here today was built in the first half of the 13thC as a late Romanesque pillared basilica with a double choir. It was around this time that Nuremberg was becoming an important centre of commerce in Central Europe. In the early 1300s the side aisles were expanded, and the high Gothic choir loft was added between 1361 and 1379. Seibald became the patron saint of aspiring commercial ventures, even though he was apparently not canonised until 1425.
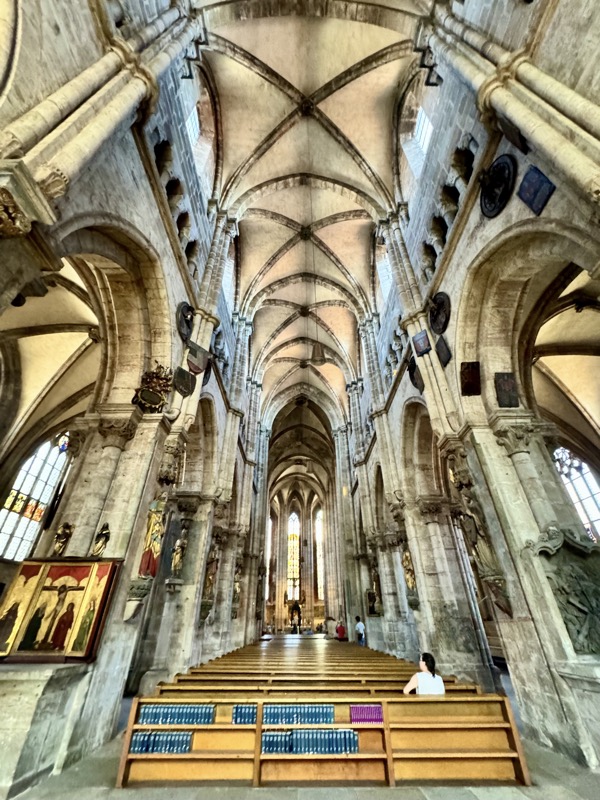

Master of the Tucher Altar, c.1440 and Elizabeth Starch Epitath, c.1450.
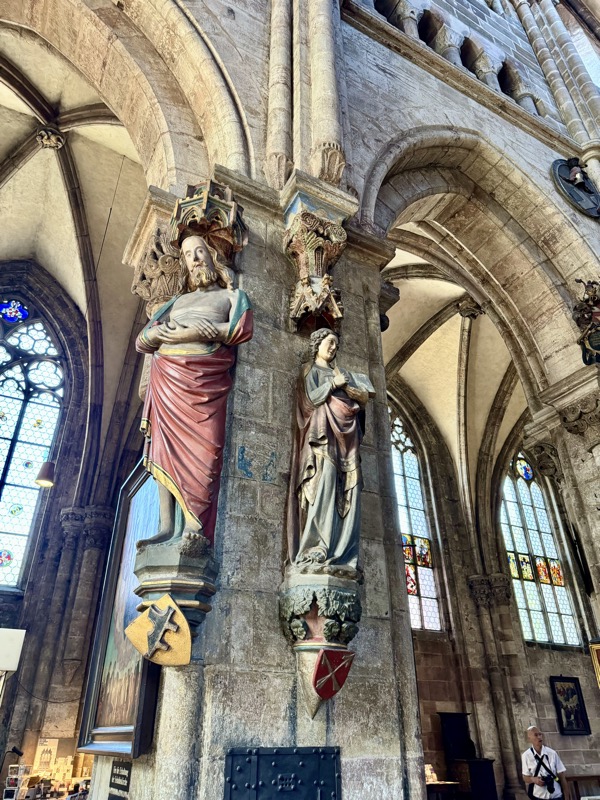


’Schüsslesfeider’, Saint Christoper, c.1442.

Most of the partially preserved stained glass in this church was donated by the families of City Council members of the Free Imperial City of Nuremberg, in the 14thC. Some was replaced c.1500, and the ‘newest’ glass in the cathedral was installed in 1601.
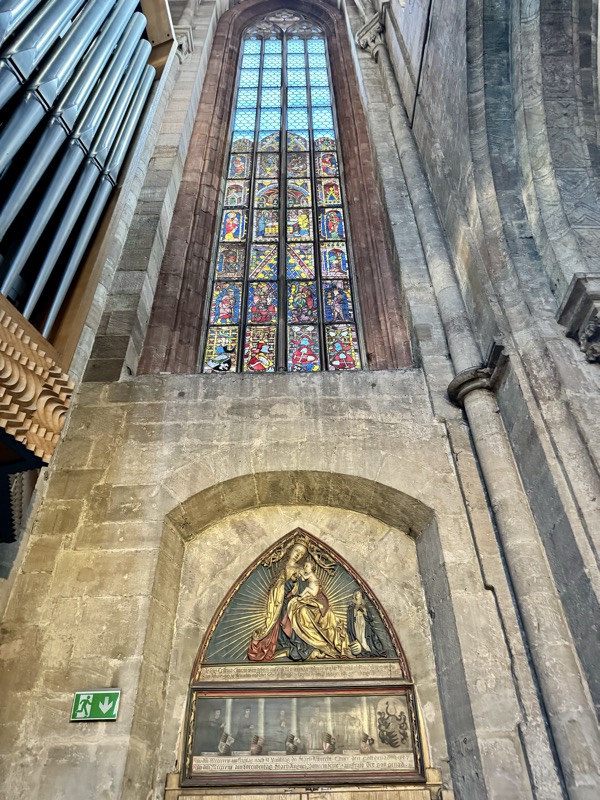
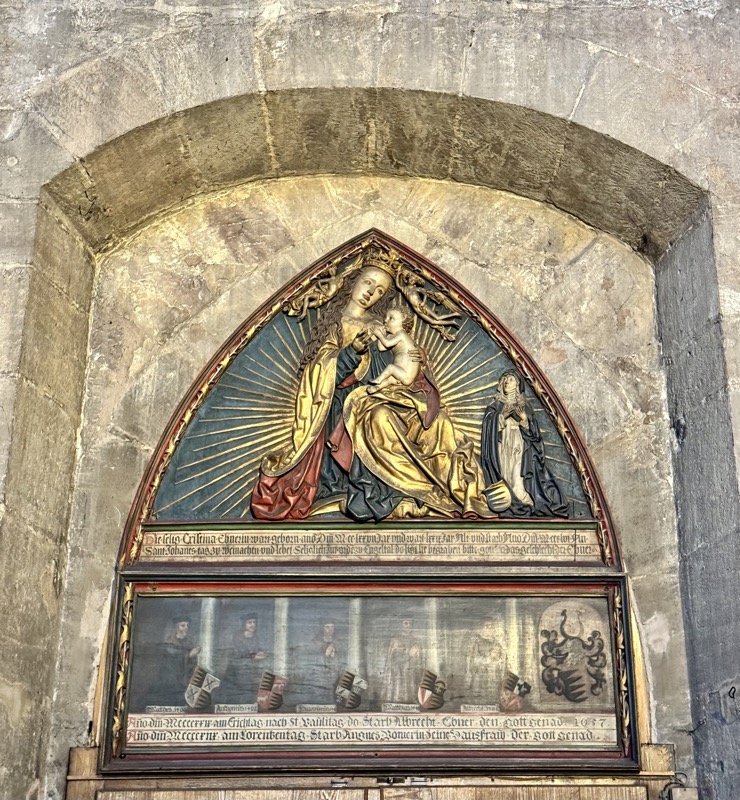



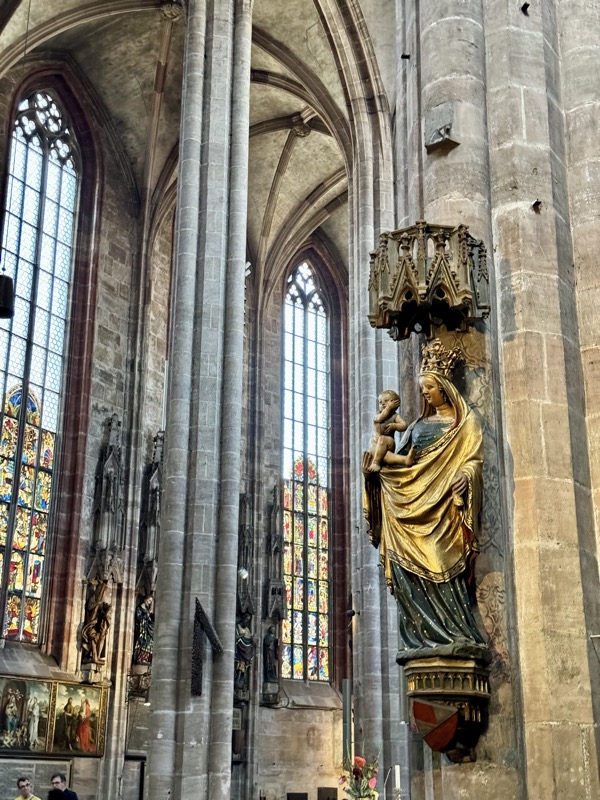
Madonna on the Crescent Moon, c.1437.

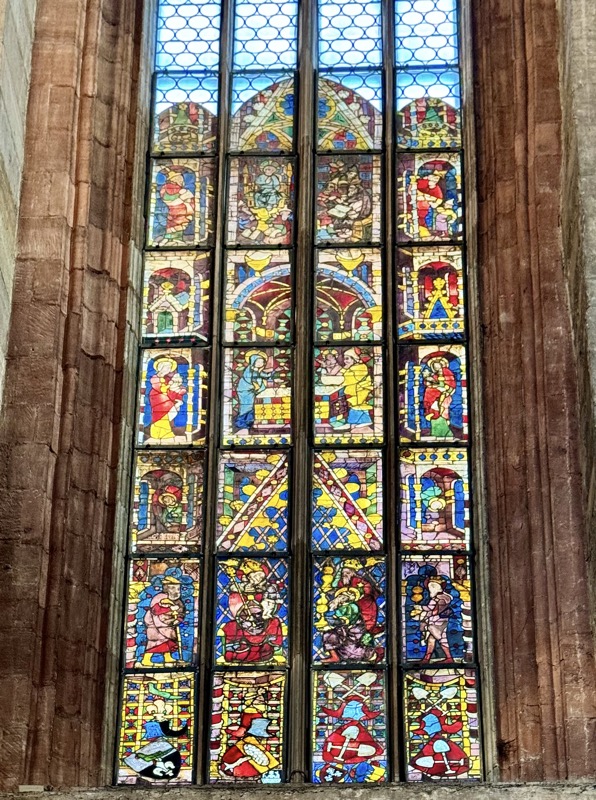
Glass: Behaim Window with the Annunciation and the Nativity, c.1330.
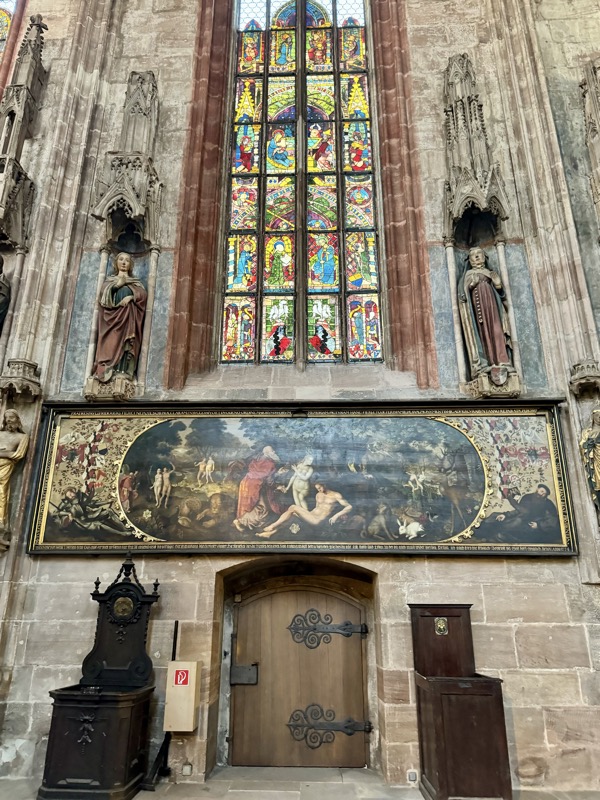
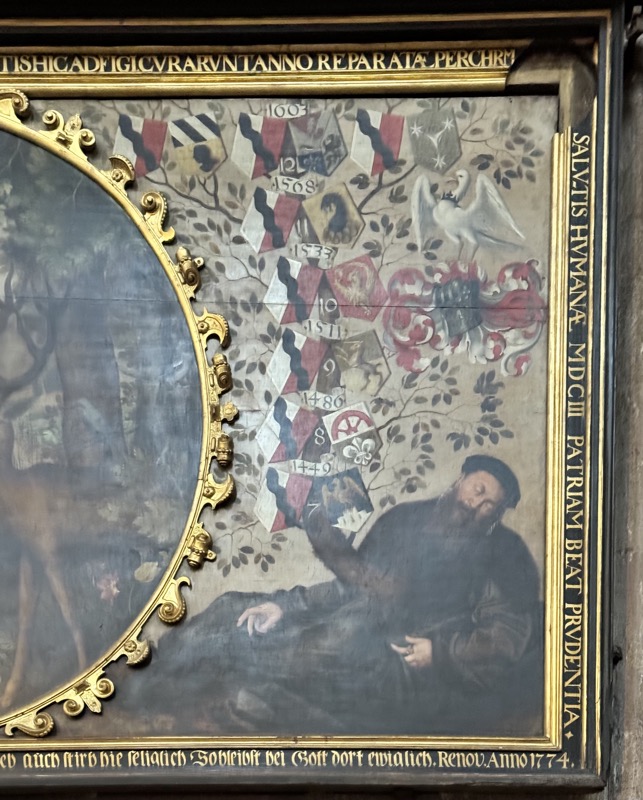



Altar of Saint Peter, c.1477.
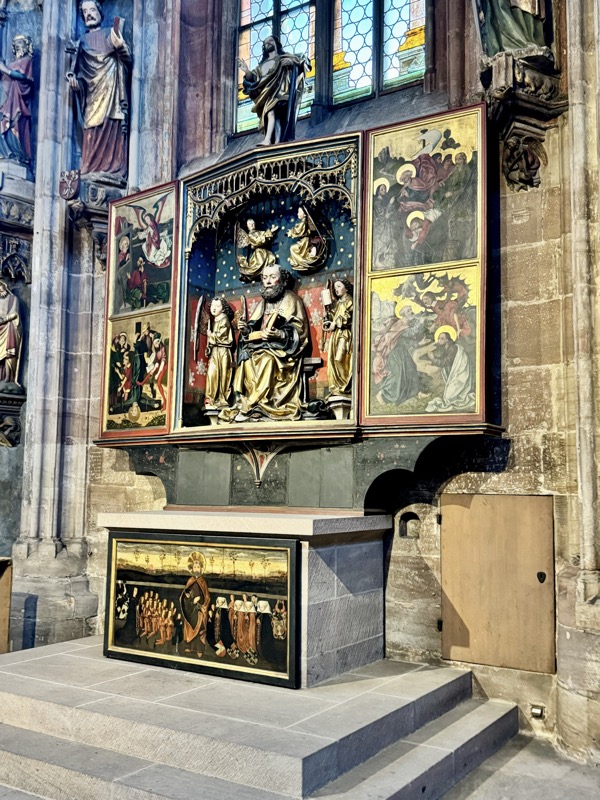
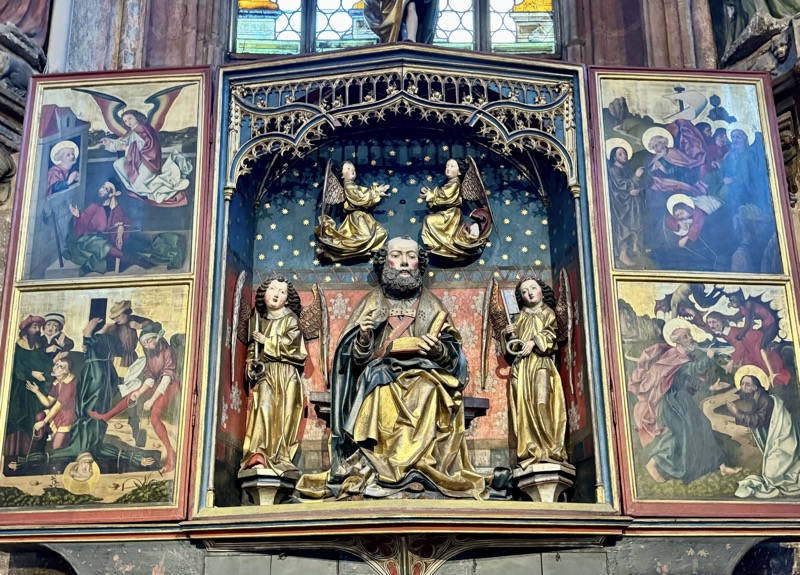
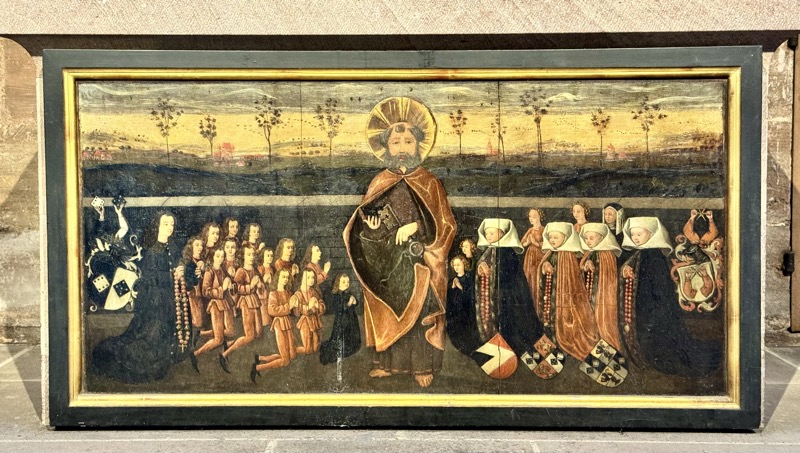



Memborial for the Schroeder-Landaeur families, c.1490-92.
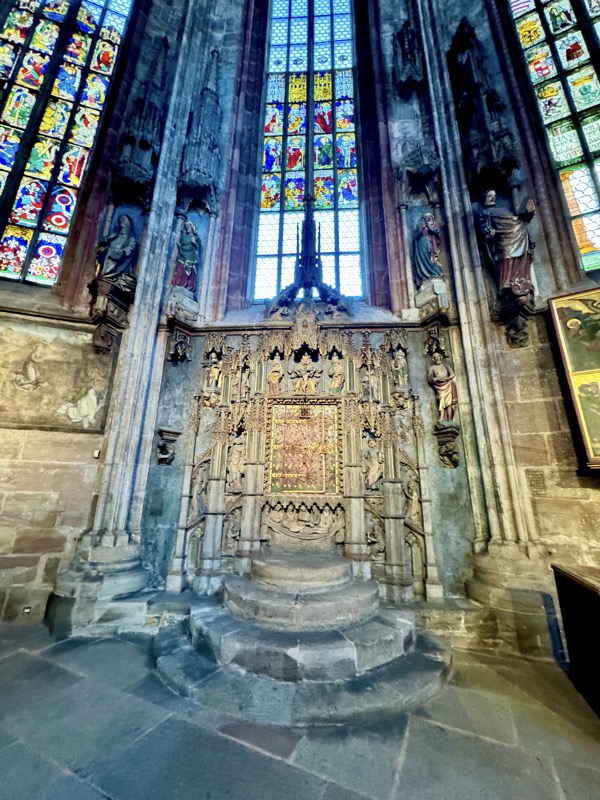

Peter Vischer and Sons tomb of St Seibald, c.1508-1519.
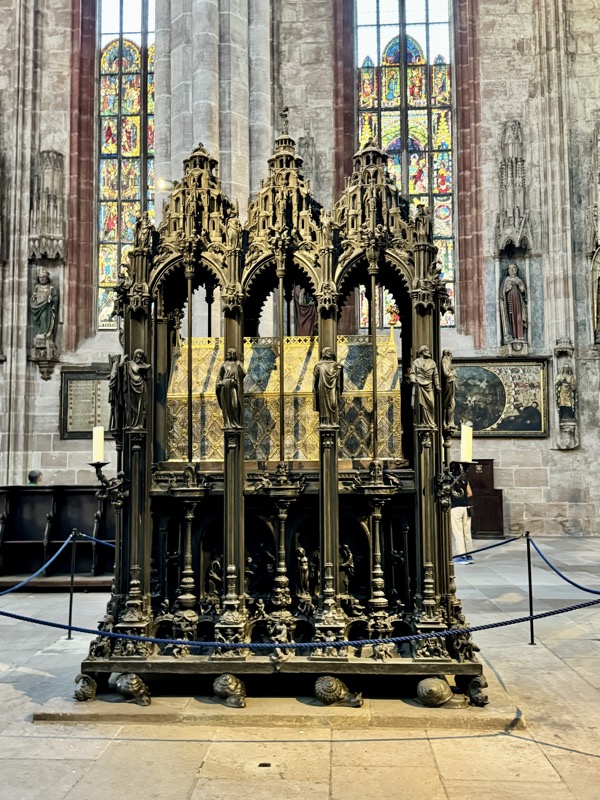
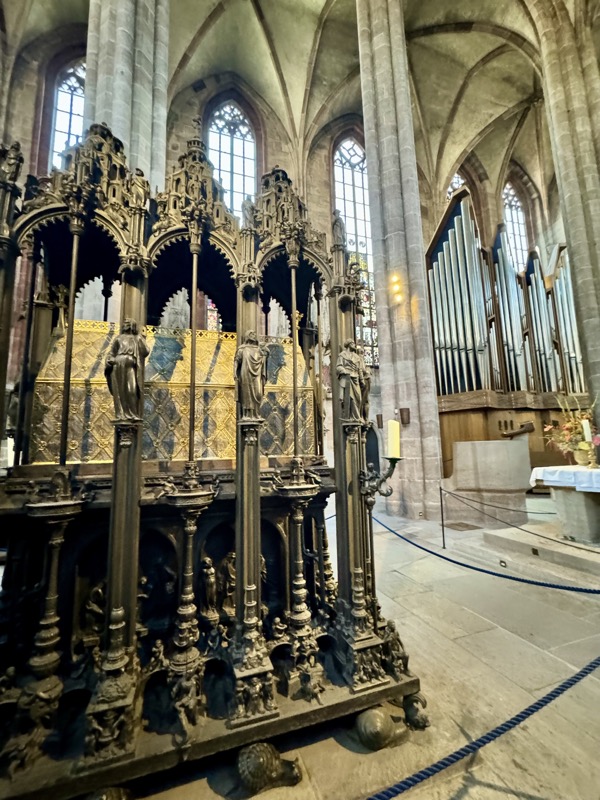



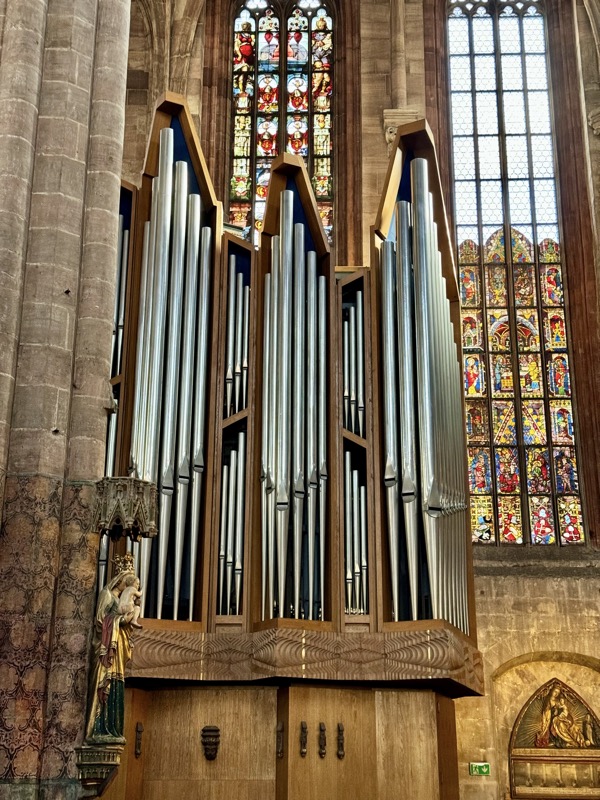
The organ was a late addition – we were just discussing how it wasn’t up in a specific organ loft like we had seen in many cathedrals, and actually looked to be a free-standing object. Then we discovered it was only added to the church in 1975.

St Catherine – originally on the Exterior of the Last Judgement Portal c.1310.
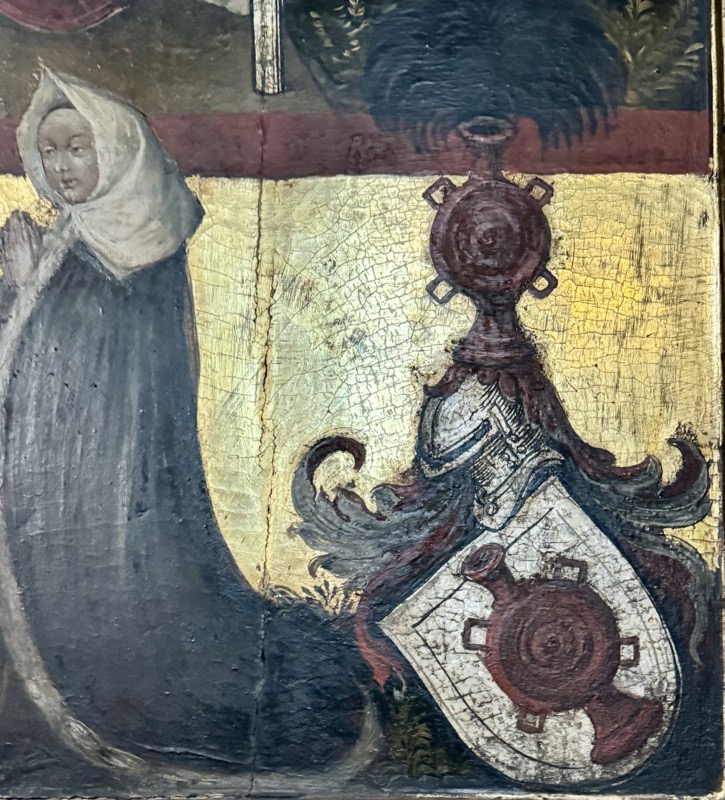



And of course the bit I’m always curious about – during WWII, between 1943 and 1945, the church was repeatedly hit by bombs and severely damaged (hence the partially preserved stained glass). As late as April 20, 1945, both towers were bombarded until fires broke out and melted the medieval bells. The first phase of reconstruction lasted 12 years and ended in 1957. There are still repair and removal of war damage happening today.

Anna Oelhafen Epitaph, c.1528.

Having a very sparse breakfast, and having skipped lunch, we gave up on our churching and went hunting for some dinner. Angus found this place which is a local Franconian ‘field to table’ restaurant – the beers, wine, water, juice tea are all sourced from Franconia; vegetables are all grown locally in Knoblauchsland, fishes are sauced from Heinl an Erlangen fishmonger, sausages come from the Nuremberg butcher, and game is delivered by someone named Waffler from his local hunting ground. It made me think of the 40 Happy Cows that Le Cinq have on a farm some 20kms out of Paris just to make butter for the restaurant! 


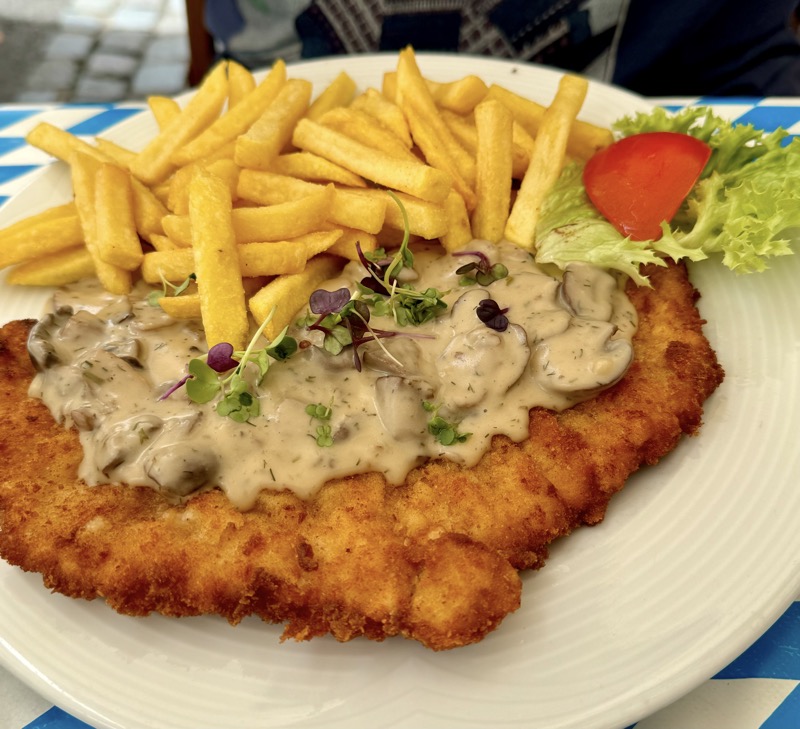
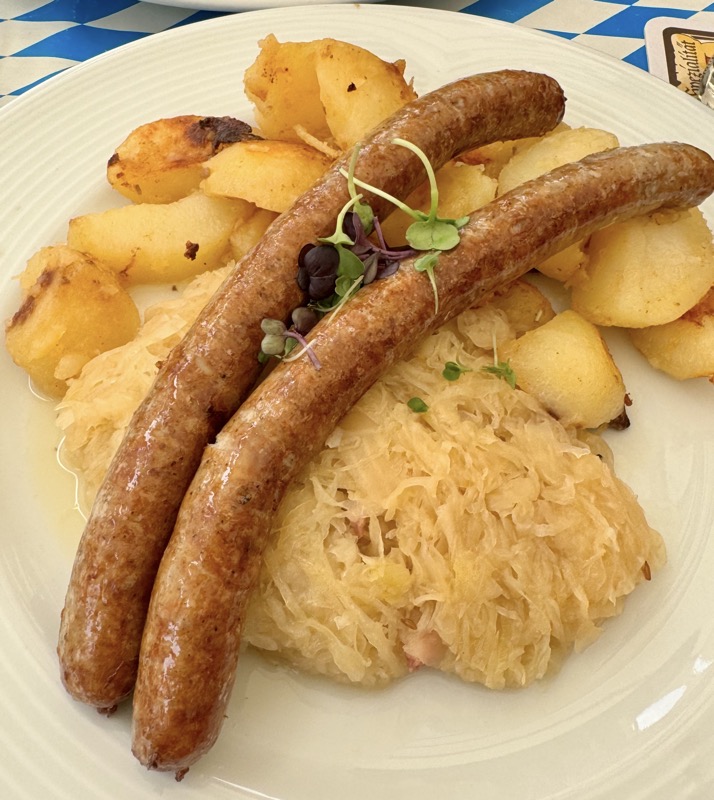
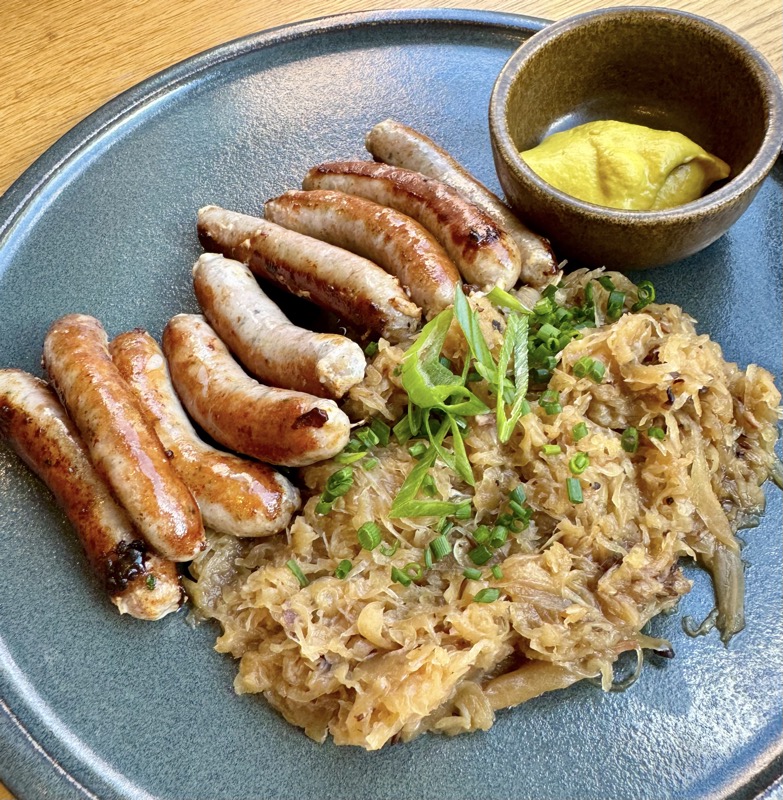
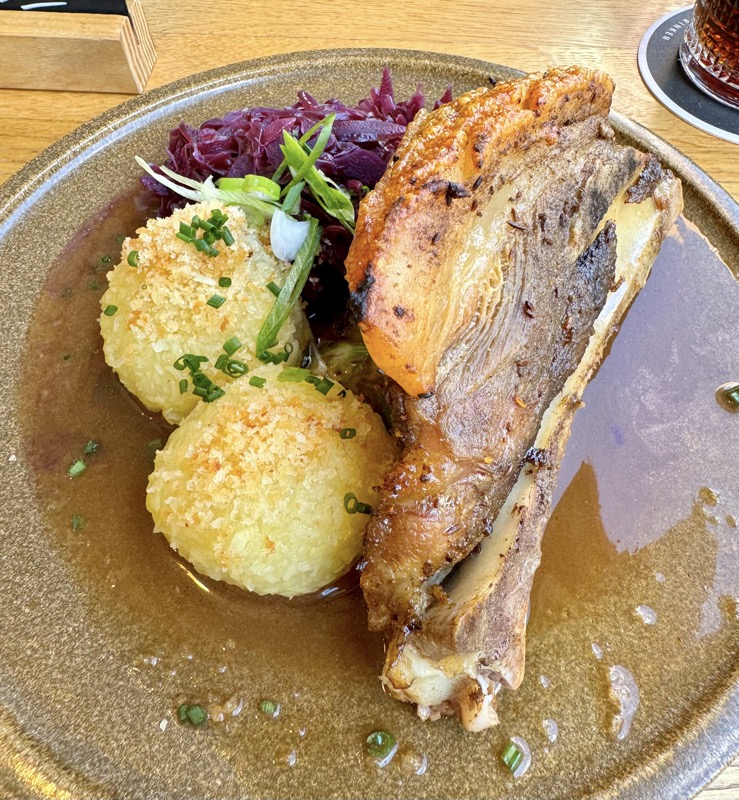
Angus opted for the bratwurst platter which came with rye bread and the most sour of sauerkraut you’ve ever tried in your life, and I opted for a pork shoulder because it seems I have a habit of panic ordering when I’m not speaking English! It was a sizeable and somewhat fatty portion that came with potato dumplings (which Angus enjoyed), and red cabbage – not sour.


After we finished our meal, we stopped in a grocery store for some toothpaste (weirdly, we both thought the other would have a decent sized tube and neither of us did!) and I saw these – these lemon wafer biscuits are, without a doubt, one of my FAVOURITE European snacks that I can’t get back home… it took all my ‘keine zucker’ willpower to not buy them, especially as they were selling them in packs of 5 for like €2.39. Insta-regret kicked in as soon as we got back! LOLi

Our next stop in Nuremberg was to ferret out Albrect Drurers house – which you wouldn’t think would be that difficult to find, but it’s easy to get turned around in the windy little medieval streets.

This is a cool house, but not Drurer’s house.
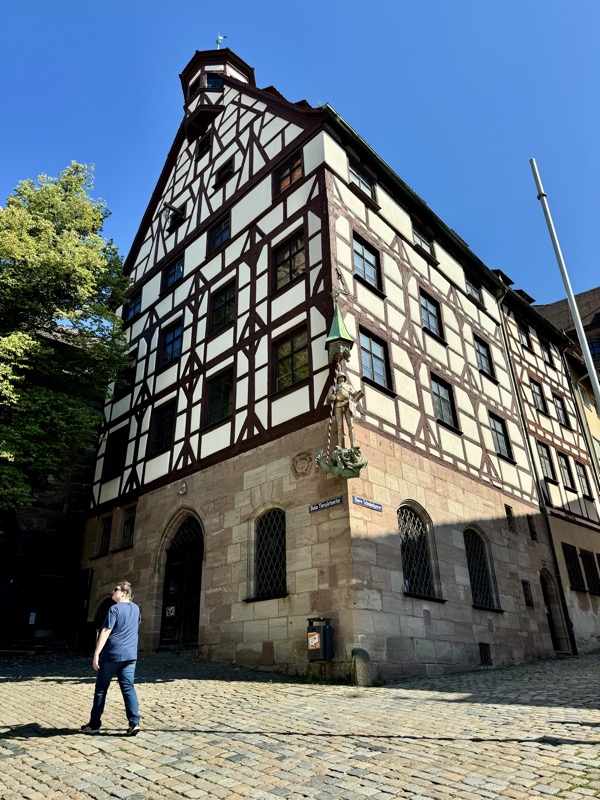
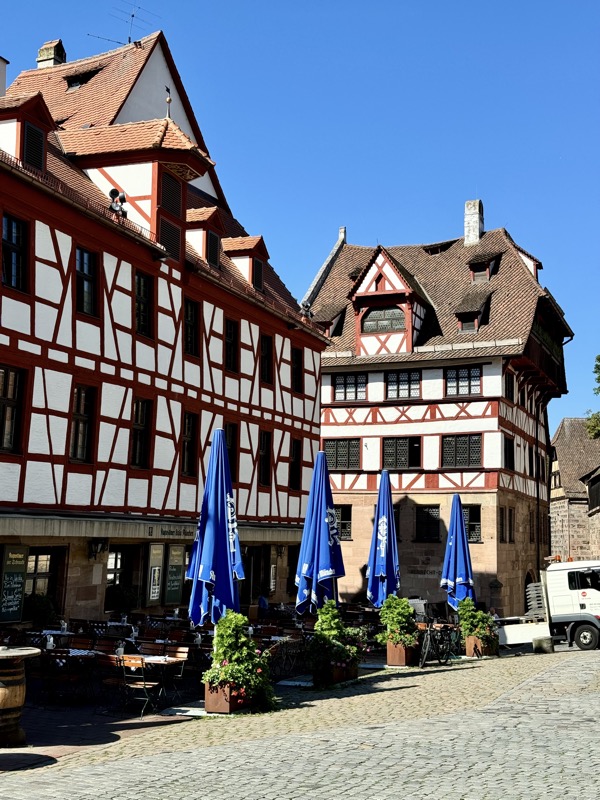


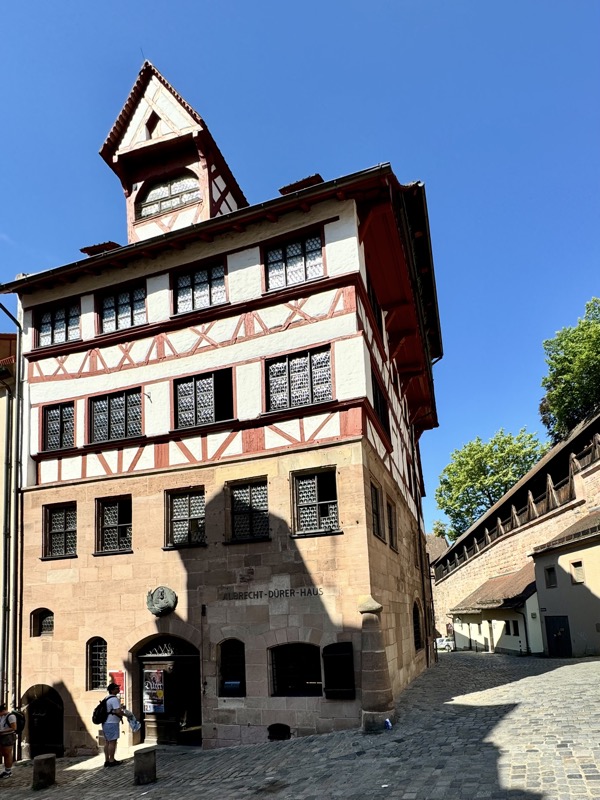
Finally found it – Albrect Dürer (1471-1528), is Germany’s most famous painter lived in this house now turned musuem.

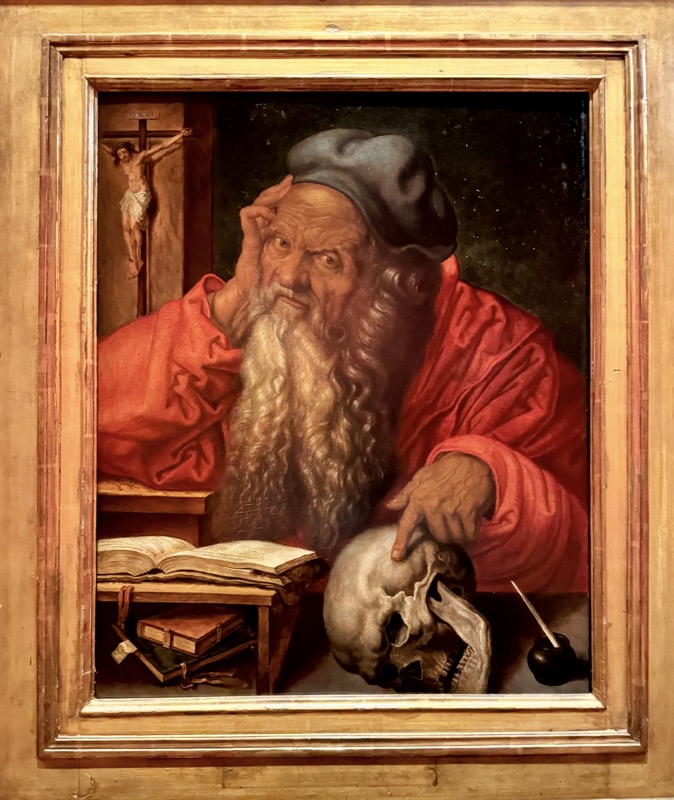
St Jerome in his Study, Albrect Durer, c.1521

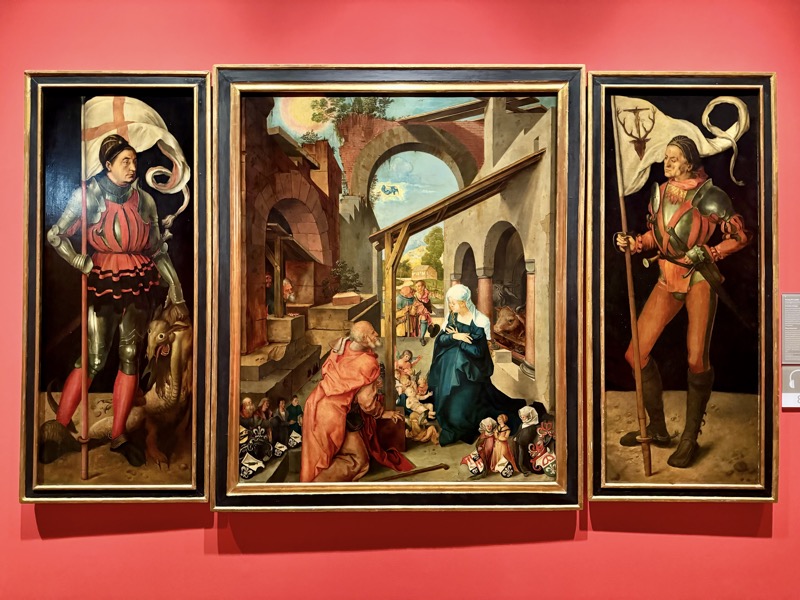
Paumgartner Altar, c.1498.

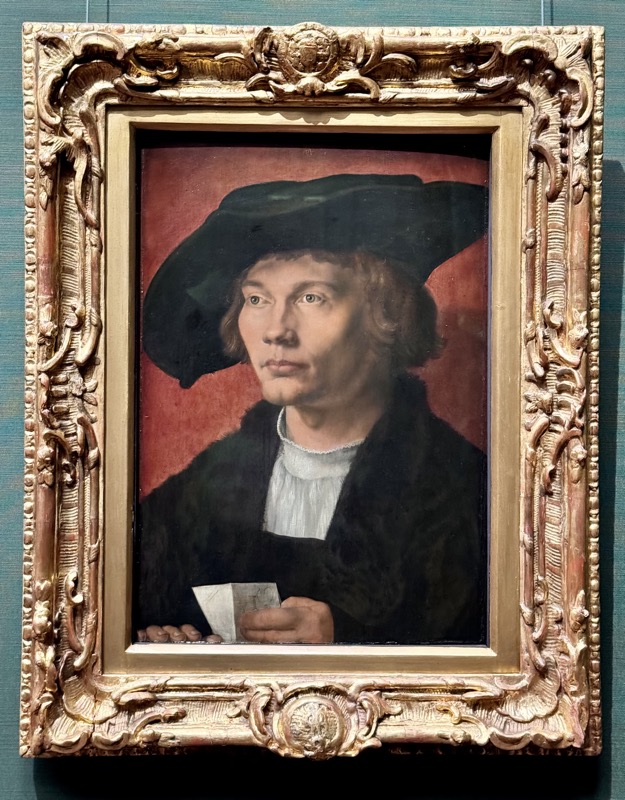
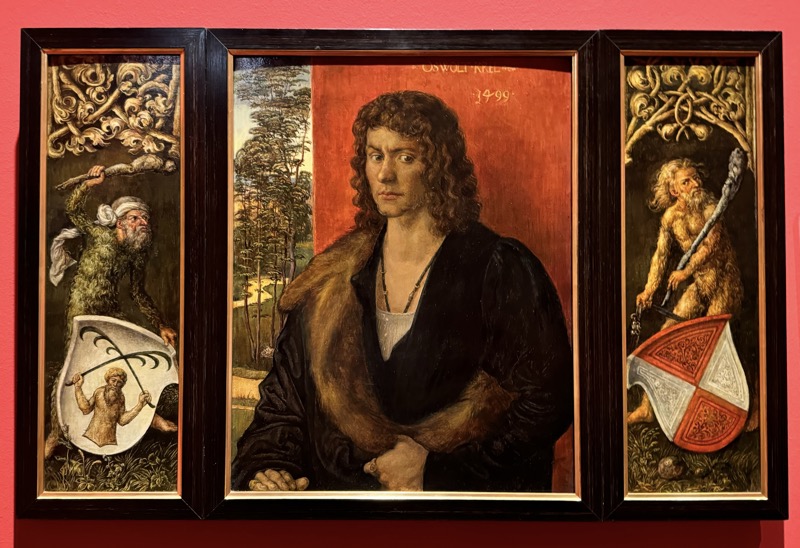
Portrait of Oswolt Krel, c. 1499.

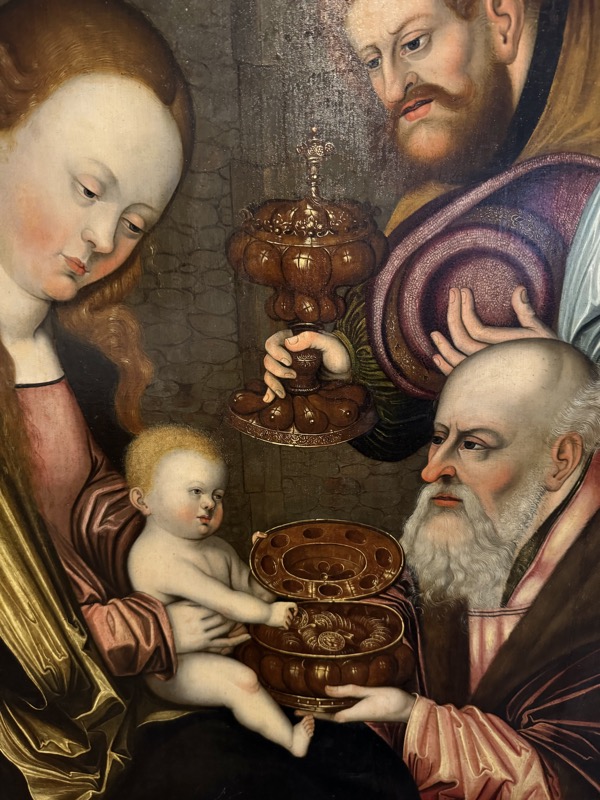
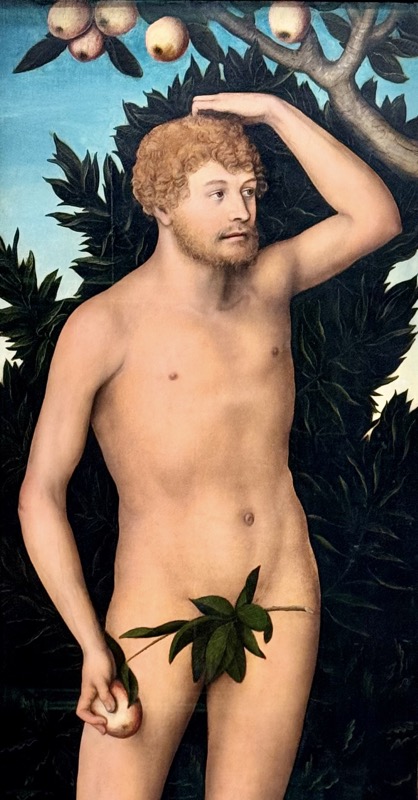
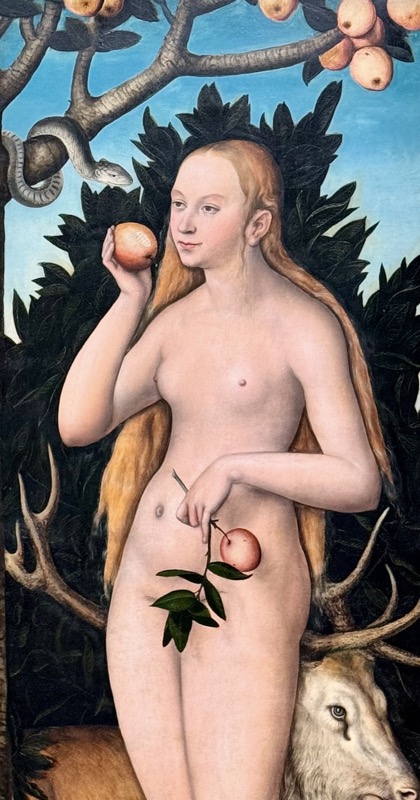
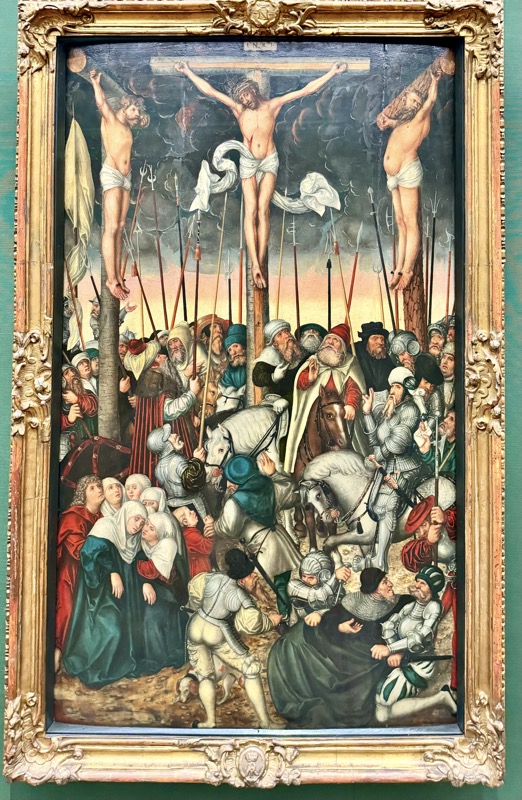
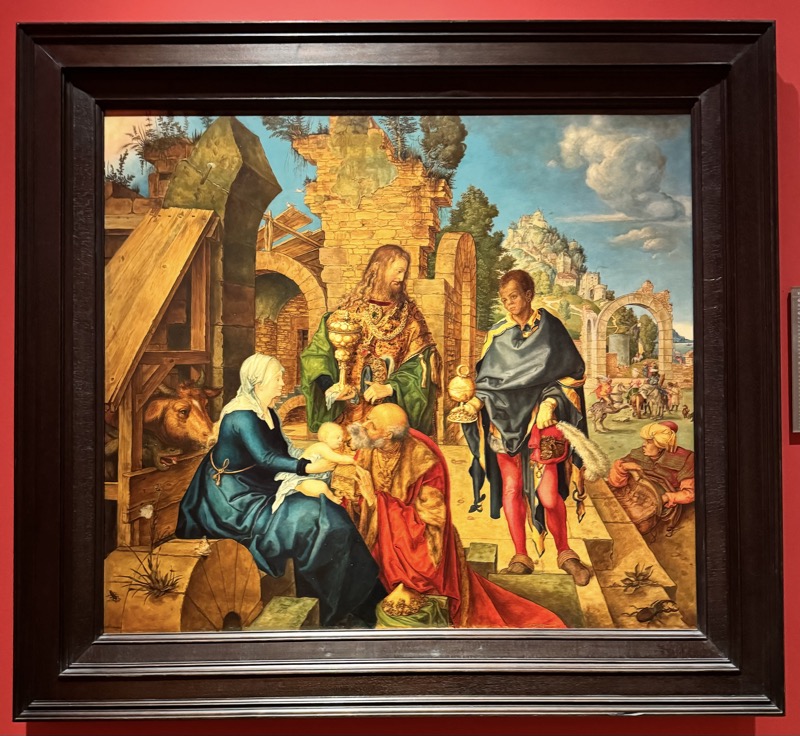
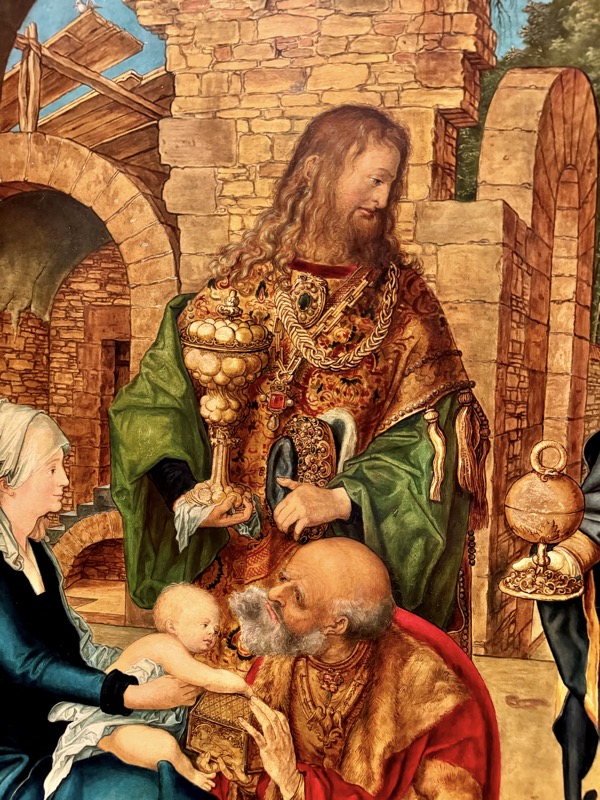
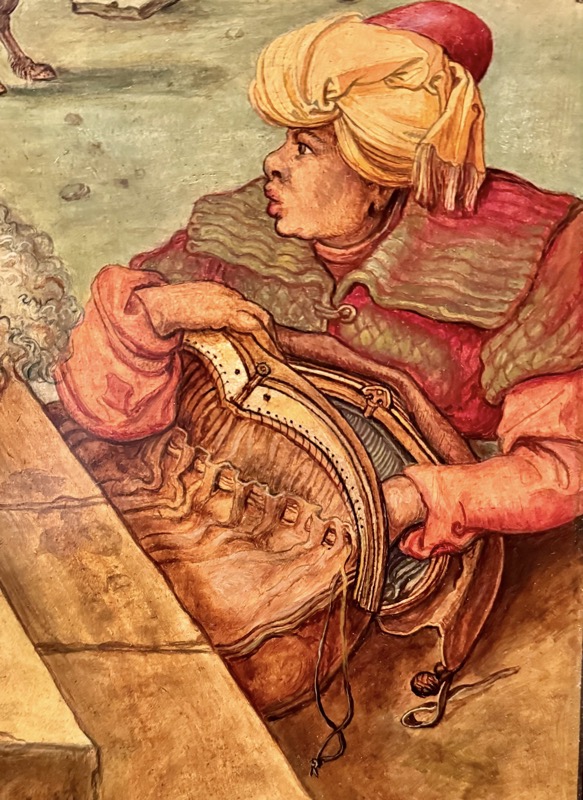
Adoration of the Magi, c.1517.
The covered chalices and chains demonstrate Durer’s background as a goldsmith.



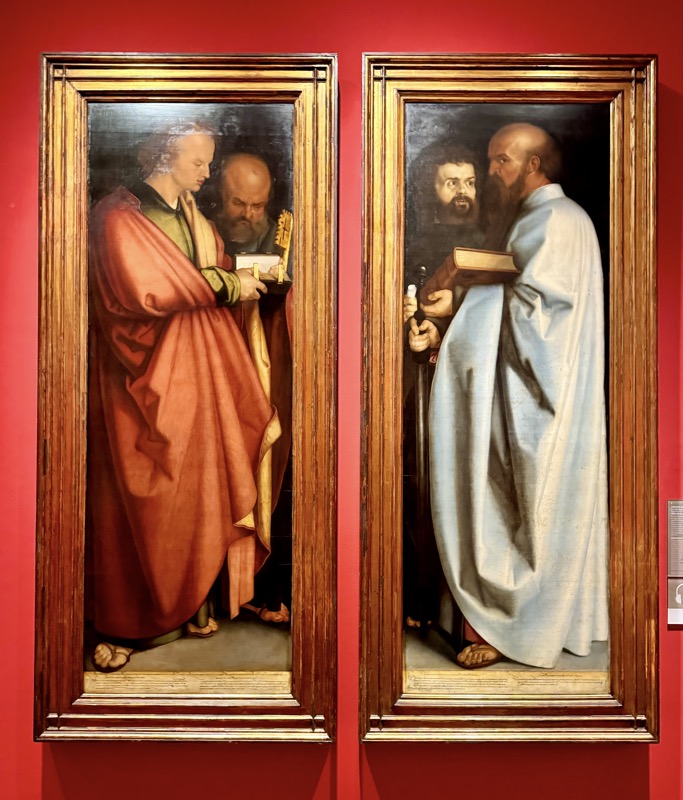
The Four Apostles, Guardians of Justice, c.1526. Guardians of Justice.

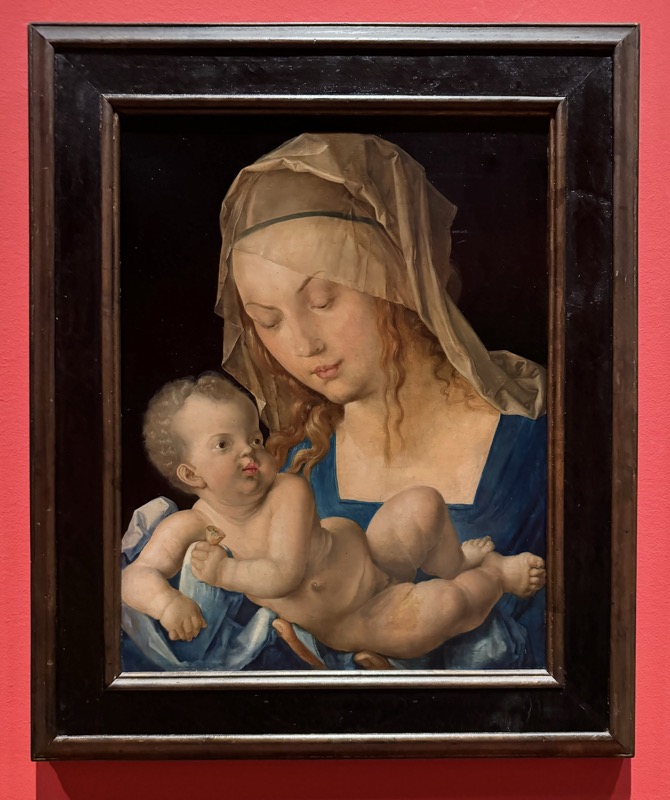
Maria with the Pear Slice, c.1512.

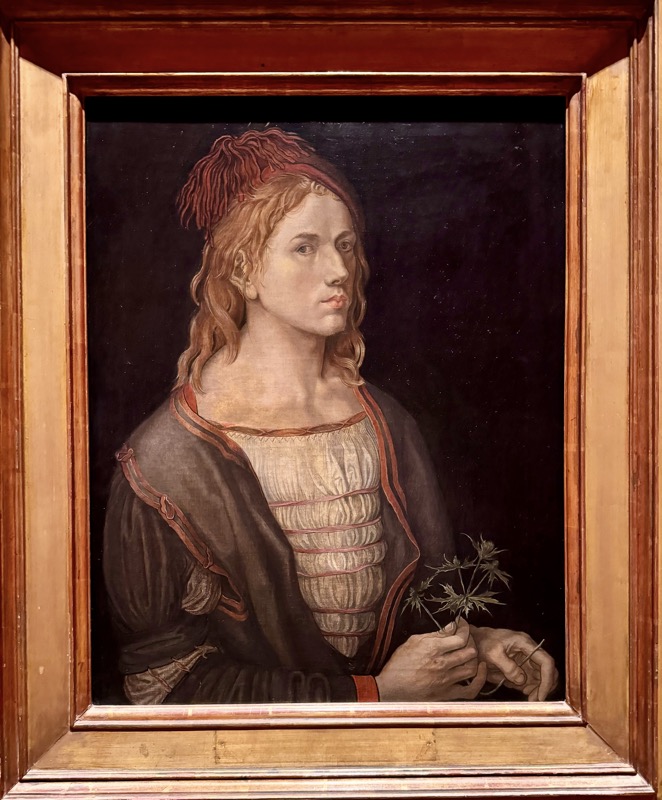
Self Portrait with Eryngium, c.1493

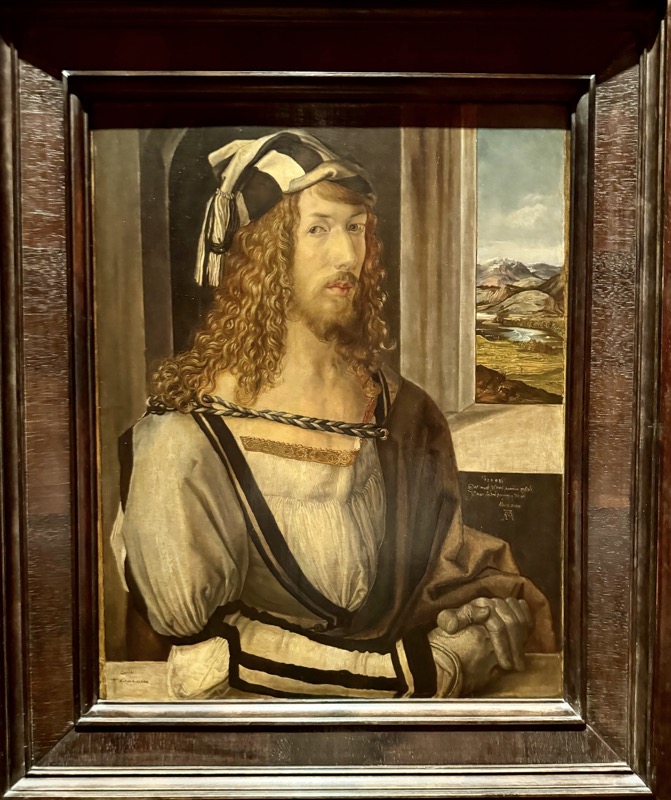
Self Portrait, c. 1498.

Dürer originally trained as a goldsmith and in 1487, ended his goldsmith’s apprenticeship with his father in order to start anew as an apprentice at the workshop of the famous painter Michael Wolgemut. Additionally, he specialised in a completely new profession: that of book illustrator and free graphic artist. Before too long his talents attracted rich and highly educated customers. In 1496, he met the man who would become his most important patron, Elector Frederick of Saxony.
Dürer’s House is a typical Nuremberg Fachwerkhaus, where he lived from 1509 to 1528. It is in Nuremberg’s Altstadt near the Kaiserburg section of the Nuremberg Castle and the Tiergätnertor. It is the only artist’s house turned museum of its kind… apparently?
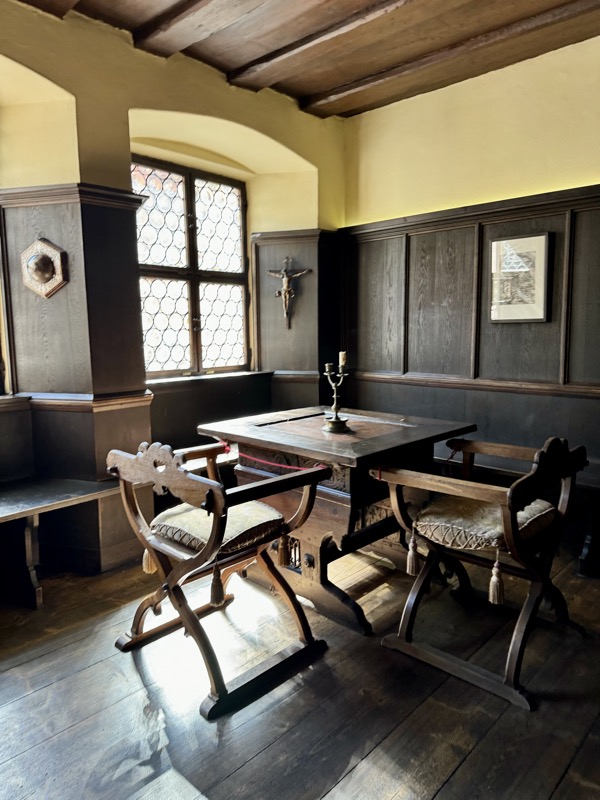

Living rooms and study spaces are furnished with period furniture. Dürer’s family life was rather out of the ordinary: in 1494, he married Agnes Frey, at the behest of both his father and hers. While Dürer’s mother had been pregnant eighteen times, his own marriage remained childless.
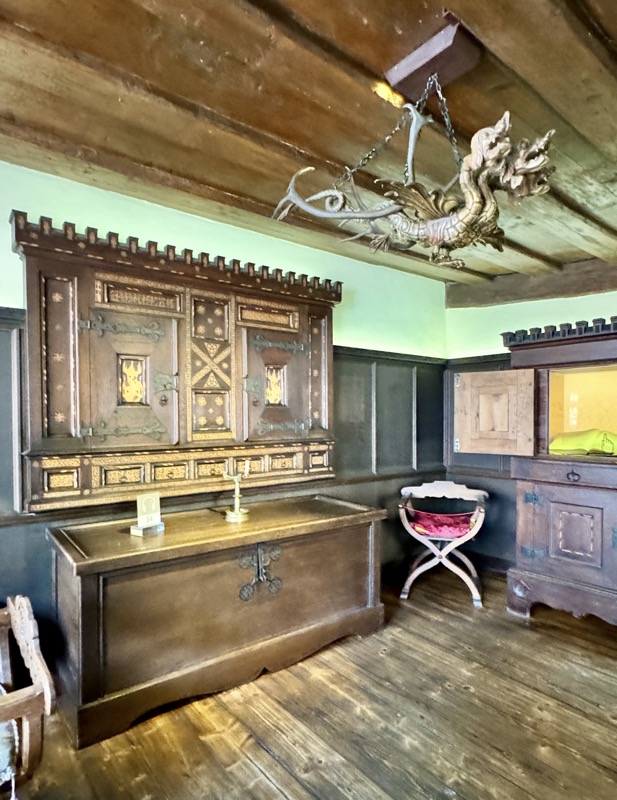

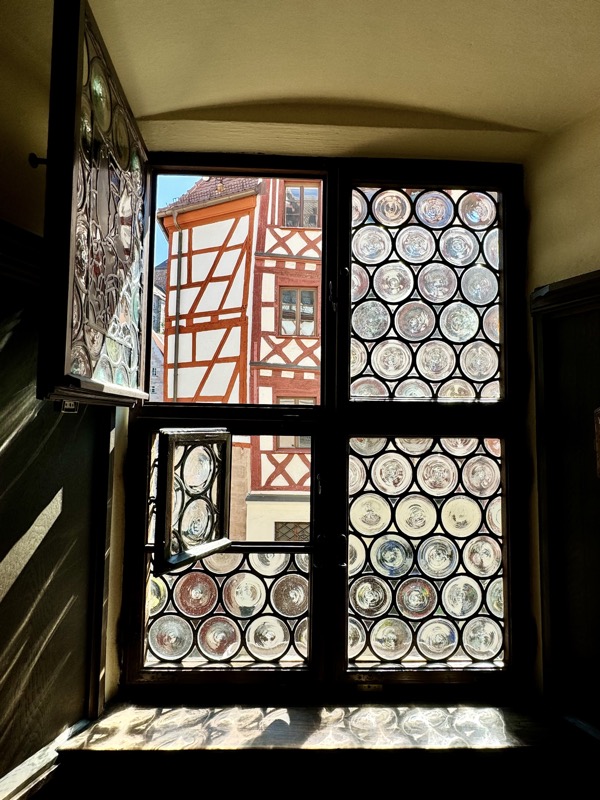
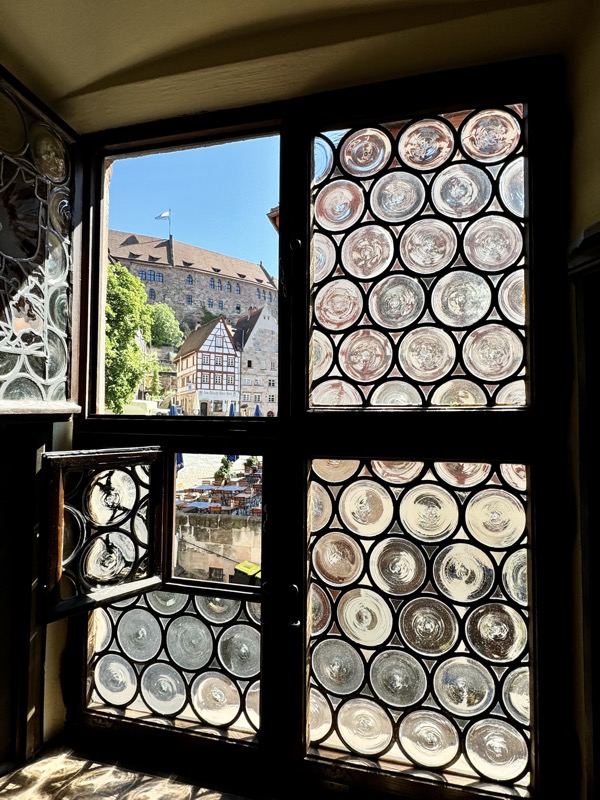
I love these windows… why don’t we make windows like this anymore?

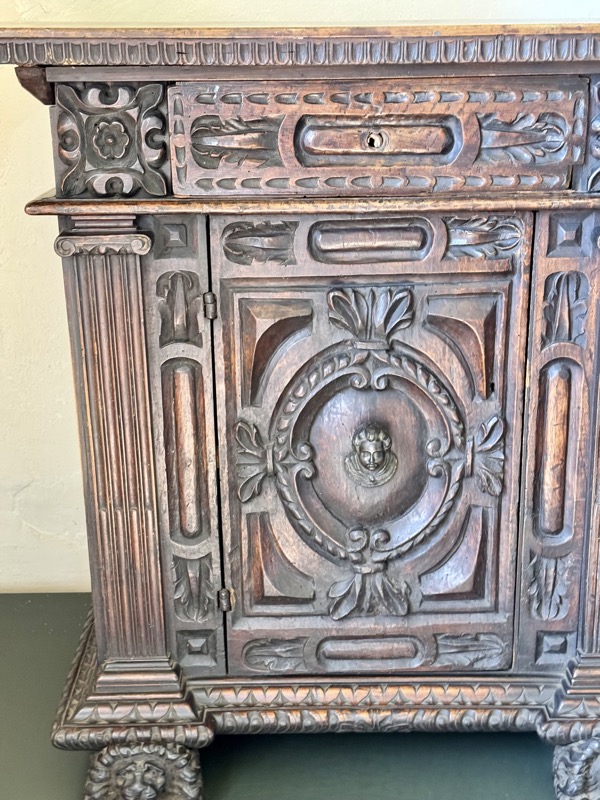
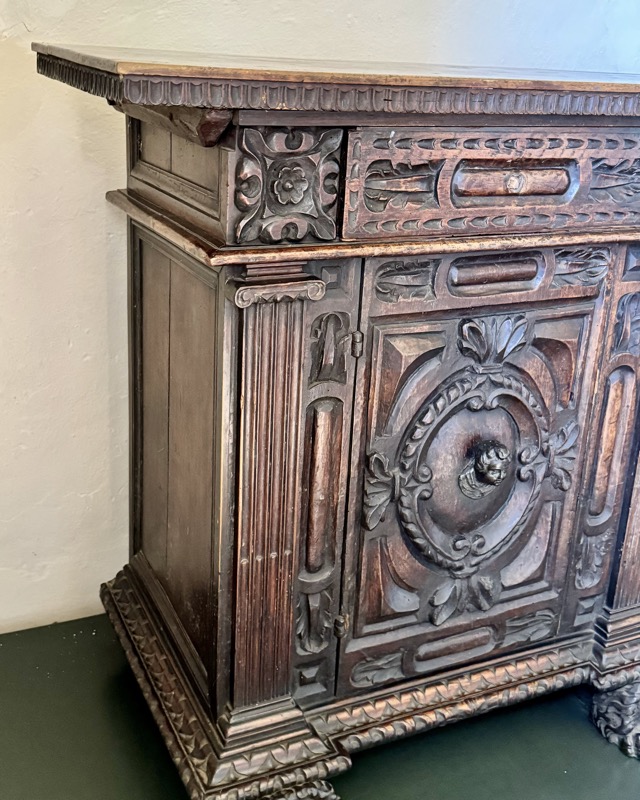
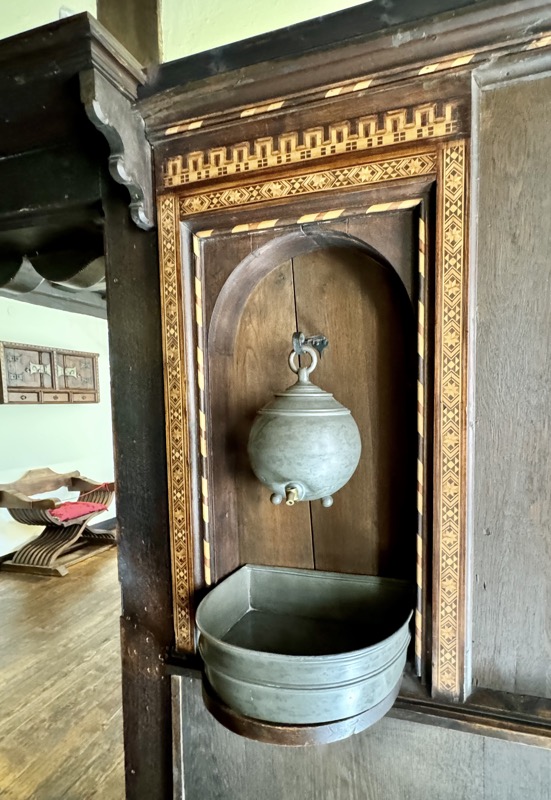
A small cupboard and a hand washing space.


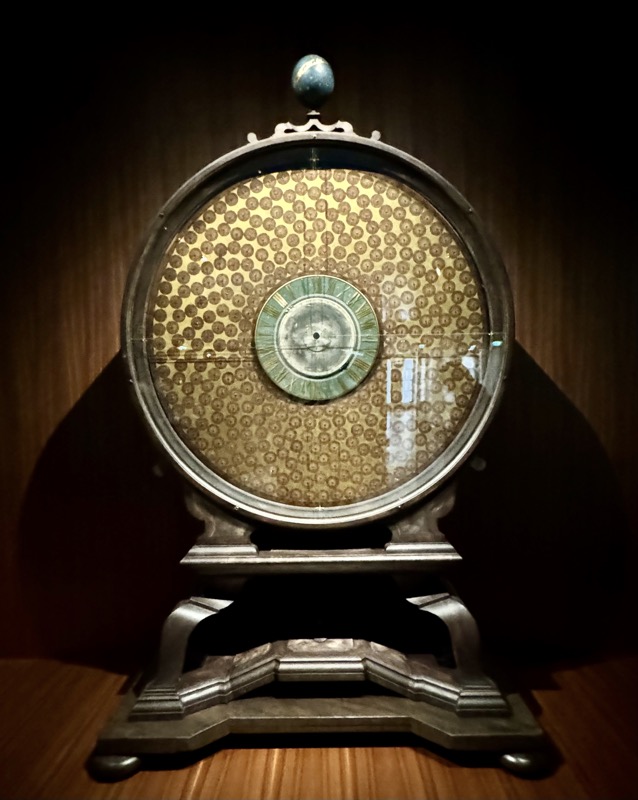
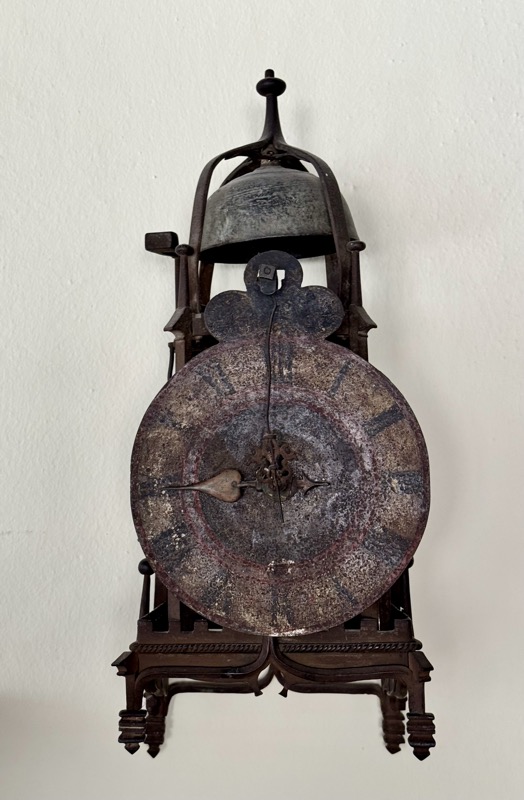
Wall clock… no information on these. But plenty of small plaques asking visitors to not touch things!

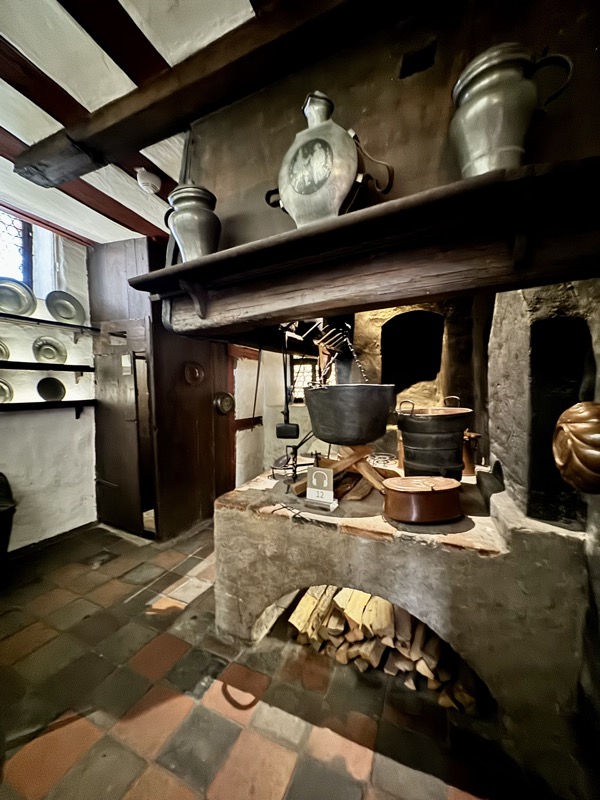
The downstairs kitchen is designed in such a way as the heat rises to warm the upper floors.
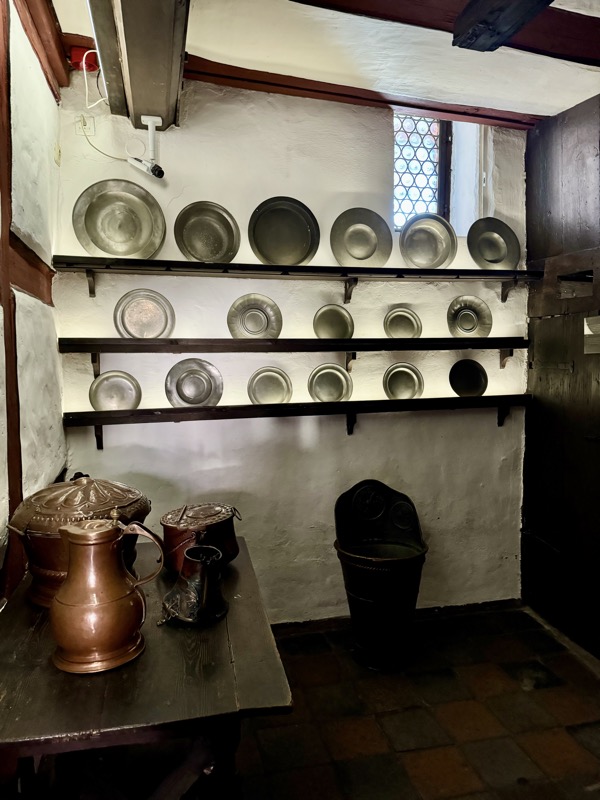
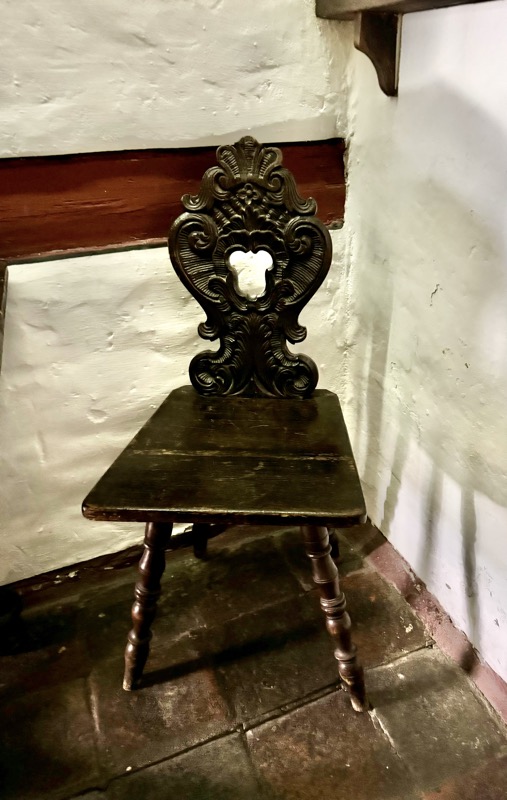
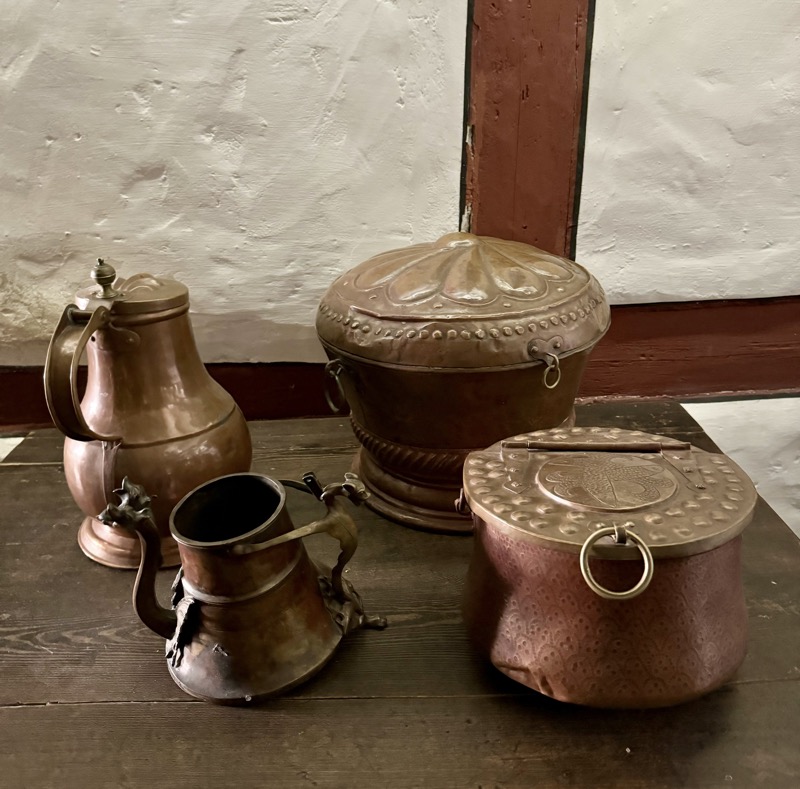
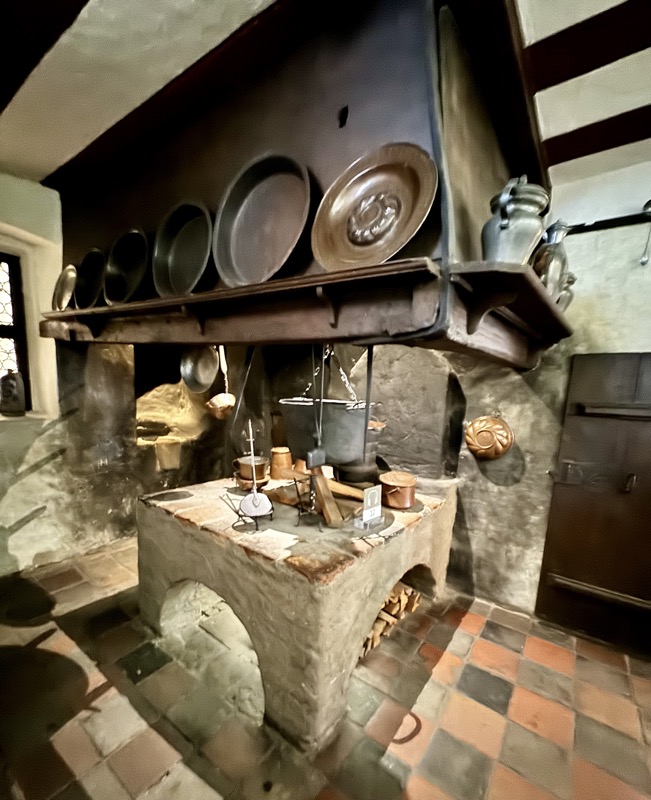
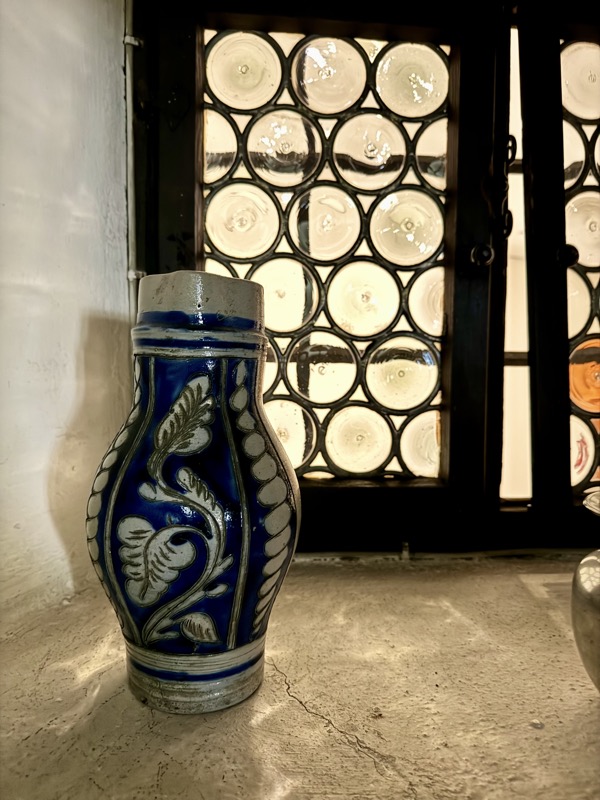






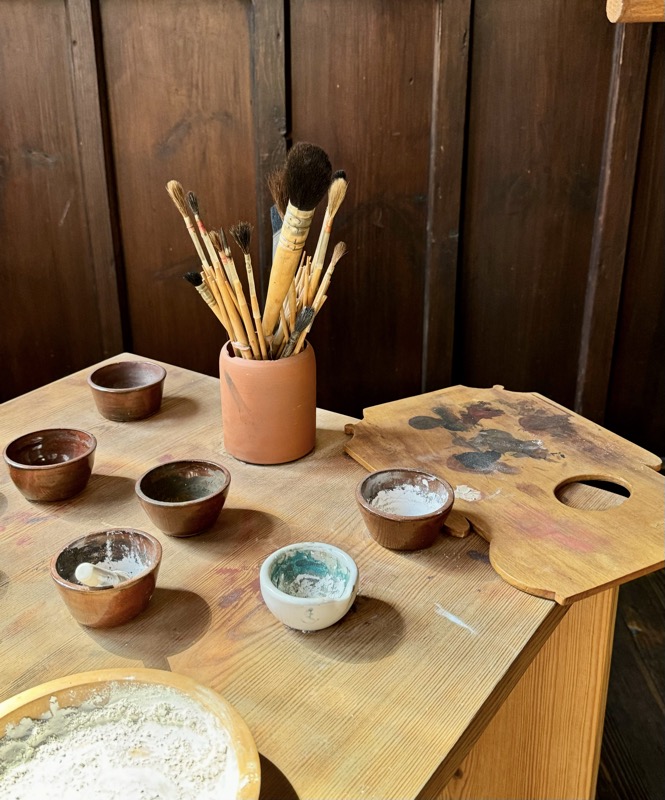
The upper floors contain a recreation of the artists workshop spaces.
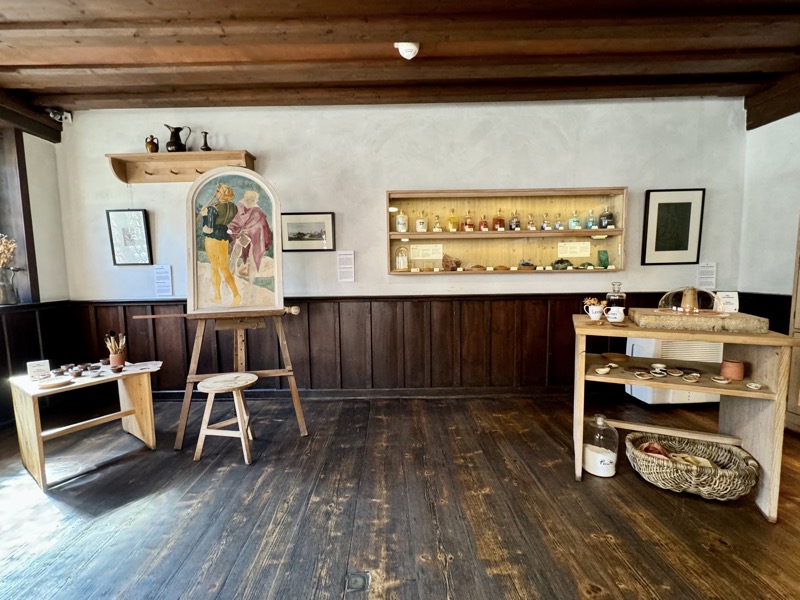
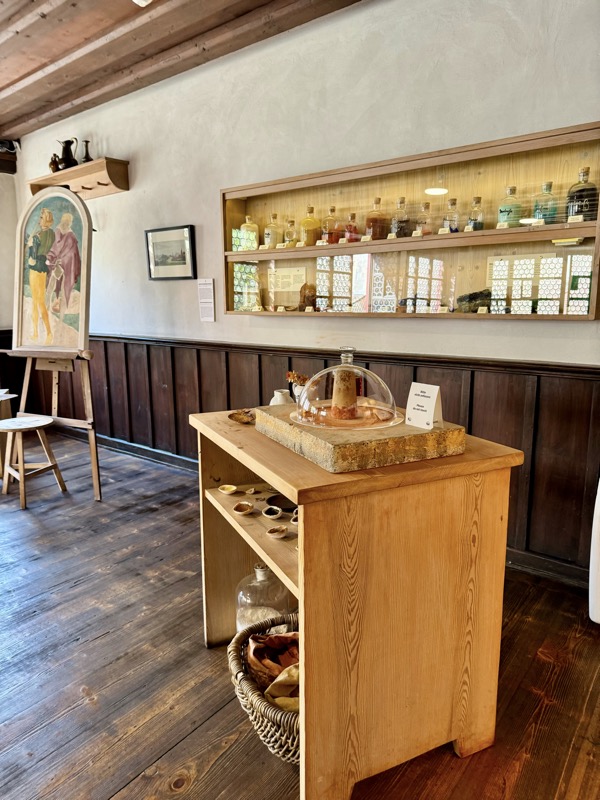
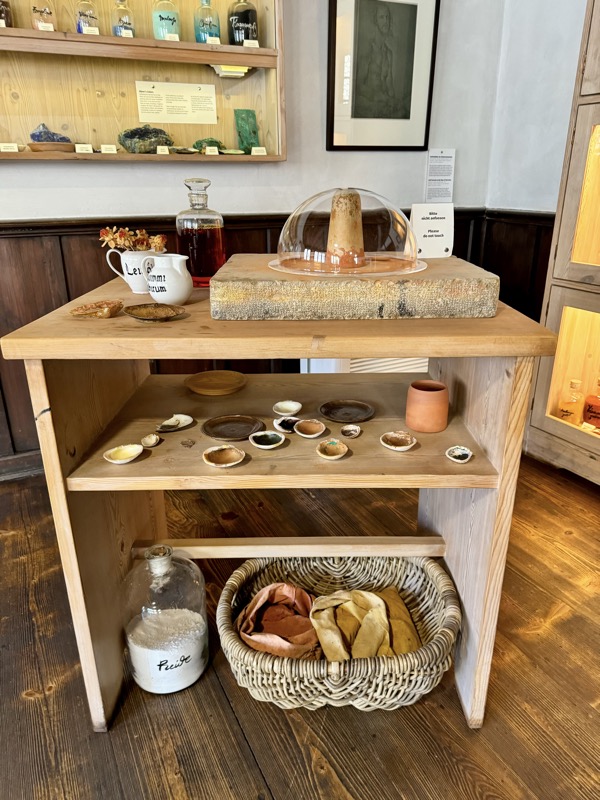
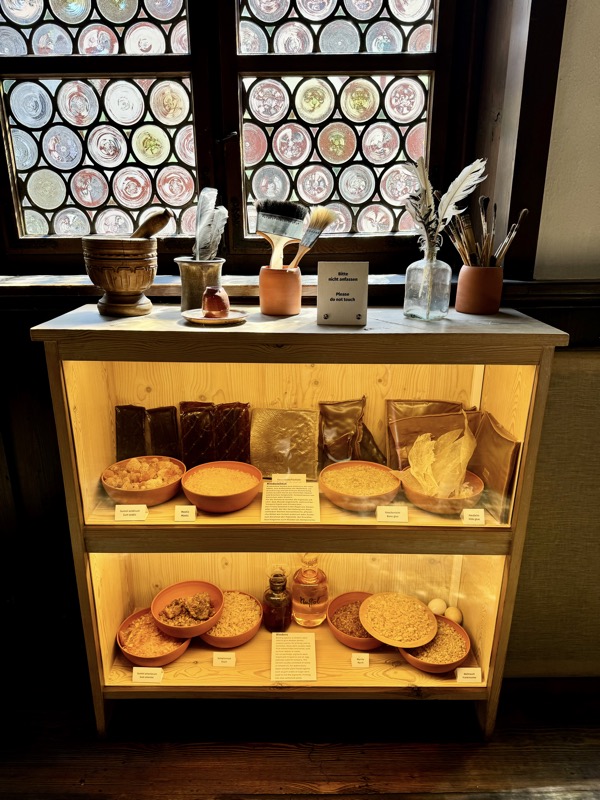





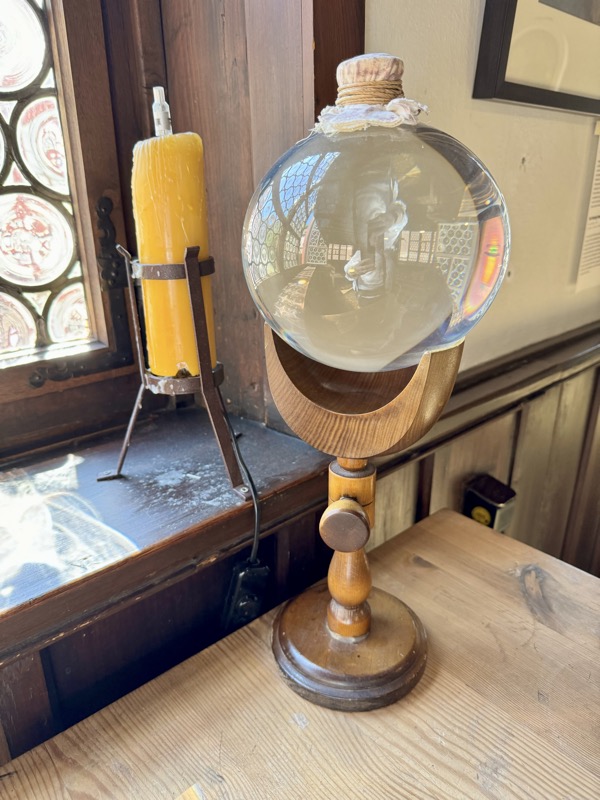
An engraving plate and a glass sphere that could be used as a magnifier.
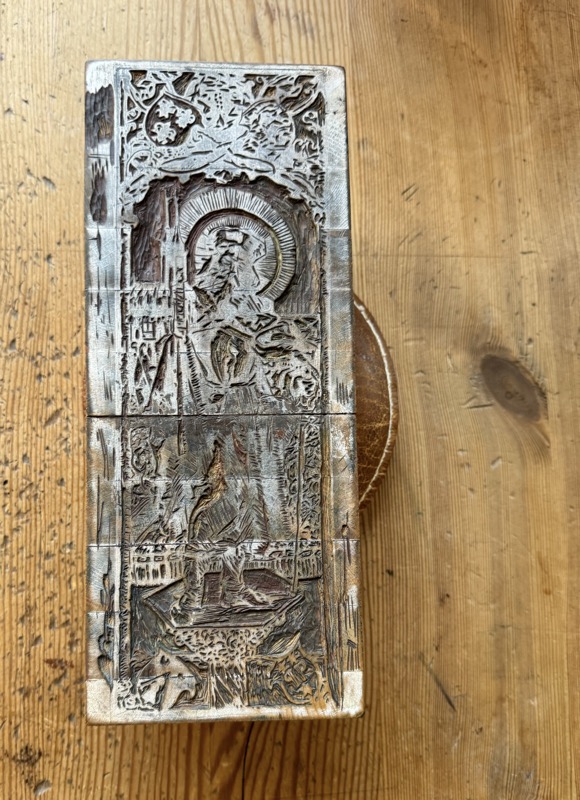





Printing systems.
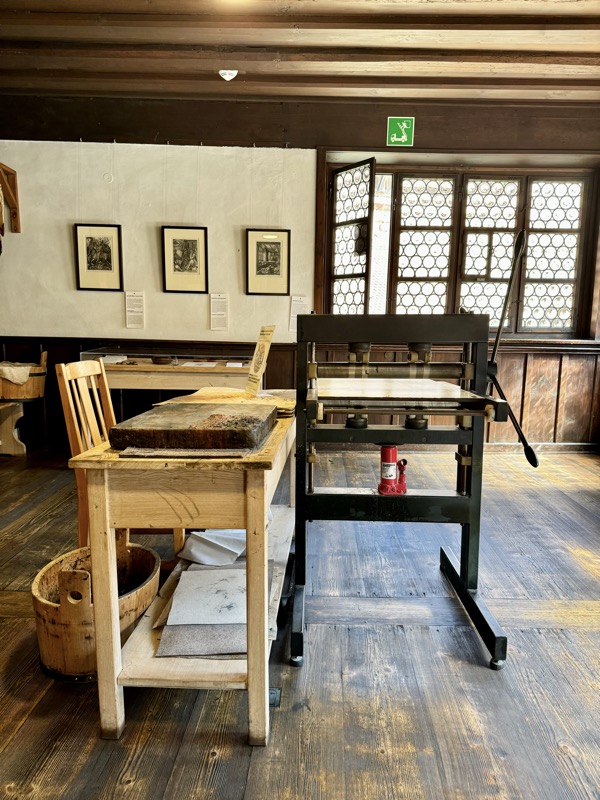
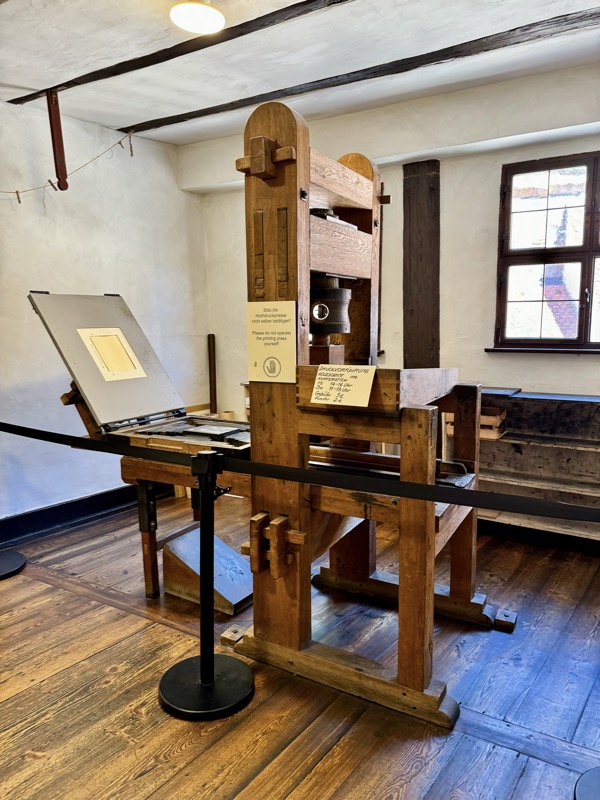


Was very cool hour or so checking out Dürer’s house… even knowing most of the art works are replicas didn’t detract from how cool it is to be walking through this living museum space with its smoky hallway and centuries old furniture. The rest of the day was spent working before we moved on!